Contents
Diphyllobothriasis – a chronic parasitic infection caused by a wide tapeworm. This helminth belongs to tape parasites. The main route of human invasion is the consumption of infected fish. The wide prevalence of this type of helminthiasis in the population of fish living in regions with a temperate climate makes us cautious about eating this product. This disease is diagnosed in Canada and North America, in Germany, France, Italy, Holland, Finland and other European countries. In Russia, diphyllobothriasis occurs in the basins of the Siberian rivers – the Yenisei, Amur, Lena, Ob, as well as in the lakes and rivers of Tatarstan, Samara, Nizhny Novgorod, Volgograd.
Who is a wide ribbon?
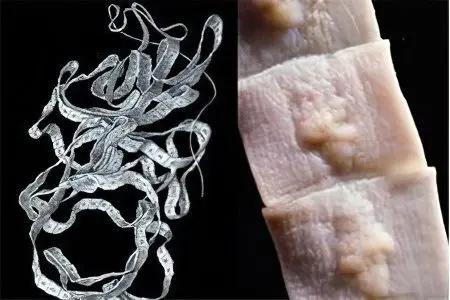
Diphyllobothrium latum is a tapeworm 2 to 10 meters long. Some specimens exceed this length. The wide tapeworm belongs to the class of cestodes (Cestoda), the family Diphyllobothriidae. It consists of a neck, on which there is a scolex (head) with two slit-like devices for attaching the helminth to the mucous membrane of the small intestine, and a body.
The body of the tapeworm consists of a huge number of segments, their number reaches 4 thousand. In mature segments, large oval eggs are formed. They are protected by a two-layer shell, on one of the poles they have a cap. Being in the intestines of the intermediate or final host, the tapeworm releases immature eggs that reach full maturity only in fresh water reservoirs.
Symptoms of diphyllobothriasis

From the moment the tapeworm is introduced into the human body until the first significant symptoms appear, it can take from 20 to 60 days. The manifestations of the disease develop gradually, they can be mild for a long time.
Symptoms of infection:
Nausea, vomiting;
Pain in the abdomen of a cramping nature;
Increased salivation (hypersalivation);
fatigue;
A slight increase in temperature to subfebrile values;
Decreased or increased appetite, weight loss;
Alternating constipation and diarrhea;
The appearance in the feces of fragments of the body of the tapeworm in the form of fragments of whitish ribbons;
Intestinal obstruction with the accumulation of helminths in the lumen of the small intestine;
Signs of anemia with vitamin B12 deficiency (weakness, tachycardia, dizziness, pale skin, swelling of the face, arms and legs, cracked tongue, atrophy of taste buds, damage to the oral mucosa);
Damage to the nervous system (numbness of the limbs, impaired sensitivity, unsteady gait);
Violations of the blood composition (decrease in the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets, blood hemoglobin, an increase in the color index, the appearance of megaloblasts, megalocytes).
The intensity of symptoms depends on the degree of damage to the body, comorbidities, diet. In severe cases, there is hepatomegaly, enlargement of the spleen, extremely low secretion of gastric juice. The accumulation of many individuals of the helminth in the intestinal lumen leads to obstructive intestinal obstruction. There are cases of latent (hidden) course of infection.
The consequences of diphyllobothriasis for human health

The consequences of the stay of the helminth in the human gastrointestinal tract:
Tissue necrosis and atrophic processes develop at the site of attachment of bothria of the tapeworm scolex to the intestinal mucosa;
There are violations of the activity of the gastrointestinal tract due to damage to the nerve endings of the mucosa and disorders of the intestinal trophism;
The waste products of a wide tapeworm sensitize the body, causing allergic reactions;
Megaloblastic anemia appears due to the fact that vitamins B1, B6, B12 are adsorbed by the parasite.
A severe form of anemia leads to neurological disorders: depression, increased irritability, hyperreflexia, paresthesia.
Ways of infection with tapeworm wide
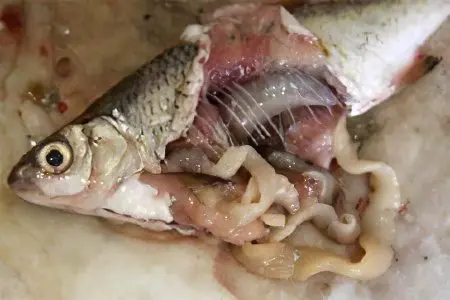
Infection with tapeworm wide occurs in the alimentary way. Parasite infestation occurs during the consumption of infected fish or caviar, which may be either lightly salted or undercooked. In the muscles or in the internal organs of such fish (chum salmon, pink salmon, pike perch, burbot, ruff, pike) there is a plerocercoid – an intermediate form of development of a wide tapeworm.
It is most likely that such caviar or fish was salted at home in violation of the proportions or salting technology. Sometimes infection occurs through contaminated dishes, knives, cutting boards. Those who prefer to eat raw fish or caviar, cook fish kebabs are at great risk.
Parasite development cycle:
From the small intestine of an infected person or animal, the eggs of the broad tapeworm enter the external environment.
In some of the eggs that fall into the water, the embryo of the tapeworm develops. If the water temperature does not drop below +15°C, the embryo (coracidia) emerges into open water after 1-2 weeks.
At a temperature not exceeding +20°C, it remains viable in fresh water for up to six months.
In the body of a freshwater crustacean that has swallowed an embryo, it turns into a larva (procercoid).
Predatory fish or fish of the cet family swallow crustaceans along with procercoids.
In the body of fish, the larvae penetrate the intestinal wall into the muscles and continue their development, transforming within a month into a plerocercoid 1 to 5 cm in size, along with bothria. This form of tapeworm development can be seen with the naked eye.
The plerocercoid, together with the fish, enters the body of the final host (human) and continues its development in the small intestine.
After 2-4 weeks, the larva turns into a sexually mature individual and begins a new development cycle.
From the egg stage to the appearance of a sexually mature individual, under favorable circumstances, 6-7 months pass. In the human body, a wide tapeworm can parasitize up to 20 years. A sexually mature female of a wide tapeworm is able to produce up to 2 million eggs per day.
In addition to humans, cats, dogs, pigs, foxes and bears can be the ultimate host of this parasite. Although they intensively secrete parasite eggs along with feces, they are not directly dangerous to others, since the embryos have not gone through the path of development to an invasive state.
Treatment of diphyllobothriasis
Before treating diphyllobothriasis, the doctor diagnoses helminthiasis. An anamnesis of epidemiological manifestations is preliminarily collected. It includes such items as living near a fresh water body, fishing, eating self-caught and salted fish.
Laboratory research:
Analysis of feces for the detection of tapeworm eggs and parts of his body;
A blood test to determine the signs of hyperchromic anemia;
Complete blood count for the detection of neuropenia and thrombocytopenia;
Biochemical blood test for the content of haptoglobin and lactate hydrogenase.
After analyzing all the indicators, the helminthologist recommends effective drugs for the treatment of diphyllobothriasis. At the preparatory stage, beriberi and iron deficiency anemia are treated. Within a month, the patient takes iron preparations, injects vitamin B12.
Drugs with anthelmintic action:
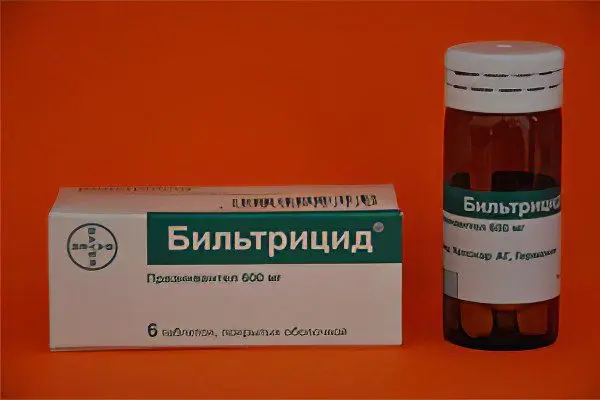
Praziquantel – leads to paralysis of the muscles of the parasite, is used to treat children from 4 years old, a side effect is a decrease in concentration.
Biltricid is contraindicated in pregnant women, the dosage is 60-75 mg/kg of body weight, the daily dose is divided into 3 doses.
Niclosamide – is used to treat children from 2 years old (0,5 g / day), the therapeutic dose for adults and adolescents from 14 years old is 2-3 g / day, accompanied by the use of laxatives.
To reduce the intensity of toxic poisoning and allergies, these drugs are accompanied by antihistamines – Tavegil, Suprastin, Cetrin, Diazolin.
Prognosis for the development of diphyllobothriasis

With careful implementation of the doctor’s recommendations, the prognosis for recovery is optimistic. After the antiparasitic therapy, unstable immunity occurs, and re-infection with diphyllobothriasis is not excluded.
Prevention of invasion with a wide ribbon
To protect yourself from infection with wide latent, you need to carefully monitor the full-fledged culinary processing of fish: fry it for at least 30-40 minutes, salt it for 10 days, freeze fish products to destroy parasite larvae.
Fishermen and workers in the processing industry should undergo timely medical examinations, especially at the time of the greatest activity of the parasite larvae. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should immediately undergo an in-depth examination by a parasitologist.









