Contents
Willebrand’s disease is a type of hemorrhagic diathesis that is inherited. The disease is characterized by increased bleeding, which develops against the background of a deficiency of plasma von Willebrand factor. In this case, the entire hemostasis system as a whole suffers. Blood coagulation factor VIII undergoes decay, blood vessels dilate, the permeability of their walls increases. All this leads to the fact that a person has frequent spontaneous bleeding, while they are localized in a variety of places and have different intensity.
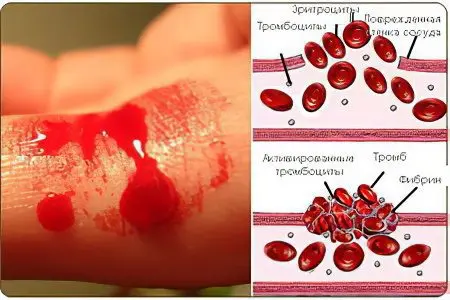
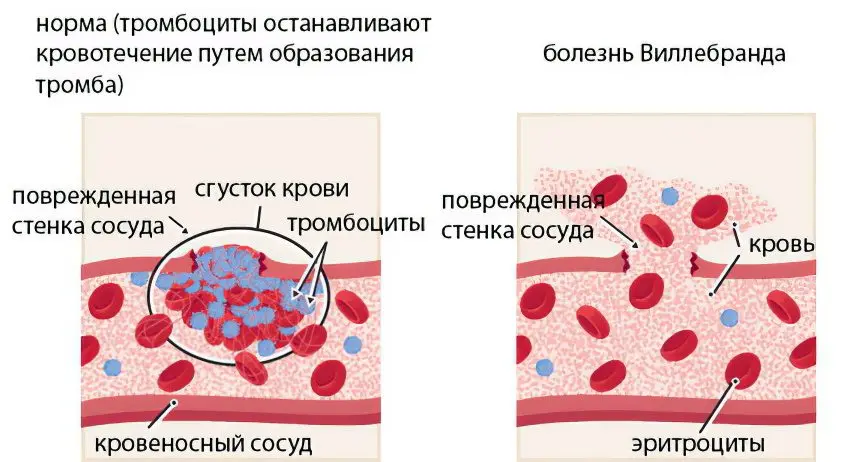
Hemostasis is due to the normal functioning of the coagulation and anticoagulation system. If the integrity of the vascular wall is violated, bleeding develops, which will continue until the anticoagulant components of the blood are activated. As a result of their work, a clot (thrombus) is formed in the blood, which blocks the formed lumen and helps to stop bleeding. Plasma factors take an active part in this process. If at least one of them is missing in the blood, the process of clot formation will be disrupted.
The von Willebrand factor is a protein component that is part of the blood and ensures adequate functioning of the hemostasis system. If it is produced in insufficient quantities, then this entails failures in the coagulation process. The von Willebrand factor is a protein that promotes platelet adhesion to damaged vascular walls. Factor VIII is produced in endotheliocytes. von Willebrand disease is inherited from parents to children. More often, women suffer from this disorder.
von Willebrand disease is also called angiohemophilia. It is this term that maximally reflects the essence of the pathology, but it is rarely used.
In past years, people who suffered from von Willebrand’s disease became disabled at an early age, their life expectancy was short. Now patients with such a diagnosis are able to live an almost full life, they can work, play sports.
Classification of von Willebrand disease
Depending on the nature of the course of the disease, the following types are distinguished:
The first type of disease, which is the most common. In this case, there is a decrease in the level of the von Willebrand factor, but in small quantities. Therefore, the work of the blood coagulation system is disturbed, but not too much. A person with this type of illness feels satisfactory. It is possible to develop bleeding that is difficult to stop, but it manifests itself during surgery or during dental procedures, and not by itself. In such people, bruises appear even from a slight pressure on the skin.
The second type of disease, in which the level of von Willebrand factor in the blood does not decrease, but the structure of the substance itself is disturbed. When exposed to the body of factors provocateurs, sudden bleeding may develop, which can be very intense.
The third type of von Willebrand disease is the most severe pathology. The patient’s blood is completely absent coagulation factor VIII, which leads to microcirculatory bleeding and accumulation of blood in the joint cavities.
The platelet type of von Willebrand disease is a pathology that should be considered separately. In this case, a gene mutation occurs in the human body, which is responsible for the platelet von Willebrand factor receptor. It is released from active platelets and prevents them from sticking together normally and attaching to the vascular wall.
Very rarely, people are diagnosed with an acquired form of the disease, which develops not from birth, but against the background of the appearance in the blood of autoantibodies to their own tissues. Past infections and stresses, injuries can become a triggering factor. This type of von Willebrand disease most often develops in people suffering from autoimmune pathologies, cancerous tumors, and thyroid diseases.
Causes of von Willebrand’s disease
von Willebrand’s disease is characterized by a violation of blood clotting, which is the most important link in the hemostasis system. At the same time, the blood coagulation factor, which is called the von Willebrand factor, is not enough in the body, or it has a number of structural disorders. This leads to the failure of the blood coagulation system, as platelets lose their ability to normal aggregation and adhesion.
von Willebrand disease is a genetic disorder. Although the disease can affect both men and women, representatives of the weaker half of humanity suffer from this disorder more often.
Sometimes von Willebrand disease is so mild that the person is not even aware of its presence. Bleeding (if it occurs) will be localized in the area of the uterus, skin or gastrointestinal tract, that is, in those organs that have a developed capillary network.
If a person has the first blood group, then the pathology can have a severe course. Ingoda, even ordinary nosebleeds can end very badly.
Symptoms of von Willebrand disease

If bleeding develops in a healthy person, then platelets are sent to the site of damage to the vessel, which, sticking together with each other, clog the existing wound. In people with von Willebrand disease, this process is impaired.
The main symptom of the disease is bleeding. They can be provoked by surgery, tooth extraction, trauma. During bleeding, a person’s condition worsens, the skin turns pale, the head begins to spin, and blood pressure may decrease. Symptoms will worsen quickly if the bleeding is extensive and intense.
Children with von Willebrand disease suffer from hemorrhagic diathesis, which is especially acute after ARVI. The organism, which is exposed to intoxication, reacts to this by increasing the permeability of the vascular walls, which threatens the development of spontaneous bleeding.
There is no cure for von Willebrand disease. Pathology has an undulating course, with periods of calm and exacerbation.
Symptoms of von Willebrand disease include:
Against the background of taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract is often observed. Also, its development is facilitated by treatment with antiplatelet agents. Bleeding hemorrhagic nodes and ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. The bleeding of the digestive organs is indicated by dark feces, which takes on a tar-like consistency. At the same time, its color becomes almost black. The patient may also vomit blood.
Hemarthrosis is bleeding into the joint cavity. A person experiences pain in the corresponding area, the functions of the joint are limited, the skin around it swells. If the bleeding is not stopped, then the swelling will increase, the soft tissues will become bluish, become tense and tight. The skin at the site of the lesion will be hot to the touch.
In addition to hemorrhagic syndrome, people with von Willebrand’s disease may have signs of mesenchymal dysplasia. In this case, bleeding will have a certain localization, they will begin to occur regularly in these places.
Over time, the symptoms of the disease may change. Periodically, a person feels absolutely healthy, since there are no signs of pathology at all. Many people diagnosed with von Willebrand’s disease do not experience any discomfort from this pathology at all. At the same time, other patients constantly suffer from regular bleeding, which is a deadly threat. The quality of life of such patients will suffer from birth. Bleeding can be so intense that it requires a hospital visit to stop it.
Symptoms of mild von Willebrand disease:
Nosebleeds that recur quite often.
Menstrual bleeding in women is characterized by profuse discharge.
Bruises appear on the skin, even with minor injuries.
Petechiae often form on the skin.
Extensive hematomas form at the site of the injuries.
If the disease has a severe course, then this will be accompanied by the following symptoms:
The presence of blood in the urine. In this case, the person will experience pain in the lumbar region, suffer from dysuric disorders.
After a minor bruise, large bruises will appear on the skin of a person. Hemorrhages strongly swell, put pressure on the nerve endings, which responds with pain.
Frequent hemorrhages in the joint cavities.
Prolonged and incessant bleeding from the gums.
Bleeding from the nose and nasopharynx, which can lead to bronchial obstruction.
Hemorrhages in the brain. This situation is potentially fatal.
In severe cases of von Willebrand disease, its symptoms are similar to hemophilia.
Diagnostics
von Willebrand disease is difficult to diagnose. Most often it is diagnosed in teenagers. To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor must study the family history in detail, carefully interview the patient. The presence of hemorrhagic syndrome and aggravated heredity make it possible to suspect this pathology.
To confirm the suspicions, the doctor will prescribe the following diagnostic measures to the patient:
All young couples who are planning a pregnancy, but at the same time are at risk, must undergo genetic tests aimed at identifying a mutated gene.
The patient’s blood is examined for the activity of the von Willebrand factor, its qualitative and quantitative characteristics are studied.
Perform a blood coagulogram and complete blood count.
To detect hemarthrosis, an x-ray examination of the joints, or their MRI and arthroscopy, is indicated.
Internal bleeding can be detected by ultrasound examination, as well as during laparoscopy.
Perform a fecal occult blood test.
It is also possible to conduct a tourniquet and pinch test.
Treatment of von Willebrand disease

The treatment of von Willebrand disease is carried out by a hematologist. You should tune in in advance to the fact that a full recovery cannot be achieved, since gene anomalies cause pathology. However, it is quite possible to improve the quality of life of patients.
The treatment is based on substitution transfusion therapy, which allows to normalize the work of all stages of hemostasis. Patients are prescribed blood products that contain von Willebrand factor. It can be cryoprecipitate or antihemophilic plasma. Such treatment makes it possible to increase the production of factor VIII in the patient’s body.
If a person develops minor bleeding, then you can try to stop it with a tourniquet and a hemostatic sponge. Thrombin wound treatment also well prevents blood loss.
To stop bleeding, the patient may be prescribed drugs such as: antifibrinolytics, hormonal oral contraceptives, Desmopressin.
Fibrin gel may be applied to a bleeding wound.
A gypsum splint is applied to a limb with an affected joint (with the development of hemarthrosis). Be sure to give the joint an elevated position. When the hemorrhage is stopped, the patient is prescribed UHF. The diseased joint must be limited in loads. If the patient’s condition is severe, then he is prescribed a puncture with pumping out blood.
Desmopressin is a drug that is prescribed to treat von Willebrand disease types 1 and 2. Taking this drug stimulates the body to produce factor VIII. The drug can be used both in the form of a nasal spray and in the form of injections. If therapy does not bring the desired success, then the patient is prescribed a transfusion of the plasma concentrate of the missing factor.
Tranexamic acid and Aminocaproic acid are antifibrinolytic drugs. They are administered intravenously or taken orally. These medicines are prescribed for recurrent uterine bleeding, epistaxis, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
If the disease has an uncomplicated course, then Tranexam can be used. In difficult cases, Tranexam is combined with Etamzilat or Dicinon.
Preventive measures
It is impossible to prevent the development of von Willebrand disease, since it is inherited. However, you can try to minimize the risk of bleeding of different localization.
For this, the following preventive measures must be observed:
Inform couples who are at risk for this disease.
Children with an established diagnosis are subject to dispensary observation.
Patients should be regularly monitored by their doctor.
Care must be taken to avoid injury.
You can not take Aspirin and other drugs that reduce the functionality of platelets.
Surgical interventions in such patients are carried out only if there are vital indications for this.
Be sure to lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right.
These recommendations will make it possible to avoid intra-articular and intramuscular bleeding, as well as the complications associated with them. The sooner the diagnosis is made and treatment started, the better the prognosis. It is unfavorable only when the disease is severe.
Video: lecture for a doctor on von Willebrand’s disease:









