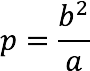In this publication, we will consider the definition, basic elements and equations (canonical and parametric) of one of the main geometric shapes – the ellipse.
Definition of an ellipse
Ellipse is a closed curve on a plane, the sum of the distances from each point of which to its foci (F1 и F2) is equal to a constant value.
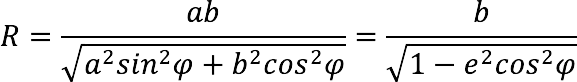
F1M1 + F2M1 = F1M2 + F2M2 = A1A2 = const
Note: is a special case of an ellipse.
Ellipse elements
For the picture above:
- F1 и F2 are the foci of the ellipse;
- A1A2 – the major axis of the ellipse passes through its foci;
- B1B2 – the minor axis of the ellipse is perpendicular to the major axis and passes through its center;
- A1O = OA2 = A is the semi-major axis of the ellipse;
- B1O = OB2 = b is the minor semiaxis of the ellipse;
- point O – the center of the ellipse is the intersection of the major and minor axes of the figure;
- A1, A2, B1, B2 – the vertices of the ellipse, the points of intersection of the curve with the axes.
- Ellipse radius (R) – a segment connecting the center of the figure with a point on its curve (in the formula below φ is the angle between the radius and the major axis).

- Ellipse diameter (d) – a segment that passes through the center of the figure and connects two opposite points on its curve.
- Focal length (s) – half of the segment connecting the foci of the ellipse.
- Ellipse focal radii (r1 и r2) are the segments that connect the foci to a point on the curve.
- ra – perifocal distance (the minimum distance from the focus to a point on the ellipse curve);
- rb – apofocal distance (the maximum distance from the focus to a point on the ellipse);
- Eccentricity ellipse (e) – stretching of the figure, characterized by the ratio of the focal distance to the major semi-axis.

- Ellipse focal parameter (p) – the segment that connects the focus of the figure and the point on the curve is perpendicular to its major semi-axis.

- Ellipse contraction factor (k) – is determined by the ratio of the minor semiaxis to the major one. Also called figure ellipticity.

- Ellipse shrink (1 – k) is the difference between unity and ellipticity.

Note: ellipse properties are presented in a separate .
Ellipse equation
Canonical equation of an ellipse
If the center of the ellipse (point O) is at the origin of the coordinate system (Cartesian), and the major axis lies on the x-axis, then the figure can be described by the equation below:
![]()
If the center of the ellipse is at the point with coordinates (x0, and0), the equation takes the following form:
![]()
Parametric equation of an ellipse
For parameter α:
![]()