Contents


Mankind has been growing crops for thousands of years. New agricultural techniques are being introduced, effective fertilizers are being developed, etc. However, from the point of view of science, the future belongs to environmentally friendly technologies that allow you to get a crop without using the soil at all. What is hydroponics, and whether it is possible to mount a hydroponic installation with your own hands, you will learn from our article.
Basic concepts of hydroponics
The essence of the technology is the creation of an artificial environment that excludes the use of soil as such. The roots of plants (namely, the roots, not the stem, otherwise the plant will simply rot) are immersed in a moisture-intensive environment, from where they extract the necessary components. The medium is periodically saturated with nutrient solutions rich in mineral salts. As a result, the harvest ripens faster than with the traditional method, and the yield is higher.

The method is universal, with its help it is possible to grow various herbs and crops, with the exception of those that are harmful to excessive moisture – potatoes, carrots, beets and other root crops.
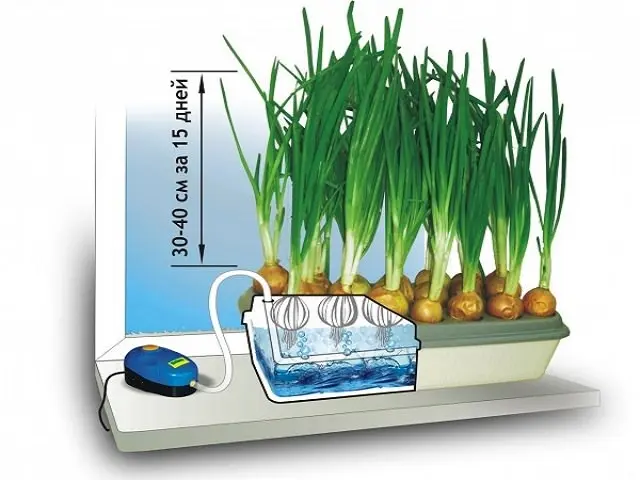
A hydroponic installation looks like this:
- A container of a suitable size is selected, which is filled with a nutrient solution.
- The container is covered with a grate (a foam sheet with holes will come off).
- The grate is sprinkled with a layer of substrate in which the seeds are placed. In this role, peat, moss, coconut fiber or expanded clay are more often used. When using foam in the bulk layer, there is no need, the seedlings pass the roots through the holes to the water itself.
- To activate the process, the substrate is abundantly moistened with ordinary water or a nutrient solution.
- As the crop grows, the roots lengthen, sinking lower and lower, plunging deeper into the nutrient fluid. Tops are formed over the lattice (styrofoam), forming neat fresh shrubs.
Video “Features of the hydroponic growing method”
From this video you will learn what are the features of the hydroponic method of growing.
Solution concentration
The yield of the cultivated crop depends on the nutrient concentration. For different plants, it varies, the main requirement is to maintain the volume constantly at the required level (this is achieved by adding water). Soft water is required, for which it is either defended or filtered. You need to change the solution every three months.
When purchasing a nutrient solution from a well-known manufacturer in a store, the concentration is selected according to the attached instructions. Possible deviations:
- for insectivorous crops, it is reduced by 3–4 times;
- if the plant grows quickly, it is increased by one and a half times;
- annual vegetable crops need a concentration exceeding the norm by 1,25 times;
- if it gets colder, the concentration is reduced by 2-3 times, while reducing the level of nutrient fluid.
Acidity of the solution
When using a bulk substrate, the degree of acidity of the impregnating solution should be minimal. This will protect the environment from the appearance of fungal bacteria and harmful microorganisms.
Here is a table of the optimal values of the acidity of the nutrient solution for different crops.
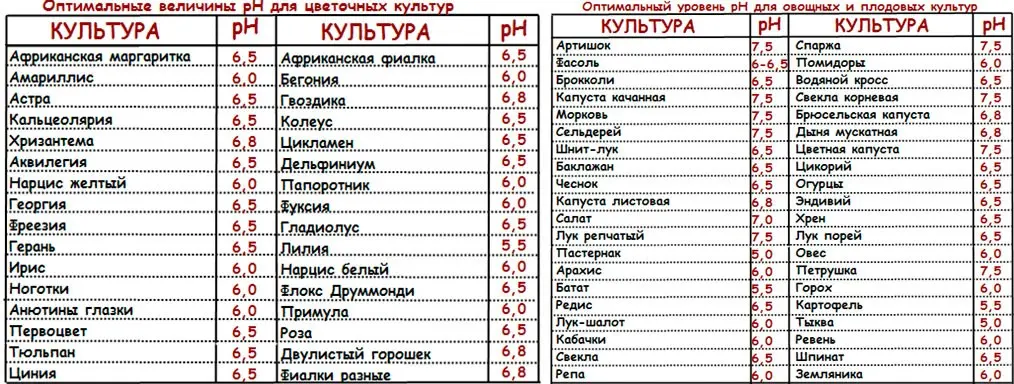
As can be seen from the table, for the bulk of plants it is enough to adhere to the acidity of pH 6,5, although there are exceptions.
In order to avoid mistakes, it is recommended to purchase a special device that measures the pH level, or use tests specially designed for aquarium environments.
Author’s advice
The history of the appearance of the method
For the first time, the implementation of the idea of growing plants without soil by artificially supplying them with food and moisture was started in Holland in the 1856th century. Empirically, over the next two centuries, scientists managed to develop basic techniques and techniques, and already in XNUMX, German botanists managed to obtain the first samples of full-fledged plants from seeds at the Leipzig-Makkern Experimental Station, using only an aqueous nutrient medium.
Over time, the technique has been improved. Modern hydroponic crop production began in 1860. The term “hydroponics” (hydroponics) was proposed in 1929 by the American phytophysiologist William Gericke.
In Our Country, the corresponding experiments were carried out by well-known scientists K. A. Timiryazev and D. N. Pryanishnikov. It was in Our Country in the late 1930s that they learned how to grow the first vegetables using the hydroponic method, putting it into practice to provide polar stations in Antarctica with vegetables.
The main advantages and disadvantages of the method
Like any new technique, hydroponics has its pros and cons.
The main advantages:
- Release of sown soil plots. They can grow those crops for which the method is not suitable.
- Economy of the occupied space. Hydroponic installations are built in several tiers, densely placing plants.
- Independence from the vagaries of the weather. Water supply and saturation with nutrients is carried out automatically.
- Purity. Cultivated crops do not get dirty in the ground.
- Safety. Installations are reliably protected from pests – rodents and insects.
- Year-round. Maintaining the required microclimate, it is possible to grow new crops all year round.
- Hydroponic crops do not need weeding, weeding.
- High yield.
And yet, many agricultural companies are hesitant to adopt the best method. This is explained by the following considerations:
Disadvantages:
- The introduction and debugging of hydroponics at the initial stage requires considerable financial investments.
- Hydroponic structures need a special microclimate, which is provided only in large greenhouses. It is difficult for a person to work in such conditions (high temperatures, high humidity).
- To achieve high yields, nitrates and pesticides have to be used.
The lack of public awareness should also be mentioned. Ignorant people mistakenly believe that hydroponics is an “unnatural method” and that the plants grown with it are supposedly capable of harming health.
Popular hydroponic systems
In recent years, hydroponics has been replenished with a number of innovations. The difference in methods allows farmers to select options according to the existing conditions. For example, there are installations based on the use of a substrate; in other methods, intermediate layers were completely abandoned, forcing the root system of plants to literally hang in the air.
Even mandatory watering is carried out in different installations in different ways. There are three options:
- Active. The nutrient solution is supplied by pumps.
- Passive. The solution is supplied using the capillary effect.
- Combined. Both principles are involved. This approach is slowly becoming common.
Consider the basic principles of operation of various hydroponic systems.
wick
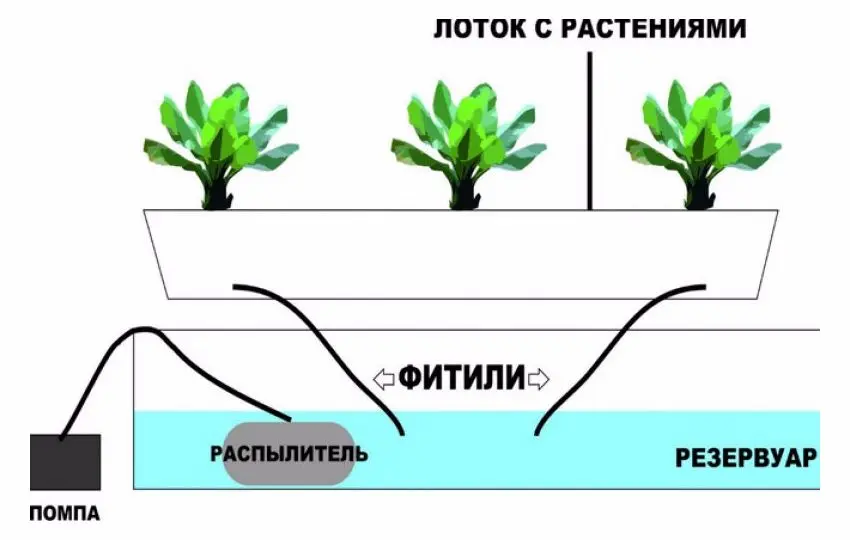
Water is supplied in a passive way, the system of wicks saturates the solution, which gradually impregnates the substrate. As a neutral filler use:
- perlite;
- vermiculite;
- coconut fibre.
With the help of the installation, it is possible to grow only slow-growing crops that are undemanding to moisture, since the throughput of the filter system is low. On small farms, it is used, for example, for growing decorative flowers.
floating platform
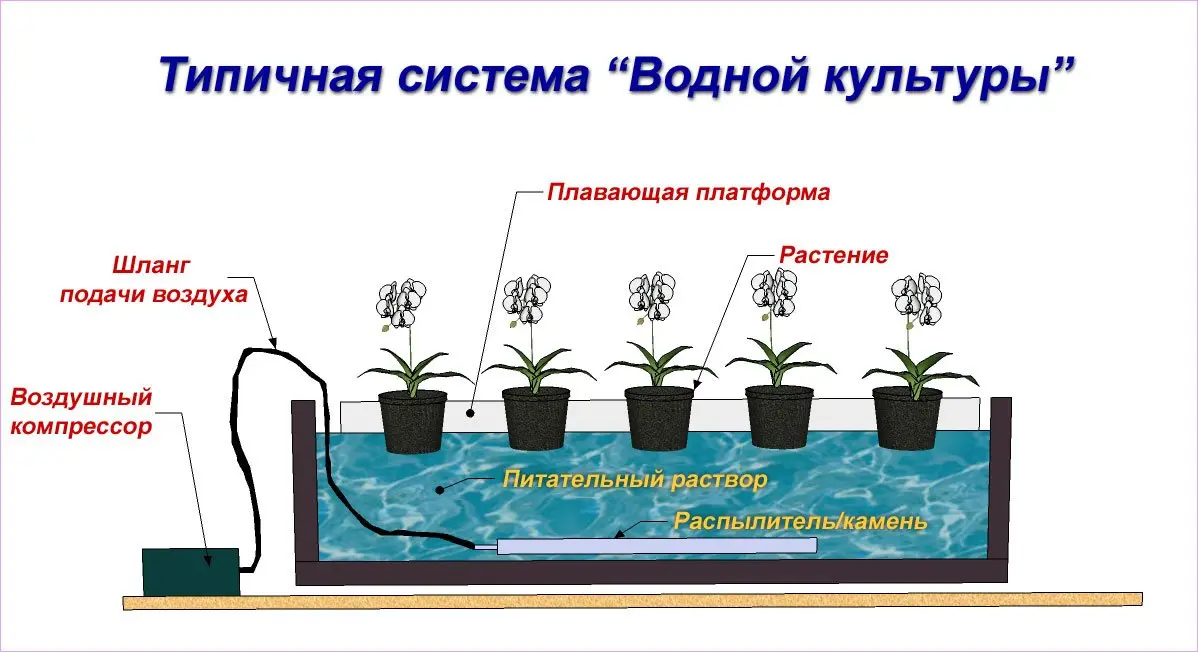
Instead of a substrate, a foam base dipped in a bath of nutrient solution. The cultivated crops are in special holes, the roots descend into the solution. Oxygenation is carried out by an active method.
It is used for growing moisture-loving plants. It does not require special knowledge, therefore it is suitable even for novice farmers.
periodic flooding
In the containers containing the roots of plants, a nutrient composition is pumped from time to time with the help of a pump. Then, according to the timer, it is outflowed into a special storage container.
The process is automated. The timer is adjusted to the growing plant. As a result, it is possible to achieve the microclimate (temperature and humidity) required in each specific case.
Nutrient layer
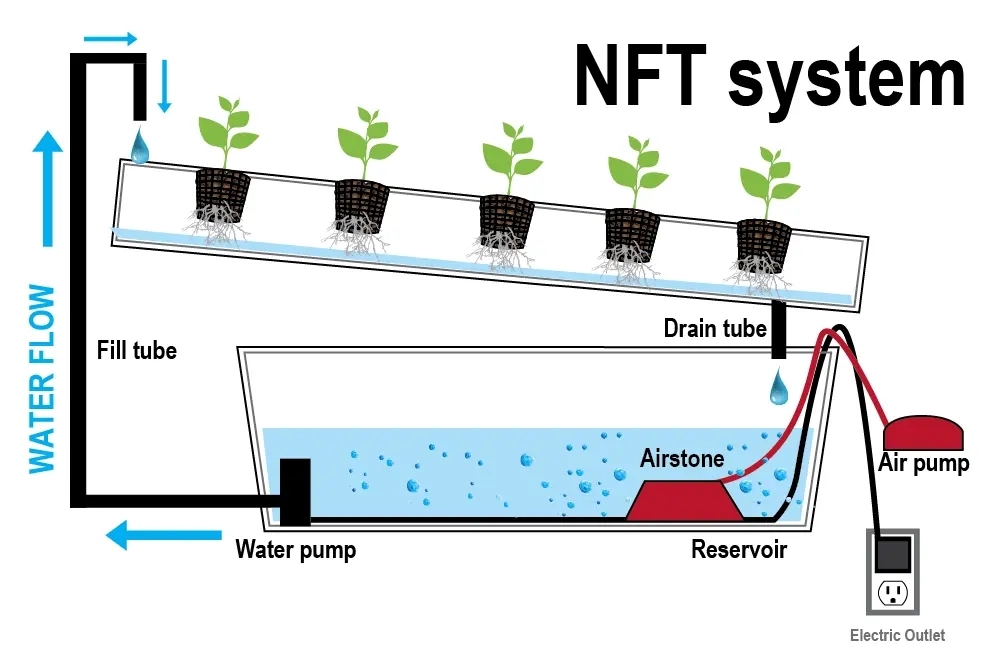
The method is based on the constant circulation of the nutrient layer located at the bottom of the bath with plants. Not the entire root system is immersed in the solution, but only the tips of the roots. The grown crops are in special fixed pots with slots, no substrate is required. Air enters from the environment through the part of the roots hanging in the air.
Electrical installation. With long-term failures, circulation is interrupted, the roots dry out and the culture dies.
Drip irrigation
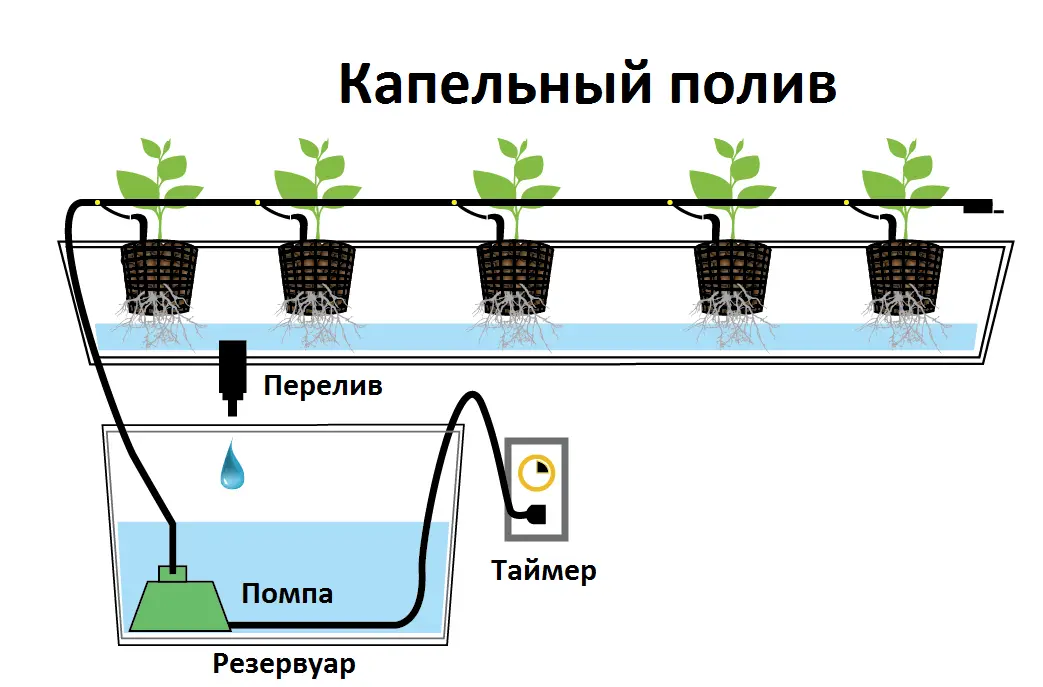
Based on the use of a substrate, which can be coconut fiber, expanded clay or perlite, as well as:
- stones, rubble;
- mineral wool;
- granular basalt.
The grown cultures are placed either in a single bath or in isolated pots. Nutrient fluid is pumped through tubes to each plant. As in the previous case, the installation is volatile – if the power is lost, the consequences will be sad for the plants.
Aeroponica
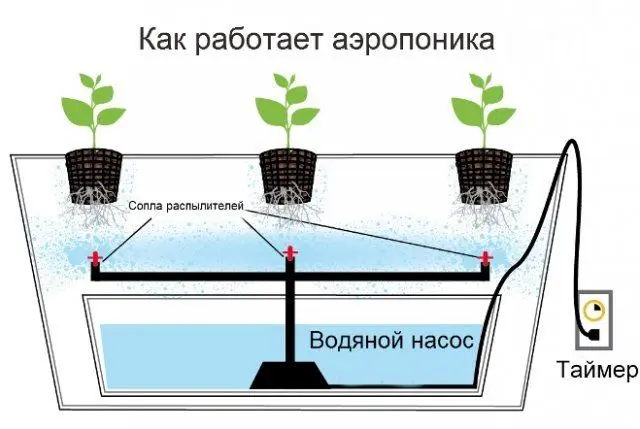
The roots are constantly irrigated with a large amount of solution. The air around is saturated with vapors that do not allow the root system to dry. The irrigation system is switched on by a timer. The system is of great benefit in countries with a hot climate.
How to build a hydroponic setup with your own hands
There is nothing complicated here. For the construction of the simplest structure you will need:
- plastic tray;
- a grate placed on top;
- substrate.
You can install it in a city apartment (on a balcony or windowsill) or in a separate greenhouse in the country.
Next, we will explain how to build a more productive plant based on the capillary method with minimal automation. We take as a basis the widespread sewer PVC pipes.
Required tools and fixtures
For work you will need:
- pipe 140 cm long and 10 cm in diameter;
- a pair of pipe plugs, a connector;
- linear atomizer;
- connecting pipes with check valves;
- compressor for aquarium;
- pots with a diameter of 10 cm for plants and lamps.
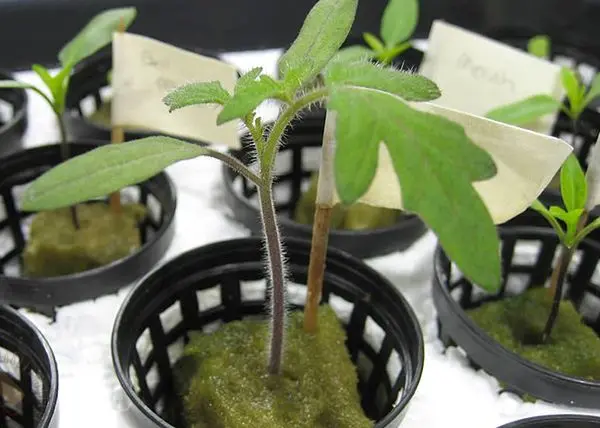
Choosing pots
Plastic pots used for growing indoor flowers will fit. Others will do, but keep in mind that they will have to drill a lot of holes. Ceramic, for example, are not suitable for this reason.
The best option is special pots with a built-in self-watering system, combined into a system to redistribute moisture.

Installing lamps
The choice on the market is large, but not all models are suitable for our purpose. Let’s analyze the most used lamps in everyday life:
- Incandescent. Cheap, but give the wrong spectrum of radiation. They consume a lot of energy, emit excess heat.
- Luminescent. Expensive, but economical, almost do not heat the air, besides, blue light is favorable for plant growth.
- LED. Expensive, but they serve for a long time, do not heat up, emit light of a suitable spectrum.
- sodium. Often used for growing plants. Expensive, you will need additional equipment.
- Plasma. Too expensive.
A bracket with lamps is attached above the landing panel. The distance is adjusted depending on the expected height of the crops grown. An electric wire is connected to the lamps, an automatic system of periodic switching on and off is organized, synchronized with the irrigation of the roots with a nutrient solution.
Preparing the soil and solution
The filler for the substrate is selected for certain crops. Most popular in hydroponics:
- gravel and expanded clay;
- sphagnum moss;
- coconut chips;
- mineral wool;
- vermiculite and perlite.
The first step is to determine the acidity of the water used to create the nutrient solution. Further, with the help of special preparations, acidity is increased or decreased, bringing it to the required level (see table above).
It is important to keep the temperature of the solution within the required range (18-24°C).
Basic rules for growing plants
Cleaned and prepared plants are placed in the plant, the roots are straightened. Fall asleep substrate. Water is poured into a container with a substrate to the required level.
The roots may not even touch the solution for the first time, when watering the substrate, the nutrient composition will reach them through the capillaries, and then the roots themselves will grow.
The care rules are as follows:
- The solution is changed 3-4 times a year, getting rid of excess minerals.
- The plant is trimmed, getting rid of dead fragments.
- Carefully monitor temperature and humidity.
- Carry out pest control.
Recently, hydroponic systems have become more productive and cheaper. This is an excellent choice for those who care about the environment, ecology and health – their own and loved ones.









