Contents

Strabismus can develop not only in children, but also in adults. This pathology can also be found under the name strabismus or heterotropia.
In people with strabismus, the eyes cannot be focused in one direction, so the patient is unable to direct both organs of vision at once to one object. One eye will be turned to one side, up or down. For some people, strabismus is a temporary phenomenon and occurs only against the background of illness or stress. Others have it permanently.
If timely treatment is not started, then strabismus will cause a decrease in vision. This problem develops in 5% of patients with heterotropia.
What it is?

Strabismus is a disease in which there is a violation of the visual axis of the eye. The gaze cannot be focused at one point, so a person perceives the same object in different ways.
The brain receives the wrong signal and processes it in the same way. To protect itself, the central nervous system excludes the diseased eye from its “zone of responsibility.” Therefore, it is wrong to consider strabismus solely as a defect in appearance. This is a serious disease that needs treatment.
Problems it can cause:
The inability to correctly estimate the size and distance to the object.
Disturbed perception of perspective.
Deterioration of coordination. If it develops in a child, then it will be difficult for him to maintain balance, he will often fall. Small children with strabismus may refuse to stand up at all.
Reduced vision, incorrect processing by the brain of information received from the visual analyzer.
Adults rarely visit an ophthalmologist. Even if their eyesight begins to deteriorate, they attribute this to the natural aging of the body and are in no hurry to solve the problem. You shouldn’t do it this way. It is important to consult a doctor on time. The sooner strabismus treatment is started, the better the prognosis.
Causes of strabismus in adults

Strabismus can be congenital or acquired. There is also a moving strabismus.
The causes that cause acquired strabismus can be identified as follows:
Atrophy of the optic nerve.
Cataract.
Belmo.
Degenerative processes of the macula.
Retinal detachment.
TBI leading to cranial nerve palsy.
Benign and malignant tumors.
Infection with viruses and bacteria, leading to the development of neuroinfection. Strabismus can occur with meningitis and encephalitis.
Stroke.
Violation of the integrity of the bottom or wall of the orbit.
Multiple sclerosis.
Myasthenia gravis.
Complications of diseases of the respiratory system.
Congenital strabismus can occur for the following reasons:
Violations of intrauterine development.
genetic anomalies.
Early onset of labor.
cerebral palsy in a child.
Hydrocephalus of the brain.
congenital cataract.
Classification
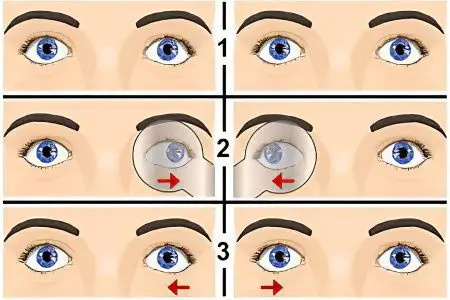
There are several classifications of strabismus, each of which is based on a certain criterion.
Depending on the time of development of the violation, there are:
Strabismus is congenital. It is diagnosed in a child in the maternity hospital. Doctors call this pathology infantile heterotropia. It is rarely diagnosed.
Acquired strabismus. A violation develops due to an infection, after serious illnesses, against the background of an injury with damage to the spinal cord or brain.
Depending on the frequency of manifestation of strabismus, there are 2 of its forms:
Temporary.
Permanent.
Depending on the involvement of the organs of vision in the pathological process, strabismus can be:
Unilateral.
Alternating.
Depending on the severity of the violation, there are:
Hidden strabismus. It can be diagnosed only in the ophthalmologist’s office using special equipment.
Compensated strabismus. It can be detected only after special tests.
Subcompensated strabismus. A person can partially control the squinting eye.
Decompensated strabismus. The movements of the eyeball are uncontrollable.
Depending on the cause of the occurrence, there are such types of violations as:
Concomitant strabismus. This disorder is most often diagnosed in childhood. The eyeball is displaced from time to time, or strabismus is present on an ongoing basis. Most often squints the eye towards the bridge of the nose.
Paralytic strabismus. It develops mainly in old age. The cause is a violation in the work of the oculomotor muscles.
Periodic strabismus.
Depending on the direction of the eyeball, there are such types of strabismus as:
Esotropia. In this type of strabismus, the pupil is closer to the bridge of the nose (convergent strabismus).
Hypertropia. The pupil of the patient goes up, can roll under the eyelid (upper vertical strabismus).
Exotropia. The pupil of a person tends to the bridge of the nose. This is the so-called divergent strabismus.
Hypotropia. With this type of violation, the pupil rolls under the lower eyelid (vertical lower strabismus).
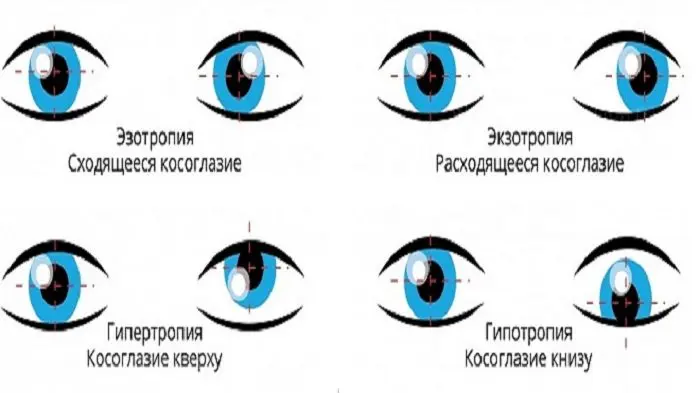
Depending on the mechanism of development of the disorder, there are 3 forms of strabismus:
Accommodative strabismus, which is divided into refractive and non-refractive. With refractive strabismus, the patient develops severe ametropia. Treatment of accommodative strabismus involves wearing glasses.
Non-accommodative strabismus. A person has abnormal refraction and ametropia. The severity of the impairment varies widely. It will not be possible to get rid of the pathology with the help of glasses. Non-accommodative strabismus develops due to unsuccessful surgical intervention on the organs of vision, in the presence of a thorn on the cornea, with pathologies of the optic nerve, or with congenital cataracts.
Partially accommodative strabismus. It is possible to cope with the violation with the help of corrective glasses, but the doctor will not guarantee the patient a full restoration of vision.
Symptoms of strabismus in adults

Most often, the symptoms of strabismus are obvious even for people who do not have a medical education.
Among them are:
Attacks of dizziness that occur unexpectedly for a person.
Double vision in the eyes.
Difficulty perceiving objects that are far away.
Difficulties with reading text and writing.
The form of the disorder affects the symptoms of strabismus.
If a patient develops concomitant strabismus, then its symptoms will be as follows:
Offset of one organ of vision to the side.
Alternate shift of the eyes to the side.
The presence of the same angle of displacement in both eyes.
Excessive mobility of the eyeball. The direction of movement may be different.
The impossibility of visualizing a three-dimensional and comparative image.
Decreased visual acuity in the affected eye.
Impaired refractive function of the eye.
To the symptoms characterizing paralytic strabismus:
Deterioration of the natural mobility of the eyeball.
Various deflection angles.
Lack of binocular vision.
Doubling in the eyes.
Dizziness.
The head will involuntarily turn towards the affected eye.
Constant squinting.
Diagnostics
With severe strabismus, there are no problems with its diagnosis. The doctor needs not only to establish the fact of the presence of a violation, but also to determine the degree of its development. The doctor should be able to recognize the pathology when it has just begun to form.
To make a correct diagnosis, research methods such as:
Assessment of visual acuity.
View of the synoptophore. The doctor gets the opportunity to assess the ability of the eyes to merge the image.
Computer refractometry. This study allows you to evaluate the refraction of the patient’s eye.
Ophthalmoscopy and biomicroscopy. The doctor examines the patient’s fundus and the condition of the retina.
Tests to determine if a patient has binocular vision ability.
Additional diagnostic criteria include:
Determination of the angle of divergence of pupils.
Identification of latent strabismus.
Identification of other disorders in the work of the eye.
Patients with strabismus and thyroid disorders require consultation with an endocrinologist. To cope with the problem, highly specialized treatment is required.
Treatment of strabismus in adults

The main tasks that need to be solved during the treatment of strabismus:
Correction of broken visual axes.
Strengthening the eye muscles.
Restoration of synchronous work of the eyeballs.
Prevent visual impairment.
Methods of treatment of strabismus in adults:
Vision correction using an optical system.
Hardware treatment.
Pleopto-orthopedic therapy.
Formation of binocular vision.
Surgical intervention.
Optical correction
Regardless of the form of strabismus, wearing glasses will not bring harm. Properly selected optics allows you to normalize refraction, get rid of spasm of accommodation, improve the functioning of the organs of vision in general.
Hardware treatment
Hardware treatment is indicated for all patients in whom strabismus leads to a decrease in vision. Such therapy allows you to suppress the activity of a healthy eye and stimulate the functioning of the affected organ.
Hardware procedures that can be prescribed to patients with strabismus:
Pleoptics. A healthy eye is simply “turned off” for a while. Therefore, a person will be forced to look only with a squinting eye. During treatment, the central fovea of the retina of the affected organ is stimulated. The irritant is a beam of light or a laser beam. Reflexology and electrical stimulation of the eyeball are also carried out.
Orthoptics. It should be noted right away that such treatment has little effect on adult patients. The therapy involves working with game computer programs that train the organs of vision. This also includes performing exercises on the synoptophore (a special ophthalmic apparatus).
Diploptic. This is a system of therapeutic measures that involves the performance of specialized exercises, the use of a reading grid and visual field separators. Exercises can be performed on special stereoscopic devices.
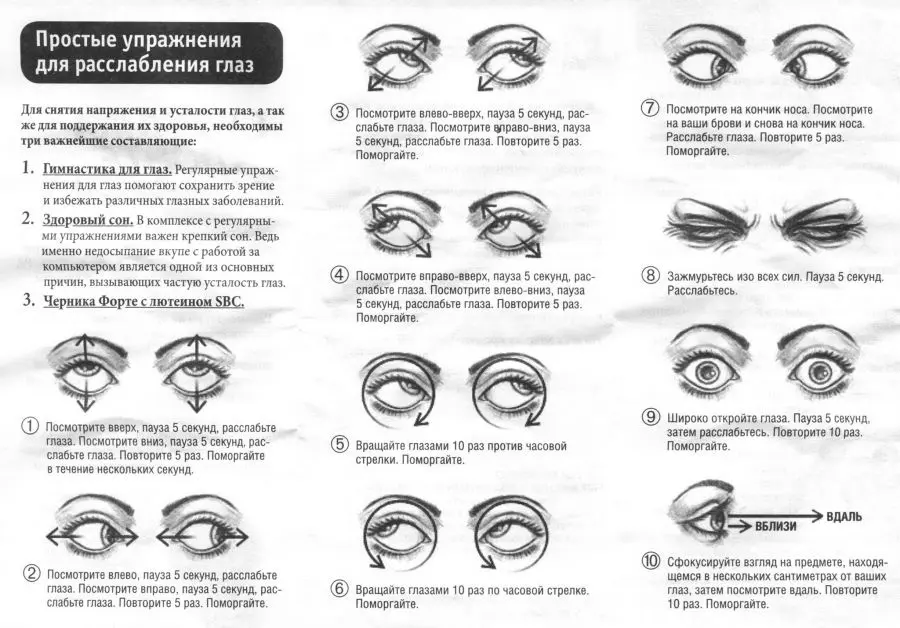
Strabismus Exercises
If a person performs the exercises regularly and to the fullest, then the result will not be long in coming. Often it is possible to cope with strabismus completely. Recommended exercises:
The person should stand with their back to the light. A healthy eye is covered with a palm. The head must be turned until the sunbeam hits the squinting eye. You need to complete the exercise 10 times.
The head must be brought back and from this position they try to see the tip of the nose.
Hands stretch forward and touch the tip of the nose with the fingers. During the exercise, you need to concentrate on the index finger, without interruption, following its movements. You need to perform the exercise until the eyes begin to water.
You will need to take a pointer and drive it in different directions. Eyes need to keep an eye on its tip.
Palms are pressed to the eyes and in this position they mentally draw the outlines of various geometric shapes.
Surgical treatment of strabismus
If it is not possible to cope with strabismus with the help of exercises, glasses and hardware treatment, the patient is operated on. It is aimed at correcting the balance of the muscles of the eyeball. Such treatment allows you to cope with the violation. To enhance muscle activity, either resection or excision is performed. If it is required to relieve muscle tension, then the doctor performs a recession.
Surgery is always used to treat patients with atypical strabismus. Even under the condition that it will not be possible to correct vision with its help, the surgeon will be able to eliminate the cosmetic defect.
Modern surgical care to eliminate strabismus:
Resection. It is aimed at shortening the eye muscle. To do this, the doctor cuts out part of it.
Recession. The muscle is moved forward or backward. After giving her an optimal position, the doctor suspends her.
Only a specialist can determine the method of surgical intervention.









