Contents
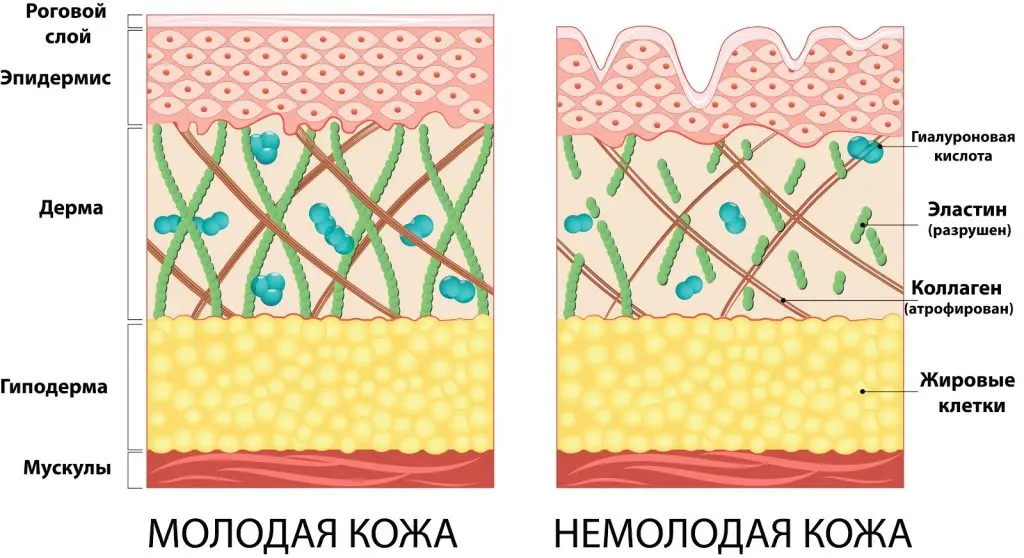
The skin consists of three layers – the epidermis, which is the outermost, the dermis and the deepest subcutaneous tissue. The changes that occur in the skin with age also apply to collagen, which is one of the main components of the matrix surrounding the cells of the dermis. What is collagen and how does it work on facial skin?
Collagen is one of the structural proteins of human skin, which performs the function of moisturizing it and protecting it from the negative effects of external factors and free radicals. Special cells of the dermis – fibroblasts – are responsible for the formation of collagen fibers. With age, the activity of these cells decreases, as a result of which the appearance of wrinkles and a change in the oval of the face are observed.
Regular use of cosmetics containing collagen helps to slow down the aging process, prolonging the youth and health of the skin.
What is collagen?
Collagen is a filamentous protein that is present in most tissues of our body. The structural component is responsible for the elasticity and strength of bones, joints, hair, nails, and skin. The very name of protein comes from the Greek word “kolla”, which can be translated as “glue”. Some experts make a clear analogy – collagen molecules, like glue, bind tissue cells together.
Collagen plays an important role in preserving the youth and beauty of the skin. Protein is responsible for its smoothness, elasticity, strength and elasticity. It stabilizes the oval of the face and evens out its tone. Collagen is also responsible for the regeneration of tissues after their damage, accelerating the healing process.
With age, the fiber content decreases. The face becomes flabby, dry, the appearance of wrinkles is observed. That is why cosmetologists especially recommend choosing beauty products with collagen content for women over 30 years old.
In cosmetology, several types of collagen are distinguished:
Why do you need collagen?
Collagen has a moisturizing and rejuvenating effect on the skin, maintains its firmness and elasticity, smooths the microrelief and evens the tone of the face. Means containing protein accelerate the healing process.
There is no age limit, in accordance with which the use of beauty formulas containing collagen is recommended. The relevance of protein application is determined by the condition of the skin. Dry, dehydrated dermis needs collagen from the age of 25, normal or oily – from the age of 30-35.
A sufficient amount of collagen in the tissues provides the skin with:
- Elasticity;
- Elasticity;
- Tone.
Lack of collagen leads to:
- loss of elasticity and elasticity of the skin;
- the appearance of lethargy;
- the formation of wrinkles;
- deformities of the oval of the face.
In addition to natural aging processes, collagen synthesis is affected by exposure to ultraviolet radiation, vitamin deficiency, constant stress, insomnia, abuse of nicotine and alcohol, and improper nutrition. All of the factors listed above can be eliminated – do not leave the house without applying a UV protective cream (even in winter), give up alcohol and cigarettes, periodically drink vitamin complexes, include a sufficient amount of protein food in your diet.
Collagen – properties and occurrence
Collagens are a family of extracellular proteins found in most tissues and organs. We find them not only in the skin, but also, among others in bones, cartilage, cornea. They constitute almost 1/3 of the total mass of human protein. This family includes about 30 types of collagen differing in structure, function and place of occurrence.
Collagen is made up of endogenous amino acids only and is rich in glycine, proline and hydroxyproline. The collagen molecule consists of 3 chains that wind around each other and form a kind of rope. The primary function of collagen is to give tissues tensile strength and maintain their structural integrity and elasticity. Collagen plays an important role in many processes, incl. in tissue repair and wound healing.
Collagen in the dermis is the basic component of the matrix surrounding cells, therefore it is crucial for its properties – flexibility and strength. In human skin we find the most collagen I. It constitutes about 85-90% of collagen in this organ, and its fibrous structure supports the skin. The second most important collagen is collagen III, which accounts for up to 15% of all skin collagens. Collagen III entwines the collagen I fibers, giving them the right position. It also affects the elasticity of the skin. Interestingly, the skin of the fetus and newborn contains more type III collagen than collagen I. Collagen III is also predominant in scar tissue. Although types I and III are dominant in human skin, it can also contain small amounts of collagen V – VIII, XII – XIV and XVI.
The influence of collagen on skin aging
As the skin ages, the collagen molecules present in it change. Fewer of them are formed due to the reduced activity of the cells that produce them – fibroblasts (cells of the dermis). Collagen fibers they become thinner and, additionally, they are less soluble. The percentage of collagen III increases. With age and under the influence of UV radiation, the activity of collagenases – enzymes that start cutting collagen into smaller fragments – increases. This leads to increased degradation of collagen molecules. In aging skin collagen fibers they become disorganized, stiff and irregularly spaced.
Lesser synthesis of new collagen molecules, their altered structure and increased degradation lead to changes characteristic of aging skin. In the elderly, we can observe poorer wound healing, a decrease in skin elasticity and the formation of wrinkles, which are especially visible on the skin of the face. Changes in the amount and distribution of subcutaneous fat or weakening of the facial muscles also contribute to the formation of wrinkles.
Will collagen help with wrinkles?
Is therefore the application of collagen for the face will reduce the wrinkles formed on it?
Collagen is a well-known protein, and due to its minimal toxicity, high biocompatibility and biodegradability, it is a very popular biomaterial. Collagen fibers are used, inter alia, in biomedicine and aesthetic medicine, incl. as a tissue filler. Collagen injected intradermally is perfect for smoothing the skin surface at wrinkles or scars. It also helps in modeling the lips or the face oval changed with age.
Collagen for the face – how to choose the right cosmetic?
However, before we turn to these quite invasive methods of improving the appearance of the skin, it is worth trying more gentle methods with the use of appropriate cosmetics. Although applying collagen to the face in the form of a cosmetic will not replenish its resources in the deeper layers of the skin, there are substances that can stimulate the production of collagen by the cells of the dermis. An interesting example of an active substance present in cosmetics is nanoplankton extract. It turns out that proteins obtained from sunflower, one of the components of nanoplankton, have the ability to stimulate cell division of fibroblasts, increase collagen synthesis by up to 279% (e.g. in Neocollagen Collagen Day and Night Cream 70+) and reduce cellular aging. The cosmetics also contain special peptides which, thanks to their small molecules, reach the deeper layers of the skin and also stimulate collagen synthesis. In studies on this type of ingredients, and more specifically on palmitic acid esters and oligopeptides, a reduction in wrinkles and improvement in skin elasticity were observed both in the subjective assessment of patients and using specialized assessment techniques after 8 weeks of using cosmetics with their content.
What foods contain collagen
A decrease in the amount of collagen in the body negatively affects the condition of not only the skin, but also the joints. To prevent this from happening, doctors recommend first of all changing the diet, paying attention to collagen-containing and protein-rich foods.
Collagen content in food
| Nutrients and vitamins | Products |
| SQUIRRELS | white meat turkey and chicken, fish, oysters, shellfish |
| OMEGA 3 FATTY ACIDS | fish oil, linseed oil |
| VITAMIN C | red bell pepper, Brussels sprouts, dill, kiwi |
| AMINO ACIDS | soy and legumes, meat, fish, nuts, apples |
| ZINC | chicken, beef, pine nuts, peanuts, beans, buckwheat |
Types of collagen
In cosmetics and cosmetology, collagen obtained from three different sources is used.
- Collagen of animal origin
It is isolated from the skin of pigs and cattle. To date, this (cheapest) type of collagen is banned from use in facial cosmetics due to the increased risk of infections and allergic reactions.
- Collagen of vegetable origin
Plants do not produce collagen. Therefore, when it comes to plant collagen, we mean hydrolyzed protein – an artificial material created on a plant basis. Most often these are wheat proteins and algae. Vegetable collagen is well accepted by the skin, but in fact it is not collagen. And the production process is quite expensive and complicated.
- marine collagen
It is isolated by a biotechnological method from the skin of fish and is considered the most acceptable, since fish collagen is close to human and is easily absorbed by the skin. Freshwater fish collagen is considered the highest quality, which, unlike marine fish collagen, does not cause allergies.
Facial collagen in cosmetics
Collagen is often used in professional masks and serums, but is less common in home use products. The reason is that collagen molecules are too large, they are not able to penetrate the skin and compensate for the lack of its own collagen. To stimulate its synthesis, other cosmetic ingredients that have proven their viability are used. Collagen in cosmetics is valued for other beneficial properties.
- Moisturize the skin.
- Give it elasticity due to the attraction of moisture.
- Prevent evaporation of moisture.
- Smooth out the surface of the skin.

Anti-aging creams often contain collagen, since its synthesis in the skin decreases with age.
Collagen based masks
Most often, they are collagen sheets to create a moisture-retaining film on the skin that fills in skin irregularities. They are used in the program of rejuvenating professional procedures.
Creams with collagen
In formulas for aging skin, collagen purposefully fights wrinkles due to the ability to increase in volume and “push out” wrinkles from the inside.
Serums with collagen
The concentrates mainly use marine collagen in combination with hyaluronic acid for the effect of filling the skin and smoothing the relief.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gyZf2e26lSU
Bibliography:
1. Czubak, Kamila A., and Halina M. Żbikowska. “Structure, function and biomedical importance of collagens.” Annals of the Medical Academy of Silesia. Flight. 68. No. 4. 2014.
2. Żelaszczyk, Dorota, Anna Waszkielewicz, and Henryk Marona. «Collagen – structure and application in cosmetology and aesthetic medicine.» Acetol. With. Cosmetol 2.1 (2012): 14-20.
3. Ganceviciene, Ruta, et al. «Skin anti-aging strategies.» Dermato-endocrinology 4.3 (2012): 308-319.
4. Tobin, Desmond J. «Introduction to skin aging.» Journal of tissue viability 26.1 (2017): 37-46.
5. Varani, James, et al. «Decreased collagen production in chronologically aged skin: roles of age-dependent alteration in fibroblast function and defective mechanical stimulation.» The American journal of pathology 168.6 (2006): 1861-1868.
6. Vaseli-Hagh, Neda, Abdolkhaleg Deezagi, and Mahvash Khodabandeh Shahraki. «Anti-aging effects of the proteins from artemia extract on human fibroblasts cell proliferation and collagen expression in induced aging conditions.» Annals of Biotechnology 3 (2018): 1-7.
7. Bae, Soon-Min, et al. «A Study on the Skin Anti-wrinkle Effect of Novel Palmitoyl Tripeptide.» Journal of the Society of Cosmetic Scientists of Korea 36.1 (2010): 65-69.
8. Robinson, L. R., et al. «Topical palmitoyl pentapeptide provides improvement in photoaged human facial skin 1.» International journal of cosmetic science 27.3 (2005): 155-160.
Kołodziejczak, Anna, et al. Cosmetology. Volume 1. PZWL Medical Publishing, 2020.









