Contents
Melanoma is best avoided. But knowing what it is and how it develops is very important. Moreover, over the past half century, the incidence of melanoma has increased sevenfold.
What is skin melanoma
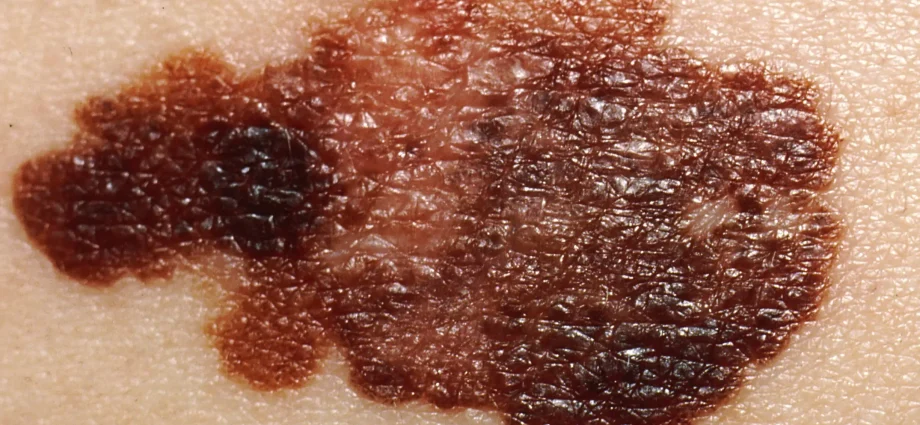
Melanoma is a malignant neoplasm, one of the most aggressive forms of skin cancer. The trouble is that the human immune system practically does not react to melanoma and does not try to fight it, so it can quickly progress and metastasize.
Cancer is the result of abnormal and uncontrolled reproduction of “crazy” cells. In the case of melanoma, trouble happens to melanocyte cells that produce the pigment melanin, which is responsible for tanning, freckles, age spots, eye and hair color. These cells are located:
in the skin – in the epidermis and on the border with the dermis;
in mucous membranes (epithelium).
Melanoma is often referred to as a “reborn mole”. Indeed, most often it develops from an already existing mole, or, scientifically, a nevus. That is why nevi must be shown annually to a dermatologist to determine their condition.
© La Roche-Posay
Risk Factors
Melanoma has many risk factors.
Exposure to the sun without sun protection or with insufficient protection.
Passion for solarium and sunbathing.
Light skin (I-II phototypes). This does not mean that representatives of other phototypes are guaranteed to be immune from melanoma. But pale skin is less protected from ultraviolet radiation.
The abundance of moles, as well as the presence of dark and prominent moles. It is believed that if there are more than 50 moles in general, this is already an additional risk factor. According to the Petrov Research Institute of Oncology, 70% of potentially dangerous nevi are congenital, and 30% are acquired.
Experienced (even in early childhood) sunburn.
genetic predisposition. According to scientists, the main role is played by the “weak link” in the immune system, which makes it difficult to resist a malignant neoplasm.
Age 50+. The average age of people diagnosed with melanoma is 57 years.
There is an opinion among dermatologists that at the entrance to the solarium there should be a sign: “You enter here for skin cancer.”
Varieties of melanoma
Superficial spreading melanoma
It accounts for about 70% of all cases. This form is somewhat more common in women aged 30 to 50 years. A suspicious mole, slightly protruding above the skin, begins to increase in size and gradually turns into a granular spot (and then a spot) with jagged edges and a non-uniform color – from brown to black.
As the name implies, at first this form of melanoma grows in breadth for a long time. And only at the second stage does it move to a more dangerous growth in depth. Therefore, it is important to monitor moles.
nodular melanoma
This is the so-called nodular melanoma. It accounts for about 15% of all cases and most often affects men. This form is considered the most unfavorable, since the malignant formation quickly begins to grow deep into the skin, which accelerates the formation of metastases. Appears as a red-brown or black nodular bump on the surface of the skin. Hence the name.
Pigment-free
Pigmentless, or achromatic, melanoma develops quite rarely, literally in 1-2% of cases. However, it is especially insidious precisely because it is simply not visible. As well as nodular, it is a small nodular, rough to the touch seal on the skin, but it may not be colored in any way, which does not prevent the tumor from progressing.
Lentigo melanoma (lentiginous)
This form accounts for about 5% of cases and usually develops after the age of 55, begins with a light flat small spot, which quickly increases in size and turns out to be not just a pigment spot, but melanoma. This shape is also called “Hutchinson’s freckle”. It is more common in women and mostly on the face. So watch out for pigmentation!
Acral lentiginous melanoma
Spindle cell melanoma
A rare form that usually develops (but not always) in childhood and adolescence. It got its name from the elongated shape of the cells that form the formation. It is a small raised bump, pinkish or flesh-colored, smooth or rough to the touch, which is rather difficult to mistake for a malignant tumor. This type of melanoma does not cause any painful sensations, it only grows – this is the main alarm sign.
The first symptoms and signs of melanoma
How to determine the initial stage
“The ABCDE method is intended for self-diagnosis of skin growths (but does not replace regular visits to the doctor for monitoring of moles).
A — АSYMMETRY (asymmetry). A benign mole is always symmetrical. If the mole is not symmetrical, there is a risk of developing melanoma.
B – BORDERS (borders). A benign mole has even, clear boundaries. In melanoma, the borders are usually uneven, like a blob.
C – COLOR (color). A mole in which several colors are present at once (different shades of brown, black) is an alarm signal. Melanoma can also become red, white, or blue.
D – DIAMETER (diameter). The diameter of the mole has become larger than the eraser on a pencil (6 mm). Benign moles are usually (but not always!), smaller.
E — EVOLUTION (change). Any change in size, shape, color, bleeding, itching, soreness is a warning sign. You need to see a doctor immediately.”
At the initial stage of melanoma, all degenerated cells are located within the surface layer of the skin – the epidermis, so it is easier to get rid of it.
Moles, at least voluminous, must be shown to a dermatologist every year.
A dermatoscope is sufficient for the initial examination, but the final diagnosis of melanoma can only be made on the basis of a histological examination of a distant formation (nevus).
Now there are even mobile applications that help assess the condition of a mole. But an urgent request, or rather a requirement: do not get carried away with self-diagnosis. Only a doctor can competently analyze the symptoms and signs of melanoma.
At the second stage of melanoma, the mole continues to transform, it can hurt, bleed, itch. The tumor grows already up to 4 mm deep, penetrates into the dermis, while remaining outwardly within the same boundaries as before. But there are no metastases yet, since the malignant formation has not yet reached the lymph nodes and large blood vessels.
How to deal with melanoma
If a diagnosis is made or even there is only a suspicion that the nevus is malignant, most often a decision is made to perform a surgical operation – the complete removal of the formation with the capture of part of the intact nearby tissues.
Risk groups
Summing up the above, we recall that the risk group includes the following categories:
lovers of sunbathing;
fair-skinned people;
people with a large number of moles and severe pigmentation;
people older than 50 years;
people with a family history of melanoma.
Not a single sunburn, even received in childhood, does not pass without a trace on the skin. Protect the children!
Which doctor should be consulted
A dermatologist, like a therapist, should be contacted at least once a year for a general examination and consultation, without waiting for alarming symptoms.
A dermatologist using a dermatoscope will examine the skin, moles, evaluate their condition and activity. Quite often, the doctor leaves himself a “memory photo” so that at the next visit you can assess the condition and development of a particular nevus.
Funds overview
Sun protection moisturizing dry face spray “Expert protection”, SPF 50 protects the skin from both types of rays (A and B), moisturizes. easy to use – can be applied directly to the face.
Sunscreen “Expert Protection”, SPF 50+, Garnier suitable for face and body, contains vitamin E and a complex of chemical sunscreens that protect the skin from broad spectrum rays.
Sun milk Sublime Sun “Extra Protection”, SPF 50+, L’Oréal Paris Enriched with antioxidants that neutralize the threat of UV damage to the skin.
Anthelios XL Compact Facial Sunscreen, SPF 50+, La Roche-Posay allows you to quickly renew your sun protection. Protects from broad spectrum rays. Designed also for sensitive skin.
Melting Moisturizing Sun Milk Lait Solaire, SPF 50, Biotherm Suitable for both face and body. In addition to an effective sunscreen complex, it contains the antioxidant tocopherol, which helps to cope with the damaging effects of ultraviolet radiation.
Sun lotion for face and body Activated Sun Protector for Face and Body, SPF 50, Kiehl’s retains moisture in the skin, contains antioxidant vitamin E and soybean oil.
Makeup base Maestro UV, SPF 50, Giorgio Armani represents complete sunscreen. Just keep in mind that UV protection is recommended to be renewed every 2 hours – the foundation is suitable for morning makeup if the main part of the day is still spent indoors.
For children
Children’s sun protection aqua cream “Kids. Expert protection”, SPF 50, Garnier designed for face and body. Waterproof and hypoallergenic product can be used by the whole family.
Children’s sunscreen dry anti-sand spray “Kids. Expert protection”, SPF 50, Garnier does not allow sand to stick to the skin and does not cause discomfort. Spray will be effective regardless of the position of the vial.
Back to the table of contents
Safety measures
Do you know how to use sunscreen? Test yourself by taking the test.
Prevention is an effective way to combat melanoma. What does it mean?
Protect yourself from the sun according to your phototype. Fair-skinned and owners of many moles need to protect open areas from the sun all year round: face and hands.
Use sunscreens with broad-spectrum filters that prevent damage to the skin from UVA and UVB rays.
Stay out of the sun between 12:00 pm and 16:00 pm during its peak period.
Renew your sunscreen every 2 hours and after swimming.
Do not forget about the most vulnerable areas (ears, parting, nose).
Get an annual check-up with a dermatologist who will check the condition of moles and age spots.
Follow all the above precautions for children too!
And remember: you can’t overdo it with sunscreen!