Contents
In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of Healthy-Food makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
What symptoms of Helicobacter pylori can be observed on the skin? What symptoms are associated with Helicobacter pylori infection? Can the symptoms of infection resemble those of dermatophytosis? The question is answered by the drug.
Definition
Helicobacteriosis is an infectious disease that affects the pylorus of the stomach, or pylorus, and the duodenum. Its causative agent is a unique pathogenic microaerophilic gram-negative bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). The bacterium got its name due to the section of the stomach in which it lives – the pyloric.
As a result, the microorganism colonizes the mucous membrane even more strongly, forms its increased susceptibility to hydrochloric acid and provokes inflammation, leading to the development of ulcerative defects.
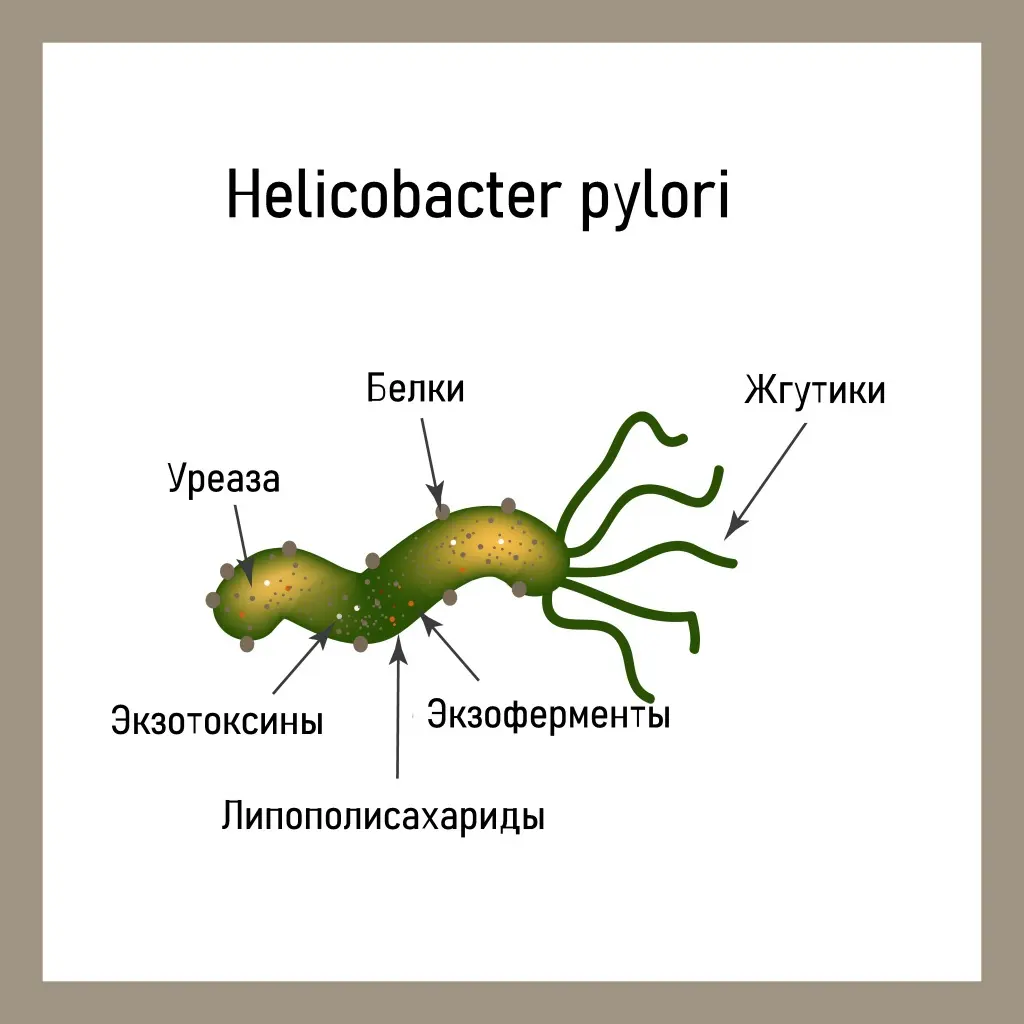
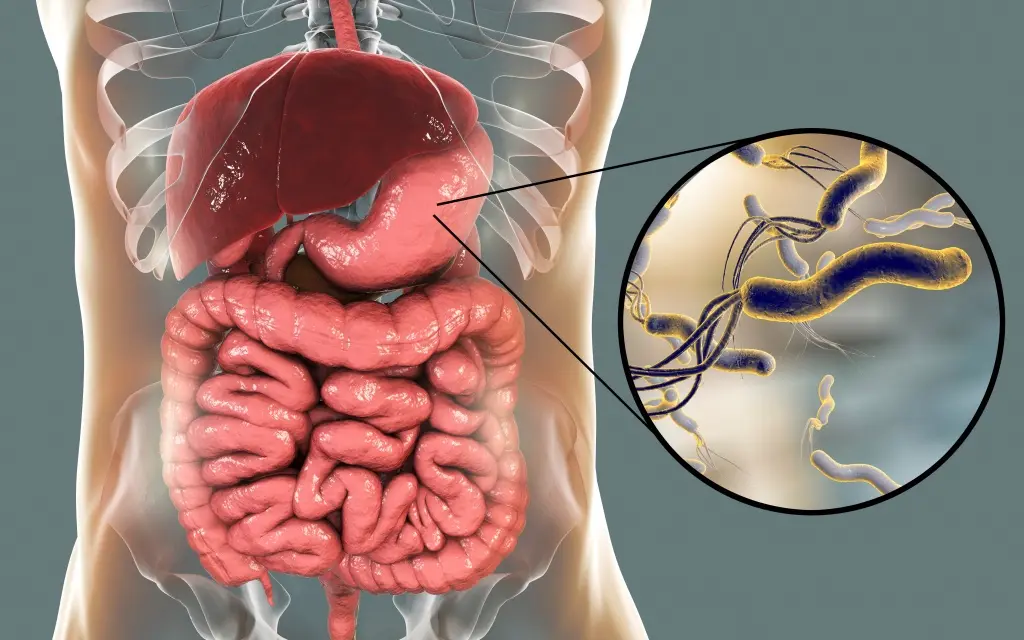 Helicobacter pylori is a spiral bacterium with a length of 3.5 and a width of 0.5 microns. It has flagella, with the help of which it freely moves along the wall of the stomach or is securely fixed on it. The H. pylori bacterium is very variable, its strains (varieties) differ from each other in the ability to attach to the gastric mucosa, cause an inflammatory process, and have varying degrees of pathogenicity.
Helicobacter pylori is a spiral bacterium with a length of 3.5 and a width of 0.5 microns. It has flagella, with the help of which it freely moves along the wall of the stomach or is securely fixed on it. The H. pylori bacterium is very variable, its strains (varieties) differ from each other in the ability to attach to the gastric mucosa, cause an inflammatory process, and have varying degrees of pathogenicity.
Helicobacter pylori, which colonizes the gastric mucosa, is a common cause of its inflammatory changes, it is recognized as the etiological factor of gastritis, and gastritis itself is an infectious disease. Depending on the state of the protective factors of the stomach, the infectious process that has arisen can proceed latently or with severe clinical symptoms of inflammation. According to modern concepts, H. pylori causes chronic gastritis in all infected individuals. This can lead to peptic ulcer disease, atrophic gastritis, gastric adenocarcinoma, or low-grade gastric lymphoma. H. pylori is a first order carcinogen.
The pathogen is relatively resistant to the environment: when boiled, Helicobacter pylori die almost instantly, when treated with disinfectant compounds – within a few minutes.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OA1XKZJ8MQM
What symptoms of Helicobacter pylori can be observed on the skin?
Hello, My name is Malwina, I’m 18 years old. Recently, I was with my school at a large integration event for secondary schools in Germany. The trip lasted 3 days, but after returning, some strange things started to happen to me. It turned out that I got acne, which I hadn’t had much before. In addition, the skin of my hands began to itch terribly. I would like to add that it didn’t start happening right after my return, but I saw the first symptoms about 1,5 months later.
The conditions we lived in were terrible. A lot of people from different countries lived in one room and some of them unfortunately looked like they had serious hygiene problems. We used shared cups and plates. Of course, I only lived with the girls. My older sister said I was able to catch Helicobacter pylori, or so she deduced from the skin’s appearance. I am asking for more information as to what they are then symptoms of Helicobacter pylori? I feel like I’ve caught some kind of ringworm or something. If so, I can send photos. I would also be grateful for information on how to treat this Helicobacter pylori, if it is this disease at all. Thank you for your response. Regards, Malwina.
- Order today The test kit for stomach ailments – home cassette tests, which includes the Helicobactr Pylori test and the fecal occult blood test.
Causes of Helicobacteriosis
You can become infected with the bacterium through contact with contaminated water or food. Infection is possible during endoscopy and when using other poorly sterilized medical instruments that have had direct contact with the patient’s gastric mucosa.
The prevalence of infection varies by geographic region, patient age, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status. According to the Moscow Department of Health (2019), the prevalence of this infection in Moscow is 60.7-88%, in St. Petersburg – 63.6%, in Eastern Siberia it reaches 90%.
Classification of diseases Diseases
associated with H. pylori:
- gastritis,
- duodenitis,
- gastroduodenitis,
- esophagitis,
- stomach ulcer,
- duodenal ulcer,
- iron deficiency anemia of unknown origin,
- stomach cancer,
- duodenal cancer.
Symptoms of Helicobacter pylori
The main manifestation of Helicobacter pylori is chronic inflammation of the stomach. In the case of a rapid primary manifestation of the pathogen, the acute period of helicobacteriosis lasts about 10 days. The general condition of patients usually remains satisfactory, sometimes there is a short-term subfebrile temperature, decreased performance.
The pains are sharp, aching, dull, occur in the upper abdomen on the left and in the center in the umbilical region. Discomfort can occur during prolonged fasting, on an empty stomach, or after a certain time after eating.
Symptoms of Helicobacteriosis depend on the clinical form of the disease and may include:
- feeling of heaviness in the abdomen after eating;
- appetite disturbance associated with sudden bouts of nausea (if the gastric mucosa is severely injured);
- causeless vomiting against the background of normal body temperature;
- heartburn (burning sensation in the esophagus and even the larynx) and belching with an unpleasant sour or bitter taste;
- chronic constipation (lack of bowel movements for three days or more);
- liquefaction of feces, the appearance of a foamy or watery consistency;
- intestinal cramps and bloating.
With a strong contamination with Helicobacter pylori, a number of atypical symptoms may occur, which indicate a significant infection and progression of the disease:
- loss of appetite to its complete absence;
- nausea may be replaced by vomiting with blood clots;
- a sharp decrease in body weight, which is not the norm;
- dry mouth and metallic taste;
- the appearance of a white coating on the tongue;
- bad breath in the absence of caries;
- seizures in the corners of the mouth;
- gum bleeding.
In the chronic course of the disease and atrophic lesions of the gastric mucosa, there are signs of iron deficiency anemia – frequent headaches and dizziness, pallor of the skin, lowering blood pressure and tachycardia.
Diagnosis of helicobacteriosis
For a long time, helicobacteriosis may not manifest itself in any way, while provoking the development of an ulcer, adenocarcinoma or stomach maltoma. In a special risk zone are people whose relatives have a history of these diseases.
Diagnosis can be invasive (endoscopy followed by biopsy of gastric tissues) and non-invasive (laboratory tests).
According to international recommendations, the methods of choice for diagnosing the bacterium and evaluating the effectiveness of H. pylori treatment are the breath test with 13C-labeled urea and the determination of specific H. pylori antigens in feces by immunochromatographic method.
The doctor explains how Helicobacter pylori infection manifests itself
Helicobacter pylori is a gram negative bacterium that causes inflammation of the lining of the stomach. The aftermath Helicobacter pylori infections can be gastric and duodenal ulcers, gastric cancer, gastric lymphoma of the MALT type, iron deficiency anemia, primary immune thrombocytopenia.
Infection with Helicobacter pylori occurs through the ingestion. Most often by using the same dishes, cutlery. Infection is very common among adults (up to 80%). Not everyone will get sick from it. Infection with Helicobacter pylori may be asymptomatic for many years. Only the presence of ulcers in the stomach or in the duodenum is manifested by dispersion. It is manifested by epigastric pain, a feeling of fullness after a meal, an early feeling of fullness, nausea and vomiting.
Quick and convenient home blood test for anti-Helicobacter pylori antibodies. You can buy it on Medonet Market.
One of the methods of diagnosing Helicobacter pylori infection is by stool examination. At Medonet Market, you can buy a fecal mail-order test, which does not require leaving your home.
The treatment is used Helicobacter pylori with two antibiotics and a medicine to reduce gastric secretions. Unfortunately, the widespread use of antibiotics without clinical support causes bacterial resistance to antibiotics. This causes some antibiotics to stop working against the bacteria. The best non-invasive test in the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection is the urea breath test. Marking is also used H. pylori antigens in the stool.
If there are indications for endoscopic examination, a rapid urease test is performed. While information can be found regarding an association of Helicobacter pylori infection with some skin lesions, it is uncertain. The symptoms presented by you do not suggest Helicobacter pylori infection, but rather an infection, e.g. fungal infection.
To make a diagnosis, you need a lot of information from the history and, above all, to look at the skin lesions. I suggest you visit your GP or dermatologist. The doctor, after collecting a complete interview, will decide on further proceedings. If necessary, the doctor will order the necessary tests, refer you to a specialist and implement appropriate treatment.









