Contents
Many gardeners do not particularly bother with choosing a place for crops and planting the main grown vegetables. And even those who have heard about the desired crop rotation in garden conditions often simply change the contents of the beds, not really thinking about the meaning of their actions. But a positive effect from random actions may not be obtained at all, while a conscious choice of one or another garden crop can help and increase its yield without the use of artificial fertilizers and dispense with chemical treatments against pests or diseases. For example, after onions, almost any garden crop can be planted next year, which cannot be said about many other herbs or vegetables.

Why you need to follow the rules of crop rotation
Growing the same plants in the same place for several years has a big impact on the soil.
- The most obvious is that the roots of any plants loosen the soil at different depths, and can even compact it.
- Absorbing a different set of nutrients, the roots change the chemical composition of the soil and are even able to affect the pH of the soil fluid, acidifying or, conversely, alkalizing the soil.
- As plants grow and develop, they can attract a variety of parasites whose larvae and spores remain in the ground after harvest.
- Plants release a wide variety of organic substances into the soil, the impact of which can be both positive and neutral, and even toxic to other representatives of the plant kingdom.
It is for this reason that it is not recommended to plant plants of the same genus or even belonging to the same family in one place in a row.
On the other hand, diseases and pests remaining in the soil can have a negative impact on crops from the same family. While other vegetables will be immune to their influence. And in a few years they will leave on their own, not finding a suitable food base for their existence.
Growing the same crops in the same place, or even belonging to the same family, necessitates mandatory additional dressings and treatments, otherwise you can completely forget about the yield.
Since ancient times, so much knowledge on the interaction and influence of plants on each other has been accumulated that not everyone is able to keep all this information in their heads. The most elementary principle of crop rotation is to alternate the so-called tops with roots. That is, plants in which a person uses mainly their aerial part (cucumbers, lettuce, cabbage, tomatoes) with root crops (carrots, beets, potatoes). Onion in this sense is a universal plant, since both the aerial part (feather) and the bulb growing underground are equally edible. So, after the onion, it is allowed to plant almost any vegetable or herb next year.
It is also customary to alternate crops with a powerful and deep root system (beans, carrots, tomatoes, pumpkin, beans, cabbage) with those vegetables whose roots are located at a shallow depth (melon, onion, radish, head lettuce, spinach, peas).
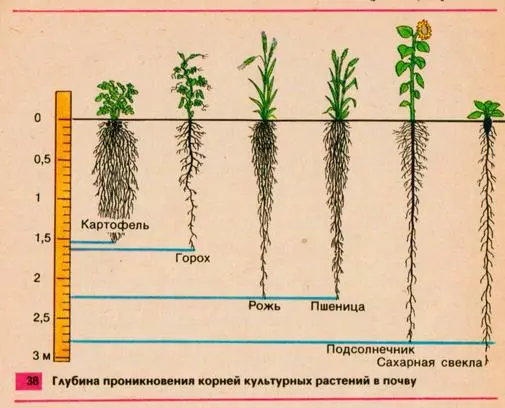
The timing of the ripening of individual vegetables is also important. After all, if some late-ripening vegetable ripened in the garden until the frost, then the soil may simply not have time to rest by the next planting season. In this case, either leave this bed “fallow” or sow any fast-growing green manure, such as mustard, which can quickly improve the quality of the soil.
But some crops that are prone to the invasion of “their” diseases and pests do not recommend returning to their original place of growth earlier than after 4-5 years. So that the earth during this time has time to be cleansed of harmful spores and larvae.
In order to constantly track the places and terms of growing certain crops in the beds, experienced gardeners recommend keeping regular records with planting patterns. Thus, it is possible not only to control the existing patterns, but even with careful observation, one can also derive one’s own laws of the influence of certain cultures on one’s followers.
What can be planted after onions
Onions can be safely attributed to one of the most popular vegetables grown in gardens. Although its perennial green forms are more likely to be classified as herbs and spices. There are many varieties of onions, each of which has its own growing characteristics. But all the bows have one thing in common – amazing healing bactericidal properties that are widely used by man up to the present. It was its bactericidal properties that created a real miracle in the gardens – after onions, almost all planted plants feel great in the beds.
By itself, onions are a medium-demanding crop. After the onion, a significant amount of organic matter always remains in the ground, and the soil itself acquires a slightly alkaline reaction. Most of all, it takes nitrogen from the soil, but phosphorus and calcium remain in reasonable quantities. Therefore, after onions, crops that need a slightly alkaline soil reaction and the presence of phosphorus with calcium (cabbage, cucumbers, tomatoes, beets, carrots) will grow best.
For other crops, its bactericidal and soil-disinfecting properties (strawberries) will be the most important.
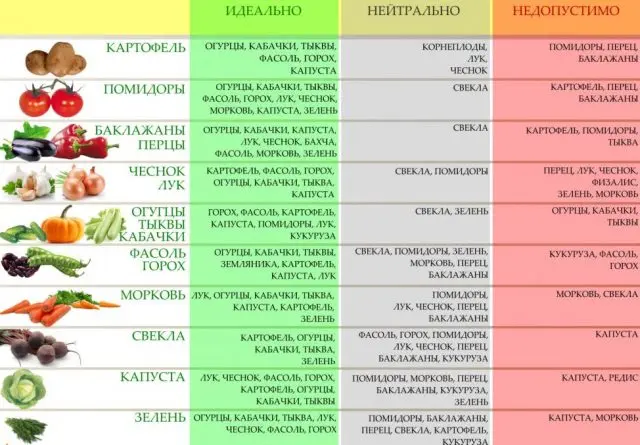
What can be planted after onions: table
The table below discusses not only options for what can or cannot be planted after onions, but also the most favorable, neutral and unfavorable predecessors and successors for other garden crops.
Is it possible to plant strawberries after onions
For many novice gardeners and gardeners, the most confusion arises about whether it is possible to plant strawberries after onions. Perhaps it seems to them that the sharp phytoncides secreted by all parts of the onion can have an adverse effect on the sweetness and aroma of strawberries. But everything happens exactly the opposite. After the onion, the earth is completely freed from those pathogenic bacteria that can be dangerous for the development of strawberries. A slightly alkaline moderately fertilized soil is ideal for its growth.
Is it possible to plant cucumbers and tomatoes after onions
For cucumbers, onions are considered the best predecessor, since these tender cucurbits do not tolerate acidic soils.
And when planting tomatoes and eggplants, the disinfection of the land will also play an additional role.
Is it possible to plant carrots and beets after onions
Since ancient times, it has been known about the favorable mutual influence of onions and carrots. Beets are able to release not too useful substances into the soil, but they themselves feel great when planted after onions.
Is it possible to plant garlic after onions
But with garlic, things are not at all as simple as with other crops. After all, they belong to the same family with onions, which means they are sensitive to the same diseases accumulated in the soil.
Therefore, garlic is definitely not recommended to be planted after onions.
Is it possible to plant pumpkin and cabbage
And with those and other vegetables, onions have excellent compatibility. Pumpkin will definitely like to grow after onions, and for any representatives of the cabbage family (rutabaga, mustard, radish, turnip, radish), all varieties of onions are excellent predecessors.
What can not be planted after onions
It is thanks to all of the above that after the onion, it is not recommended to plant only the onion and garlic itself. And there is one exception to this rule. Leek can be grown in one place for several years without tangible losses in yield and appearance of the vegetable.

For other vegetable crops, there are no restrictions on planting after onions. But next year, they try not to plant greens and various bulbous flowers (grouse, tulips, daffodils and others) in this place.
If you want to quickly get rid of harmful influences, the beds are sown with green manure (rye, lupins, marigolds, mustard), which are able to put the earth in order in the shortest possible time.
Conclusion
After the onion, you can plant almost anything next year except for those plants that belong to the same family with it. For the rest, onions will bring considerable benefits and will contribute to their favorable development.









