Contents
Most people learn about what a blood clot is only after the death of a loved one. Only later does it become clear that a terrible tragedy could have been avoided if you showed at least a little interest in your health and listened to the reactions of your own body. At a time when a blood clot comes off, a person can die in just a few minutes, and even doctors will no longer be able to help him. Knowing the causes and symptoms that indicate thrombosis, you can save your life and the life of a loved one.
A blood clot is a blood clot that forms inside a vessel, although normally it should not be there. Thrombus separation is a condition that poses a direct threat to life, so all patients with diagnosed thrombosis need hospitalization. Every year, one in 250 people die from the consequences of thrombosis. Moreover, the disease often develops in young people.
The particular danger of blood clots is reduced to the suddenness of the pathological condition. In about 30% of cases, the first arterial thrombosis is fatal. A person dies quickly, within 30 minutes from the appearance of the initial signs of the disease.
How is a thrombus formed?
Human beings need blood in order to live. It circulates through the vessels, delivering nutrients, protective elements to the organs, which help in the fight against viruses and bacteria. If a person is injured, then the blood coagulates, thereby blocking their access to the body. The ability of blood to form clots and clog the lumen of a vessel with them can sometimes play a cruel “joke” on a person, which will lead to disability or even death.
Blood has fluidity so that it can clot at the right time, the mechanisms of the coagulation system are turned on. It starts the formation of protein fibrin filaments, which clogs the vessel, preventing excess blood from seeping out.
Also, the human body has an anticoagulant system that fights the formation of blood clots in those tissues that have not lost their integrity. If at some point there is a failure in the functioning of these two systems, then blood clots begin to form in the vessels.
They are located near the inner wall of the vein, passing through several stages:
The thrombus begins to grow in the place where the vessel is damaged and inflamed. Most often this happens against the background of thrombophlebitis. The body reacts to the inflamed vessel by activating the blood coagulation system. It triggers the production of fibrin fibers, which are concentrated near the site of inflammation.
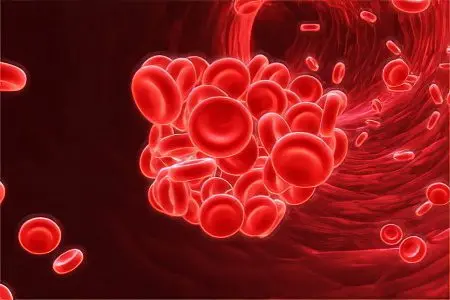
In fibrin fibers, erythrocytes and platelets begin to become entangled.
New blood cells that are brought in with the blood stream continue to “stick” to the clot, making it bigger and bigger. It increases in size, becomes denser and can come off at any moment.
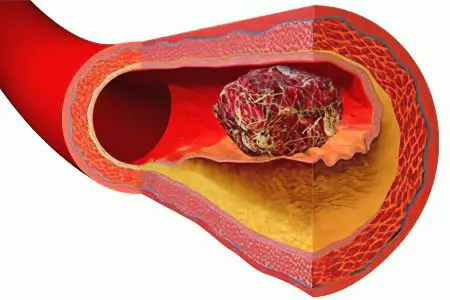
Blood clots can also form in arteries when a vessel narrows. Cholesterol plaques that have grown on the arterial walls are an obstacle to normal blood flow, as a result of which a clot of fibrin filaments and platelets begins to grow.
Risk factors for blood clots:
Belonging to the male sex, age over 40 years.
Belonging to the female sex, age over 50 years. An increased risk of thrombosis is caused by menopausal changes in the body.
Dehydration of the body.
A cancerous tumor of a malignant nature.
Alcohol abuse.
Serious nutritional deficiencies.
Taking certain medications. Of particular danger in terms of the formation of blood clots are hormonal contraceptives.
Transferred operation.
Violation of the normal flow of blood through the vessel as a result of its compression.
Pregnancy.
Leg vein injuries.
Heart failure.
Infections.
Threats to human life are blood clots that form in large vessels. Their separation will lead to the rapid death of the patient.
Causes of a blood clot

The thrombus may be parietal or may be floating. If a thrombus is located near a cholesterol plaque, then it is less likely to come off than a floating thrombus. The latter “sits” on a thin leg, which has a weak attachment to the vascular wall. It is floating thrombi that most often lead to the development of pulmonary embolism and strokes.
Also, wandering blood clots may be present in the body, which pose a serious threat to life.
A blood clot can come off as a result of the following influences:
The blood flow is greatly accelerated.
A thrombus formed in a wide vessel.
The leg of the thrombus is weak.
After detachment, the thrombus begins to travel with blood flow through the vascular bed. At this time, it often breaks up into small fractions. Once in a vessel that does not exceed its size, a clot clogs it. This entails a cessation of blood flow and disrupts the nutrition of the limb or organ. This pathological condition is called occlusion.
Signs of a blood clot

If it is recognized in a timely manner that a blood clot has come off in a person, this can save his life.
The consequences of the disaster may be as follows:
A blockage of a blood vessel in the brain is called a stroke. Its main features: speech disorders, facial asymmetry, impaired coordination of movements, paralysis of the limbs. If a blood clot enters a cerebral vein, then the person will suffer from dizziness, headaches, blurred vision, etc.
If a thrombus enters the coronary arteries, then the patient develops a myocardial infarction. A person experiences severe pain in the region of the heart, in the neck, abdomen, between the shoulder blades.
A mesenteric thrombus leads to intestinal embolism. In this case, a person experiences severe pain in the abdomen, which occurs unexpectedly, against the background of absolute well-being. This is the reason for the immediate call of the ambulance brigade. If a person is not provided with emergency assistance, this will lead to the death of intestinal tissues, infection of the peritoneal cavity and death.
When a blood clot clogs a vessel that feeds a limb, it can lead to its gangrene. Symptoms of embolism of the veins of the arms or legs are severe pain, blue tissue in the appropriate place.
Blockage of the pulmonary artery by a thrombus is the most serious condition, which often ends in the death of the patient. A blood clot can enter the pulmonary artery from the veins of the lower extremities. Most often this happens against the background of thrombophlebitis. With PE, a person can die in a few minutes from heart or lung failure.
If a person has one or more of the above symptoms, you should not hesitate to contact a doctor. When a thrombosis is suspected, this should be told to the doctor, which will facilitate the diagnosis. If a person knows that he suffers from atherosclerosis, thrombophlebitis, coronary artery disease and other diseases that are associated with a risk of a blood clot, you need to inform the doctor about this.
It is worth noting that about 50% of people who have had thrombosis did not experience any pathological symptoms until an acute circulatory disorder occurred.
The following signs may help to detect a blood clot:
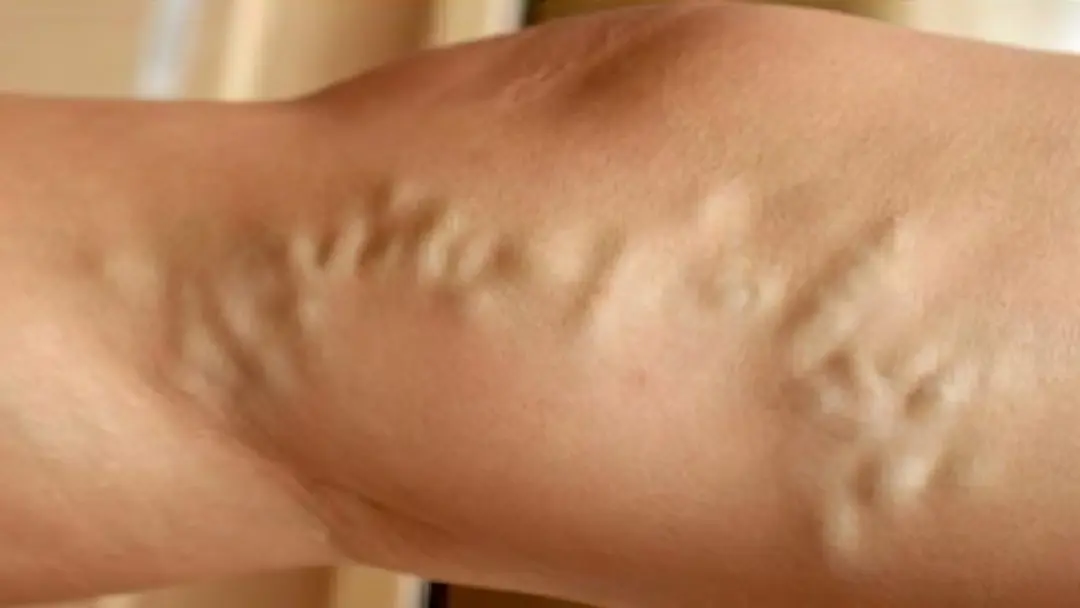
Most often, blood clots are localized in the veins of the lower extremities. The developed system of veins that appear under the skin can suggest the idea of thrombosis. The vessels can be compacted, sometimes they become inflamed, which can be seen by the redness of the skin and the pain that occurs when touching them. If you touch this area, you can feel the heat.

A thrombus that has formed in deep veins can make itself felt by swelling in a characteristic place, general malaise and inexplicable jumps in body temperature.
If a blood clot breaks off – what to do?

If a blood clot has come off in a person, then it is impossible to hesitate to call an ambulance brigade. Moreover, even a doctor cannot make an accurate diagnosis without special equipment. Therefore, the victim must be urgently hospitalized.
There can be two treatment regimens for thrombosis: either the patient is prescribed a medical correction, or they are sent for surgery.
Drug therapy includes:
Administration of anticoagulants. These drugs help thin the blood.
Course treatment with statins.
Appointment fibrinolytic.
The appointment of thrombolytics, which are necessary for the dissolution of a blood clot.
If the problem cannot be solved with the help of drugs, or a person develops complications of thrombosis, he is shown an operation called thrombectomy. It is also possible to install special cava filters that will “catch” blood clots, preventing them from clogging vital vessels.
How to prevent a blood clot
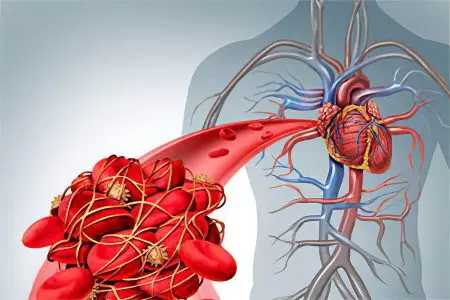
People whose blood relatives have suffered from thrombosis will have a high risk of developing a similar disease. Therefore, you should be regularly examined by a doctor to detect dangerous vascular growths. Modern medicine has all the necessary tools to detect a blood clot and prevent its separation.
If a person’s blood is characterized by increased clotting, he will be prescribed drugs (antiplatelet agents). Sometimes they need to be taken for life. It should be noted that only a doctor can recommend them, otherwise you can cause serious harm to your own health.
If the doctor diagnoses a blood clot that can come off with a high degree of probability, then the patient is urgently hospitalized and prepared for surgery.
So that the blood does not stagnate in the veins, it is necessary to move as much as possible, engage in physical education, and walk a lot.
If the patient has a risk of a blood clot, then he is shown strict bed rest. Self-treatment of thrombosis or expectant management in this case is unacceptable.
A menu with eating foods that lower blood cholesterol should be a priority. This will prevent the formation of atherosclerotic deposits on the vessels, and therefore reduce the risk of thrombosis. To this end, you can include in the diet of sea fish, seafood, broccoli, spinach, new potatoes, dairy products.
Thrombosis Prevention Strategy

The Society of Cardiology, established in Europe, has developed its own strategy for the prevention of thrombosis.
It was compiled taking into account the main risk factors leading to the development of the disease, and was called “0-3-5-140-5-3-0”:
0 – completely abandon such a bad habit as smoking. And this statement applies even to those people who are passive smokers. Inhaling tobacco smoke means being at risk for thrombosis.
3 – every day you need to walk at least 3 km on foot, and also play sports for 30 minutes.
5 – every day there are vegetables and fruits, 5 servings.
140 – the maximum pressure indicator should not exceed 140/90 mm. rt. Art.
5 – the indicator of total cholesterol in the blood should not exceed 5 mmol / l.
3 – the level of low-density lipids must be at least 3 mmol / l.
0 – do not get better, do not acquire diabetes mellitus.
If you follow this “health code”, then the risks of developing thrombosis are significantly reduced.
Sometimes it happens that a person learns about thrombosis only in a hospital ward. The disease is often asymptomatic. Therefore, prevention of thrombosis should become a way of life. In addition, you should carefully listen to your body, which always gives signals of trouble.