Contents
In this publication, we will consider the definition, main elements, types and possible cross-sectional options for one of the most common three-dimensional geometric shapes – cylinder. The presented information is accompanied by visual drawings for better perception.
Cylinder Definition
Next, we will elaborate on straight circular cylinder as the most popular type of figure. Other species will be listed in the last section of this publication.
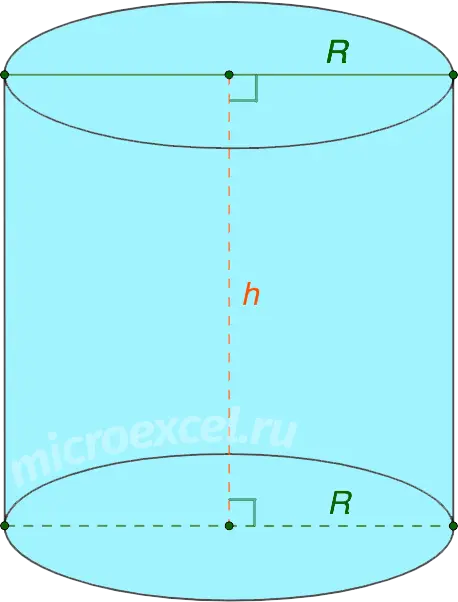
Straight circular cylinder – This is a geometric figure in space, obtained by rotating a rectangle around its side or axis of symmetry. Therefore, such a cylinder is sometimes called rotation cylinder.
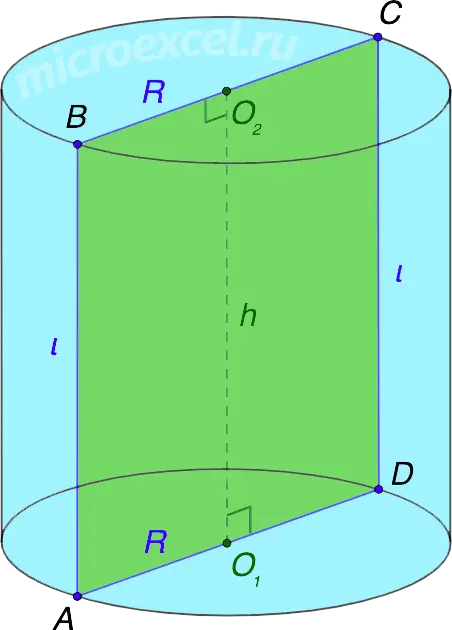
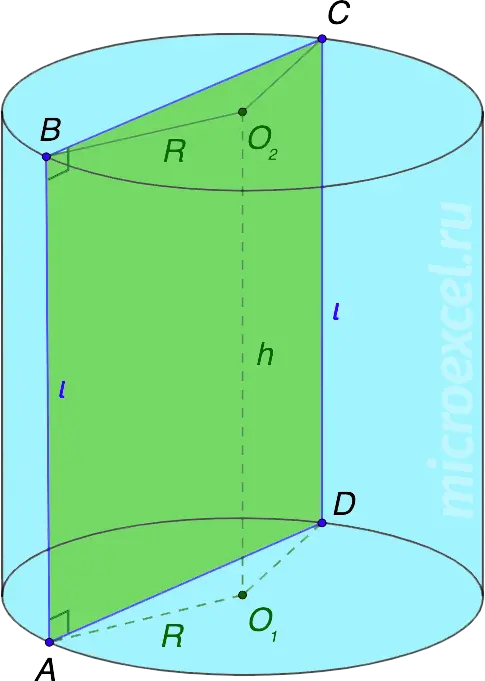
The cylinder in the figure above is obtained as a result of the rotation of a right triangle ABCD around the axis O1O2 180° or rectangles ABO2O1/O1O2CD around the side O1O2 at 360 °.
The main elements of the cylinder
- Cylinder bases – two circles of the same size / area with centers at points O1 и O2.
- R is the radius of the bases of the cylinder, segments AD и BC – diameters (d).
- O1O2 – the axis of symmetry of the cylinder, at the same time is its height (h).
- l (AB, CD) – generators of the cylinder and at the same time the sides of the rectangle ABCD. Equal to the height of the figure.
Cylinder reamer – lateral (cylindrical) surface of the figure, deployed in a plane; is a rectangle.
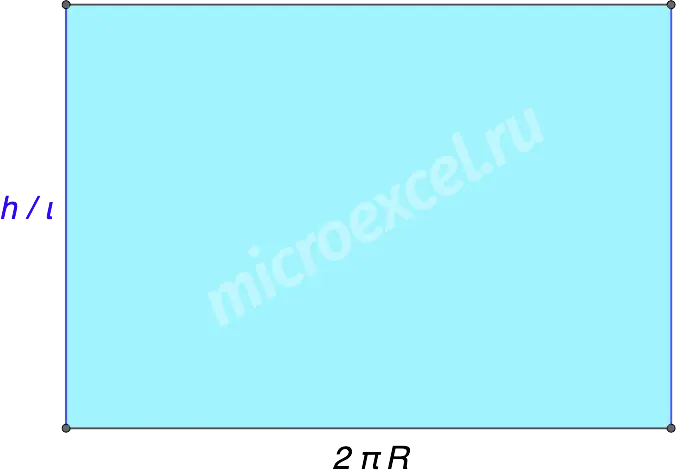
- the length of this rectangle is equal to the circumference of the base of the cylinder (2πR);
- the width is equal to the height/generator of the cylinder.
Note: formulas for finding and cylinder are presented in separate publications.
Types of cylinder sections
- Axial section of the cylinder – a rectangle formed as a result of the intersection of a figure with a plane passing through its axis. In our case, this is ABCD (see the first picture of the publication). The area of such a section is equal to the product of the height of the cylinder and the diameter of its base.
- If the cutting plane does not pass along the axis of the cylinder, but is perpendicular to its bases, then the section is also a rectangle.

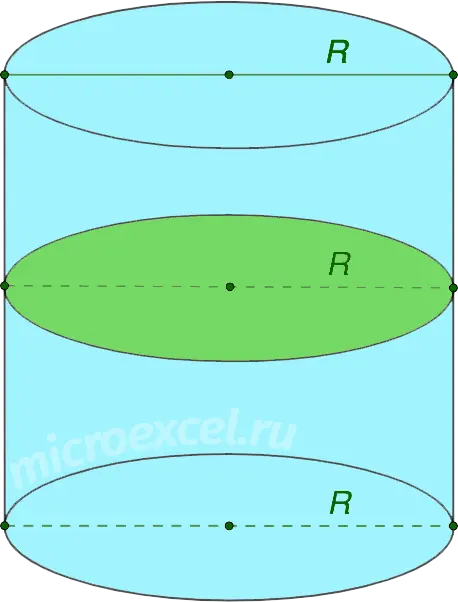
- If the cutting plane is parallel to the bases of the figure, then the section is a circle identical to the bases.

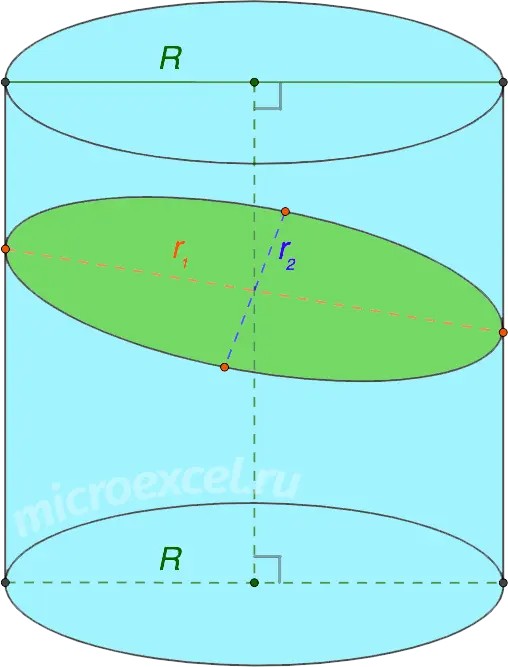
- If the cylinder is intersected by a plane that is not parallel to its bases and, at the same time, does not touch any of them, then the section is an ellipse.

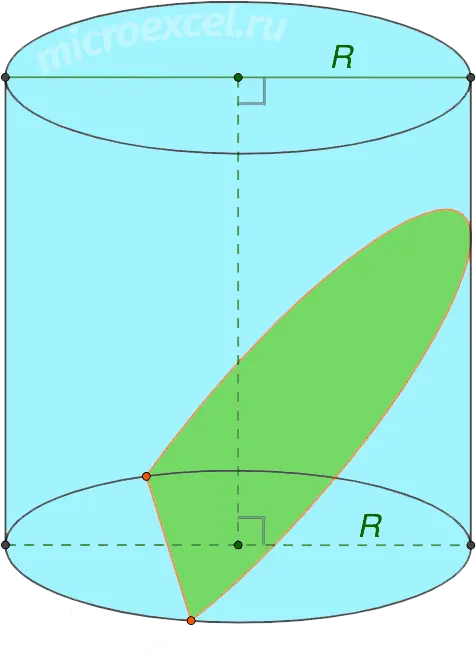
- If the cutting plane intersects one of the bases of the cylinder, the section will be a parabola/hyperbola.

Types of cylinders
- straight cylinder – has the same symmetrical bases (circle or ellipse), parallel to each other. The segment between the points of symmetry of the bases is perpendicular to them, is the axis of symmetry and the height of the figure.

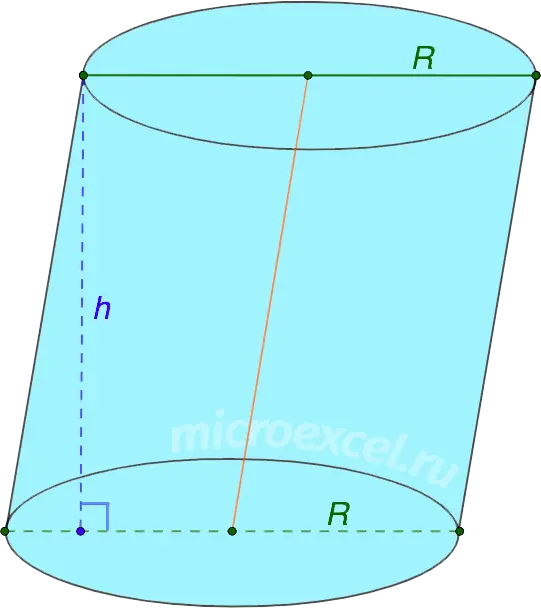
- inclined cylinder – has the same symmetrical and parallel bases. But the segment between the points of symmetry is not perpendicular to these bases.

- Oblique (beveled) cylinder – the bases of the figure are not mutually parallel.

- circular cylinder – the base is a circle. There are also elliptical, parabolic and hyperbolic cylinders.
- equilateral cylinder A right circular cylinder whose base diameter is equal to its height.