In this publication, we will consider what a vector is, how it is designated, and also what types there are. We will accompany the theoretical information with drawings for better perception.
Vector definition
Vector is a directed segment. In other words, this is a segment of a certain length, which is directed in a specific direction.
A vector has a beginning and an end. The figure below is the dots. A и B, respectively. The direction of the vector is indicated by the corresponding arrow.
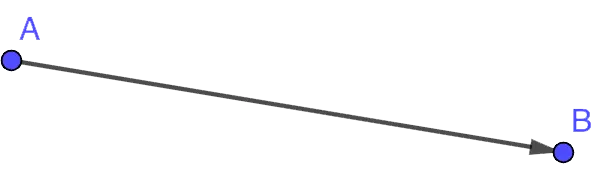
A vector is denoted by writing its points (the beginning, then the end) with a vertical bar on top, i.e. in our case – AB.
An alternative designation is a small Latin letter, for example, a.
Note: finding the length of a vector (|AB| or |a|) we discussed in detail in a separate .
Kinds of vectors
1. Zero – the beginning and end of the vector are the same. Usually referred to as 0. The length of the null vector is zero.
2. Single is a vector whose length is equal to one. Also called ortho.
3. Collinear vectors lie on the same or parallel lines.
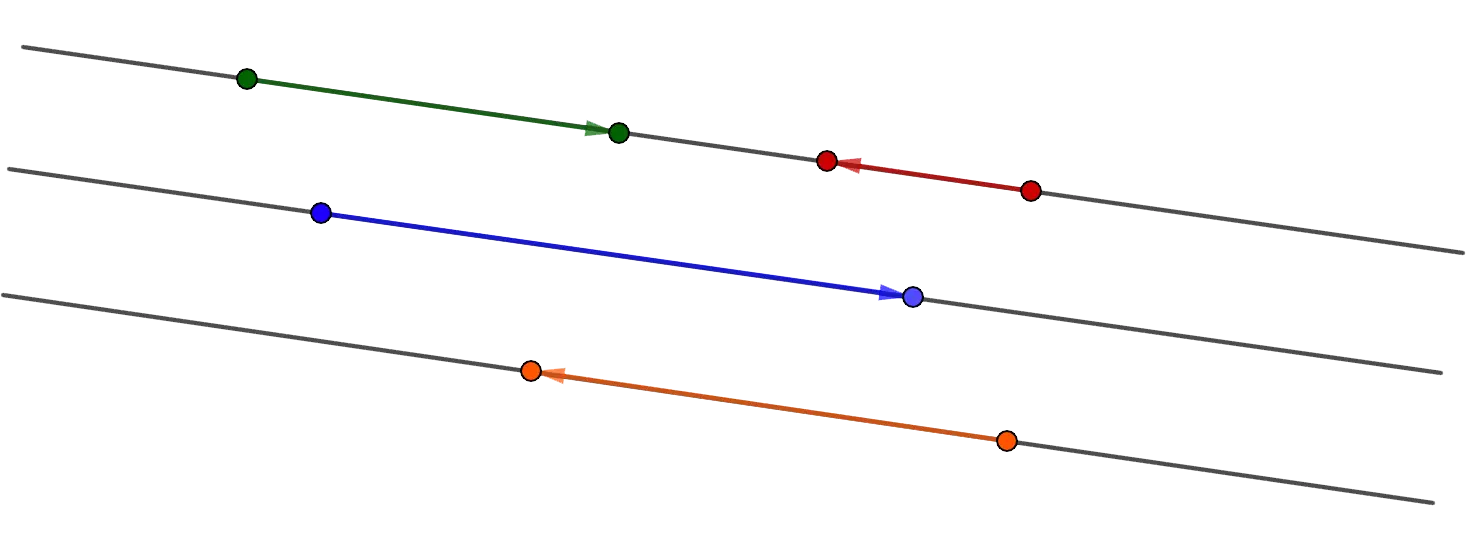
4. Co-directional are collinear vectors whose directions coincide. For example, in the figure below a и b are co-directional.
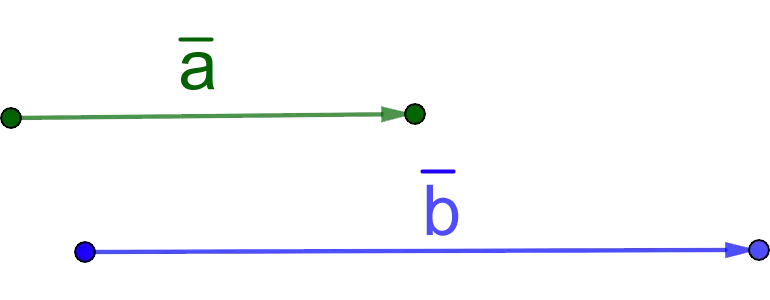
Designation: a ↑↑ b.
5. Opposite directions are collinear vectors whose directions are opposite.
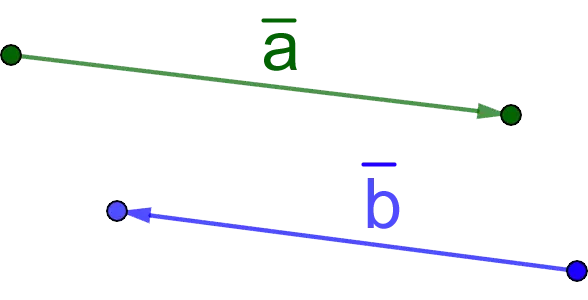
Designation: a ↑ ↓ b.
6. Coplanar are vectors parallel to the same plane or lying on the same plane.
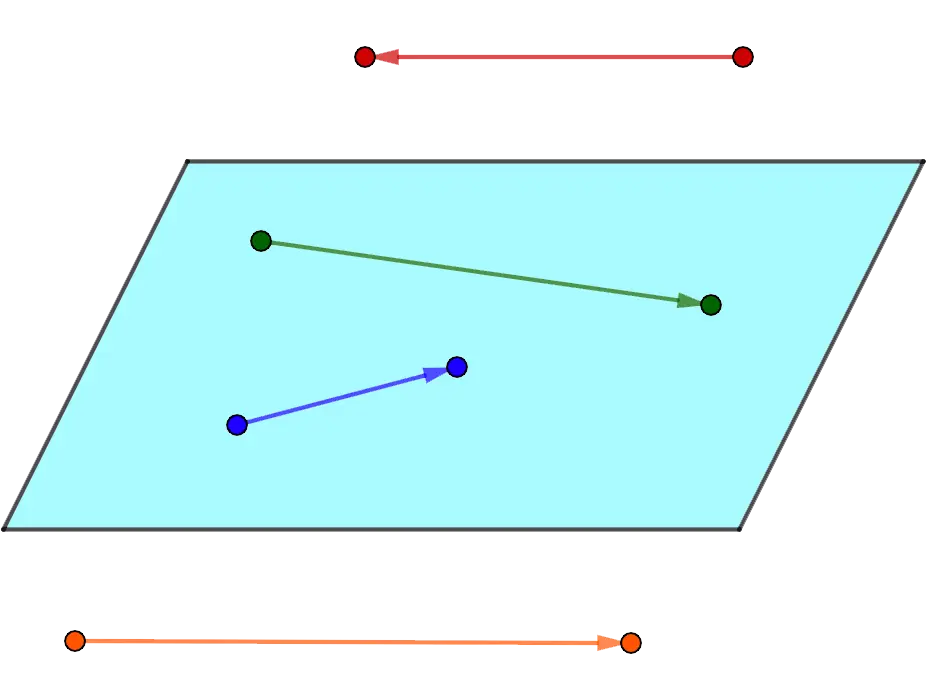
Note: any two vectors are coplanar, since there is always a plane parallel to both of them.
7. Equal – vectors having the same length and direction, as well as lying on the same or parallel lines.
Note: for vector AB at an arbitrary point C in space, it will be possible to construct only one single vector (for example, CD) of the same length.