Contents
What is a managerial approach that is used in situations where it is necessary to design new solutions in an ever-changing and unstable world?
About the expert: Anastasia Totok, entrepreneur, business consultant, representative of the Presencing Institute (Theory U) in our country. Co-curator of the Entrepreneurship in the New Economy program at MACS. Curator and conceptual editor of Dr. Otto Scharmer’s books in Russian: “Theory U. Leadership from the Future” and “Fundamentals of Theory U”.
How Theory U Came About
At the end of the last century, representatives of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) proposed to apply the experience of innovative entrepreneurs in Silicon Valley to solve economic and social problems, including global ones, affecting all of humanity. Over the course of four years (from 1996 to 2000), they conducted 150 conversations with prominent leaders of the world’s most innovative companies (Google, HP, Xerox, Shell, and others), with leading scientists and philosophers, as well as with world spiritual leaders. The researchers were looking for an answer to how, in a rapidly changing world, some companies are able to find solutions that do not just follow trends, but set them.
The collected knowledge was systematized, decomposed into stages of application and tools. The stages of constructing a solution describe a curve resembling the English U, hence the name of the approach was born.
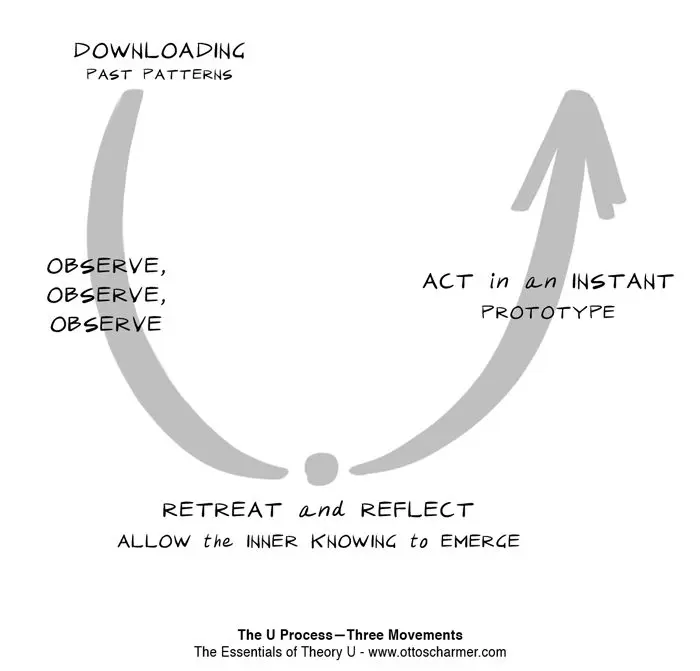
How Theory U Works
In ordinary modern management practices, the use of feelings as a tool for decision-making is excluded. Theory U proposes not to try to look for answers only rationally, but to listen to feelings, making them an equal tool with the mind.
Theory U proposes to carry out all actions today based on the goal that we want to achieve in the future. That is, learn and plan your steps based on the desired future, and not from the past.
A simple example: the owner of the store, who invests in the development of the network today, expects that in five to ten years he will own it and sell goods. He builds on his 20 years of experience owning a store and selling merchandise. What he doesn’t take into account is that more than 2017 offline clothing stores closed in the US in 9,5 alone, a 53% increase since the 2008 Great Recession. Shopping centers are also being squeezed out and bankrupt. If you now look at the activities of this owner today, expanding the network may no longer seem such a profitable investment.
In this example, we see a mistake that destroyed such giants as Kodak, Motorola, Polaroid, Nokia, General Motors and many others in an instant. These companies built on their long successful history and did not want to look into the future, ignored new economic and social trends, did not foresee the future.
Theory U connects thoughts and feelings to make decisions and determine the desired future.
We often use this approach in everyday situations, but forget about feelings in business life, which is why we meet unhappy leaders. If you do not pay attention to your feelings when making everyday decisions, you should not be surprised that the result is not happy. As a result, people build a business that does not bring moral satisfaction, create a life in which there is no joy, or go to an unloved job every day, because when choosing it, they are guided by prestige, high salary, distance from home, or any other social norm, but not by heart and feelings.
Theory U Tools
Theory U proposes a systemic decision-making path that includes seven successive stages.
1. Clarification of the situation
Often people begin to solve a problem without understanding who all the stakeholders are, what their hidden interests are, what relationships and interconnections are between them. Without this clarification, you run the risk of constantly receiving new introductory, unforeseen circumstances will arise.
2. Collection of information
After clarifying the problem to be worked on, we usually begin to collect all available information on it. Here people use their mind, data analysis, statistics and other available tools. The main thing at this stage is to keep yourself from constructing a solution. This is the most common mistake – having received a lot of information in conventional modern techniques, people immediately try to draw conclusions based on it and solve the problem.
3. Vacation
The third stage is very simple and complex at the same time. In Russian, there are proverbs on this subject: “Morning is wiser than evening”, “We need to sleep with this thought.” The meaning of these expressions, as well as the whole stage, is to free the mind from the accumulated information. The task is to swim out of the heap of data, step back to look at the situation from the outside.
4. Connecting with feelings
At this stage, it is important to download information and take a break to allow something new to be born. For leaders who are used to being constantly on the move, the hardest thing is doing nothing. In my practice, there were cases when company executives could not cope on their own, so I had to take them out of town for several days, taking away all means of communication so that their minds could rest and turn off.
5. Manifestation of the new
After the reboot, new solutions will begin to appear. At this stage, a person expresses his feelings in relation to what is happening: he can draw, write words or assemble an image of his decision from Lego. This is necessary to convey to your team the vision of a leader without distortion. Feelings are very difficult to convey in words, so at this stage it is necessary to use improvised – often art – means.
6. Solution design
At the sixth step, you need to construct a solution and take everything that was previously expressed there. Together with the team, prototypes and minimally working solutions of the final product are created.
7. Implementation
At this stage, information is collected and analyzed about how the decision affects the social and environmental situation, how it turned out to be useful and improved people’s lives, whether this decision brought the team closer to the desired future that they want to create. In fact, this is a return to the beginning of the U curve – clarifying the situation and collecting information on it. That is, the U process is an endless way of creating and testing an innovative product.
Principles of Theory U
Theory U won’t work without the three basic principles on which the personality of a leader is based.
1. Open Mind – Curiosity
You need to constantly ask yourself the question: “What do I not know yet?” If a person goes into the world with the mindset that he knows everything about him, if he is not ready to accept other points of view, then he will continue to use the information that is becoming obsolete in his head.
2. Open heart – empathy
Understanding the true motives and feelings of the interlocutor, a person can count on honest feedback, which means building a more complete picture of what is happening, and not invented only in his head. Often this is a problem for high-ranking managers: few people can tell them to their face what is really happening, as they are afraid of condemnation and anger.
3. Open Will – Courage and Courage to Innovate
It is important to have the will to go against the trends, to actually say what you think, even when this opinion is contrary to the majority. The majority never create innovations, they are created by white crows, those few who go against the current.
Who applies Theory U and how?
This management approach is used by Alibaba, Daimler, Eileen Fisher, Federal Express, Fujitsu, Googl, Hewlett-Packard, Shell Oil, The World Bank and others, as well as by the UK and Chinese governments.
In our country, the principles and tools of Theory U at the beginning of 2020, with the height of the first wave of the pandemic, helped the non-profit sector to solve social problems: four NGOs and one government organization used this methodology to find new ways to interact with their beneficiaries. The retail chain “Azbuka Vkusa” used this approach to develop the company’s strategy in the field of sustainable development.
In 2019, VkusVill and TealTech Capital applied the methodology to develop the potential of startup teams. In addition, Theory U tools are used to build corporate culture in companies such as Rostelecom, X5 Retail Group and Tinkoff Bank.
Subscribe also to the Trends Telegram channel and stay up to date with current trends and forecasts about the future of technology, economics, education and innovation.










