Contents
- What are asteroids
- History of the discovery of asteroids
- Chemical composition and color of common asteroids
- Where are the asteroids
- The largest groups of asteroids
- Asteroids and comets: similarities and differences
- The largest asteroids
- Methods for studying asteroids
- An asteroid is approaching Earth! What to do?”
- Space missions to asteroids
In the past few years, people have often discussed the possibility of an Earth-Stellar collision. Trends understand what asteroids are, how they appear and whether they can destroy all life
What are asteroids
Asteroids are solid rocky bodies that revolve around the sun. By this they repeat the behavior of the planets, but they cannot be called that because of their small size. They belong to the category of “small bodies of the solar system”. Although there are millions of them, their total mass is less than that of the Moon.
Asteroids formed about 4,6 billion years ago, during the early formation of the solar system. Then the future planets experienced the stage of “planetesimals”. During this period, small cosmic particles are gradually attracted to each other, the temperature in the center rises, due to which they melt and form a protoplanet. The current asteroids are “by-products” of that process. Scientists suggest that many satellites of the planets are former asteroids, which were “captured” by the gravitational field of a large object, forcing them to revolve around it.
History of the discovery of asteroids
Asteroids were discovered by accident: in 1801, the Italian astronomer and priest Giuseppe Piazzi discovered the largest of them and named it Ceres in honor of the Roman goddess of fertility. It now qualifies as a dwarf planet. Since then, scientists began to regularly find asteroids: by the second half of the 100th century, the number of recorded objects exceeded 1921, by 1 – over 1981 thousand, and by 10 – over 800 thousand. Now this number exceeds 1980 thousand. In 66, it was put forward the hypothesis that it was the fall of an asteroid about XNUMX million years ago that led to the extinction of dinosaurs.
According to scientists, this asteroid landed in the region of modern Mexico. Most amphibians could die within hours or days of falling due to the sudden rise in ambient temperature. This collision could cause irreversible climate change, increase the acid content in the atmosphere and change the composition of the oceans.
Chemical composition and color of common asteroids
Scientists divide asteroids into classes based on their composition. Here are the three most common ones:
- Class C asteroids. Colour: greyish. Consist of carbon and a number of other substances, including silicon. This is the most common type, which includes about 75% of all asteroids.
- S class asteroids. Colour: greenish or reddish. Consist of silicon, nickel and iron. The second most common type, includes about 17% of all asteroids.
- M class asteroids. Colour: reddish. Composed of nickel and iron. Remains of metallic cores of planetesimals.
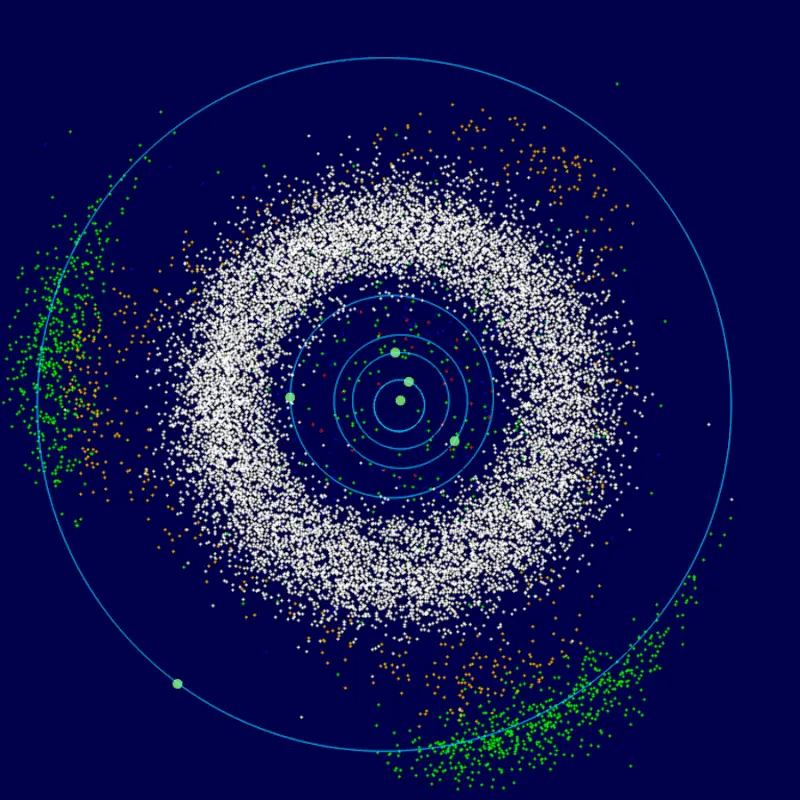
Where are the asteroids
Most asteroids in the solar system are found in the main asteroid belt, between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It circulates more than 200 asteroids with a diameter of more than 100 km, from 1,1 million to 1,9 million with a diameter of more than 1 km, and millions of small ones. As scientist Vladimir Busarev writes, here they move in a “safe” zone, where the gravitational influence of large planets on them is minimal. It was because of Jupiter that another planet could not arise at the site of the main asteroid belt during the birth of the solar system. Its gravitational field prevented the formation of nearby planetesimals, so the particles did not coalesce and continued to move around the Sun in the form of asteroids.
The largest groups of asteroids
Asteroids are located in the solar system not only in the main asteroid belt.
- “Trojans” и “Greeks”, which were named after the heroes of the Iliad, are located at the “Lagrange points”. In these parts of space, the gravitational influence of the planet and the Sun is equivalent. Jupiter has more than 10 Trojans and Greeks. Neptune has 30, Mars has nine, and Earth and Uranus have one each.
- “Hilda’s family” contains more than 1 thousand Trojan-like asteroids. It lies behind the main belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
- “Kuiper Belt” located at the edge of the solar system, next to Neptune. It is similar to the main asteroid belt, but differs from it in size: 20 times wider and 20–200 times more massive. It contains small bodies of water, ammonia and methane, and at least four dwarf planets, to which modern science classifies Pluto.
Asteroids and comets: similarities and differences
A comet differs from an asteroid only in composition: stardust and ice instead of metals. When approaching the Sun, substances begin to evaporate, due to which the famous “tails” are formed.
A meteorite is an asteroid or its fragment that has reached the Earth’s surface. About 20 meteorites hit our planet every day. They do not pose a danger, since the vast majority of their size does not exceed the size of a stone that can be held in the palm of your hand. According to NASA, meteorites that can destroy a city or cause a devastating tsunami collide with the Earth every 1-10 thousand years.
Large meteorites, 400 m in diameter, capable of causing a global cataclysm, on average fall on our planet every 100 thousand years. Nevertheless, scientists are working on all options to combat the potential threat.
The largest asteroids
It is difficult for researchers to measure asteroids due to their irregular shape and different albedo (surface reflectivity). If you count by approximate diameter, the first ten will look like this:
Methods for studying asteroids
- In 1991, the NASA research vehicle “Galileo” sent close-up images of asteroids from the main belt to Earth.
- In 2001, another agency space probe, NEAR Shoemaker, for the first time in history, successfully made a soft landing on the asteroid Eros. After working on it for two weeks, he stopped communicating.
- In 2006 Japanese machine “Hayabusa” (translated as “Falcon”) landed, took samples, and then took off from the asteroid Itokawa. In 2010 he returned to Earth.
- In 2019 year “Hayabusa-2” successfully landed on the distant asteroid Ryugu, which is located 280 million km from Earth. In 2020, a capsule with soil samples collected by the probe flew to Earth.
- NASA sent a mission in October 2021 “Lucy”, which will study “Trojans” for more than 10 years.
An asteroid is approaching Earth! What to do?”
In 1998, US congressmen asked NASA to record all asteroids and comets with a radius of 1 km or more that could be in Earth’s orbit. Since then, NASA astronomers have discovered 95% of asteroids, and some of them could hypothetically lead to the end of the world. Now none of them threaten our planet. Nevertheless, the US Congress raised the bar back in 2005 by ordering NASA specialists to find all asteroids with a radius of 140 m or more. They are also called “city killers”, since they are able to wipe out a metropolis from the face of the Earth. The probability of encountering them in any century is about 1%. Now NASA has found about 40% of them. It will take another 60 years to discover the remaining 30%.
Space missions to asteroids
But what to do when a dangerous asteroid flying towards the Earth is discovered? Hollywood has a lot of ideas, from the atomic bomb explosion in Armageddon to the splitting into useful resources in Don’t Look Up. However, astronomers agree that the most effective way is much simpler: just change the course of a celestial body. At the end of November 2021, NASA launched the DART project spacecraft. It weighs 600 kg and looks like a car-sized box with solar panels on the sides. In the fall of 2022, it should crash into the satellite of the asteroid Dimorph at a speed of 24 thousand km / h. The latter does not pose a threat to the Earth, but the collision should prove that the flight path of asteroids and comets can be changed. If the experience is successful, NASA will develop a similar strategy for any potential space threat in the future.










