Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
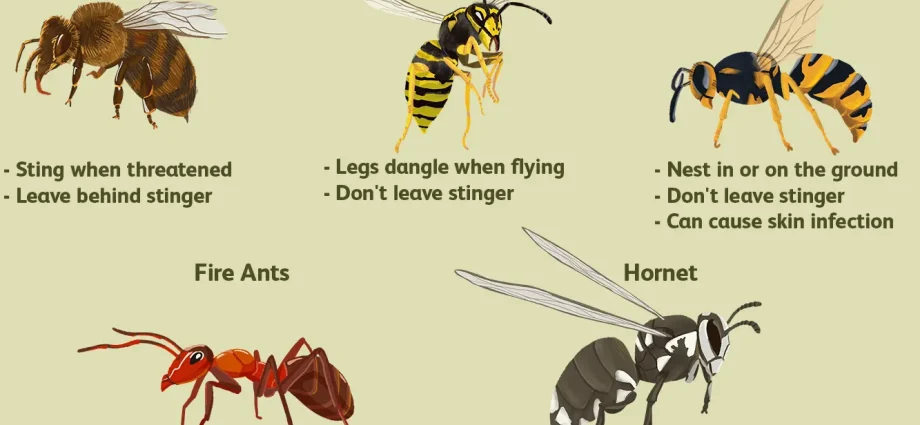
A wasp or bee sting is usually not fatal. For most people, it only means a painful sting. However, in Poland, a dozen or so people die every year due to the stings of these insects.
- A sting of 100-200 bees can kill. Sometimes only one insect is enough – if a severe allergic reaction occurs, the venom can turn out to be a deadly poison
- Bees or wasps can be particularly dangerous – they can suffocate
- The allergist reassures, however, that for most of us, stings are not a threat. There will be swelling, redness, itching, but after a few days the symptoms should disappear. If this does not happen, an appointment with a doctor is necessary
Insect venom allergy – wasps and bees
An adult can die after a swarm attack and stings of 100-200 bees or wasps, and a child of about 50. The cause of death is the toxin contained in the sting. Sometimes, however, only one insect is enough. Death is then caused by an allergic reaction. It occurs in 0,3 to 7,5 percent. people. The risk of its occurrence is increased by short and irregular intervals between stings and severe allergic attacks in the past.
More serious allergic reactions are caused by bee venom more often than wasp venom.
As a rule, bees provoke more serious reactions in the body than wasps. The highest number of deaths from allergies following a sting occurs in patients over 60 years of age, as they suffer from cardiovascular and respiratory diseases more often. Stings around the mouth or throat of a person are also life-threatening. Then, suffocation may occur as a result of the closure of the respiratory tract by increasing allergic swelling.
A particular risk of such a situation arises in the case of swallowing a wasp or a bee. Dangerous swelling may also appear when an insect bites us on the neck.
It is estimated that a dozen or so people die each year due to stings. According to the allergist prof. Peter Kuna, the number of fatal stings may be even greater because the cause of death is not always correctly identified. – Someone dies in the meadow due to circulatory failure and no one checks if the victim has not been stung by a bee before. And it was she who could have been the cause of death – says prof. Marten.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction after a sting
Insect venom is a perverted, an overreaction of the immune system on substances introduced into the body. It’s like shooting a fly from a cannon. As a result of a sting, specific antibodies are formed in the body. When the venom comes into contact with the antibodies present in the blood during the next attack, substances begin to be released, causing the blood vessels to widen and the plasma to penetrate the vessel walls.
Skin itching and swelling appear. The patient is anxious, may experience shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain and dizziness. Your blood pressure drops, and you may faint and pass out. The brain, heart, and other organs begin to become ischemic. If the victim is not treated, he or she may die. Adrenaline administered in such a situation increases the pressure and improves the blood supply to the vital organs – the brain, heart, lungs and kidneys. After 3 to 5 minutes, the sting comes back to consciousness.
Adrenaline for allergy
– Patients often ask to be prescribed adrenaline in case they get stung. They claim that this has never happened to them and therefore do not know if they are allergic to insect venom. Meanwhile if someone has never been stung by a bee or wasp, he must not be allergic to their venom. The first sting can only be dangerous if it occurs in the mouth or throat, for example if we swallow an insect. Then the swelling can lead to suffocation. In summer, the best way to avoid such a situation is to check if there is bee or wasp in the vessel from which we are drinking – says allergist Aleksandra Kindracka.
Adrenaline is essential in patients who are allergic to wasp or bee venom, who have lost consciousness in the past or serious reaction after a bite these insects. In the event of another incident, only administering adrenaline immediately after the bite prevents the patient from fainting and may save his life.
People who know they are severely allergic to Hymenoptera venom must have an adrenaline syringe or pen with them. The patient passes it to the side of the thigh. Another person can easily give the injection to the victim.
Home remedies for wasp or bee stings
– A person who has lost consciousness after a sting should consult an allergist. The doctor will order confirmation tests allergy to bee or wasp venom and consider whether it is possible to desensitize the patient – explains Dr. Kindracka. Those who only have a strong local reaction after a bite require neither adrenaline nor desensitization.
For most of us, a wasp or bee sting is not fatal. When we are attacked, the sting must be removed – the bee leaves it in the body. A pharmacy can obtain a special device that sucks the sting and pulls it out. After the sting, painful redness and swelling appear. You can then make cold compresses, e.g. with baking soda. Dissolve a teaspoon of baking soda in half a glass of water. The skin can be covered with a soothing gel, available in pharmacies.
After a bee sting, remove the sting from the skin.
After two or three days, the lesion disappears. For severe reactions, you can take an over-the-counter antihistamine. If home remedies do not help, contact your family doctor who will write a prescription for a steroid ointment.
– If the sting is on the eyelid and causes significant swelling, seek the help of an ophthalmologist – advises Dr. Kindracka.
If you have allergic symptoms after a wasp bite, it’s a good idea to do blood tests. They are available on Medonet Market at an attractive price.
Long-term desensitization in the case of wasp or bee venom allergies
There is no method that can completely prevent you from being stung. Therefore, people with a strong allergic reaction may become desensitized. Desensitization therapy it consists in administering small doses of venom on an outpatient basis. It takes several years. – Effectiveness of wasp venom desensitization is higher and amounts to over 95%, compared to bee venom immunotherapy, which is about 80%. – says prof. Marten. Children and patients with milder forms of general reaction feel more easily desensitized. The best effectiveness is achieved after five years.