In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
Why is the blood thick? What does thick blood indicate? What is the effect of thick blood on health? Is it a consequence of genes, or is blood density influenced by, for example, lifestyle and diet? Is there any way to change the density of the blood? The question is answered by the drug. Katarzyna Darecka.
- Our reader’s mom heard from the doctor that her blood was thick. “I admit that this was the first time I saw it, so I have no idea what to think about it”
- The doctor notes that there is no such term in medical language, “it seems to be rather colloquial”
- “He might have meant that the patient became dehydrated due to the lack of sufficient fluid intake, which caused the blood to thicken, or ‘thick blood'”, notes the doctor
- The medic may have also meant an excess of red blood cells in the bloodstream, which increases the concentration of the blood
- More information can be found on the Onet homepage
Why does the blood become thick?
Hello, I have a question about my mom. Mom is 65 now, has some problems with the circulatory systembut it was nothing serious. Yesterday she saw a doctor who mentioned something about how she has thick blood. I admit that this was the first time I saw it, so I have no idea what to think about it. What is thick blood? My mother did not ask the doctor in detail, and I am a bit worried, is she sure she understood the doctor correctly, and if so, can such thick blood have any effect on her health?
This is important to me mainly in the context of her previous cardiovascular problems, because I think these issues can be linked. What is the cause of the thick blood? Are these any genetic issues or are they due to diet and lifestyle? Mum should eat healthier, but unfortunately I am not able to persuade her to replace meat and processed products with larger amounts of vegetables. Please explain what thick blood actually is, what they are causes of thick blood and most importantly – is thick blood dangerous to health? Is this condition even treated somehow?
The doctor explains where the thick blood comes from
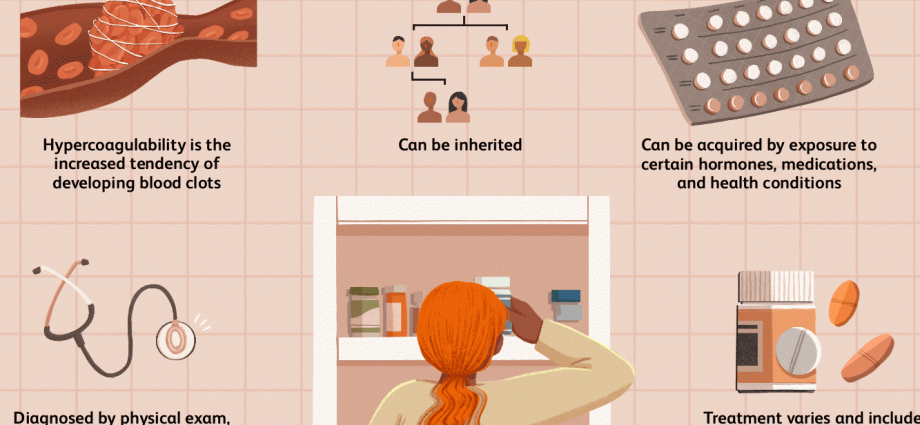
It’s hard for me to judge what the attending physician might have meant. To find out exactly, it is worth asking the specialist who makes this statement during your next visit. There is no such statement in the medical nomenclature, it seems to be rather colloquial. I believe he may have meant that the patient became dehydrated due to a lack of sufficient fluid intake, which caused blood thickeningor “thick blood”. Another thing your doctor might have meant is an excess of red blood cells, or erythrocytes, in the bloodstream, which increases the concentration of the blood.
What can also be hidden behind the notion of “thick blood” are all of them states of hypercoagulability, which may result in the formation of blood clots, which may prove very dangerous – as they may cause, for example, a stroke or pulmonary embolism. Diseases that may contribute to the state of hypercoagulability include: neoplastic diseases (polycythemia vera or polycythemia vera, Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia), autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, antiphospholipid syndrome), genetic diseases, congenital (factor V Leiden mutation, protein deficiency C and S).
Perform a mail order genetic test for the V Leiden mutation without visiting a collection point. You order this diagnostic test through Medonet Market.
You should see your doctor immediately if you develop symptoms such as haemoptysis, palpitations, fainting, shortness of breath, chest pain radiating to the arm, arm or jaw, sudden weakness or numbness of the face, arm or leg, sudden speech difficulties , sudden vision problems.
Anyone at risk of developing a thromboembolism should follow these rules:
- Avoid sitting for long periods, e.g. when flying in an airplane or traveling by train. It’s worth getting up every now and then and walking. During long car trips, make stops to be able to walk.
- Play sports, lead an active lifestyle.
- Drink plenty of water, a minimum of two liters a day – dehydration can promote blood clots.
- Change your current lifestyle, if it was unhealthy – if you are overweight and obese, lose weight, maintain blood pressure within the normal range, stop smoking, exercise regularly.
– Lek. Katarzyna Darecka
In order to support the proper functioning of the circulatory system and ensure proper blood density, it is worth using appropriate supplementation. At Medonet Market you can buy Omega 3 + K2 and D3 – a dietary supplement for the circulatory system at a bargain price.