In this publication, we will consider the definition, main elements and types of one of the most common shapes in space – a cone. The presented information is accompanied by corresponding drawings for better perception.
Definition of the cone
Next, we will consider the most common type of cone – straight circular. Other possible variants of the figure are listed in the last section of the publication.
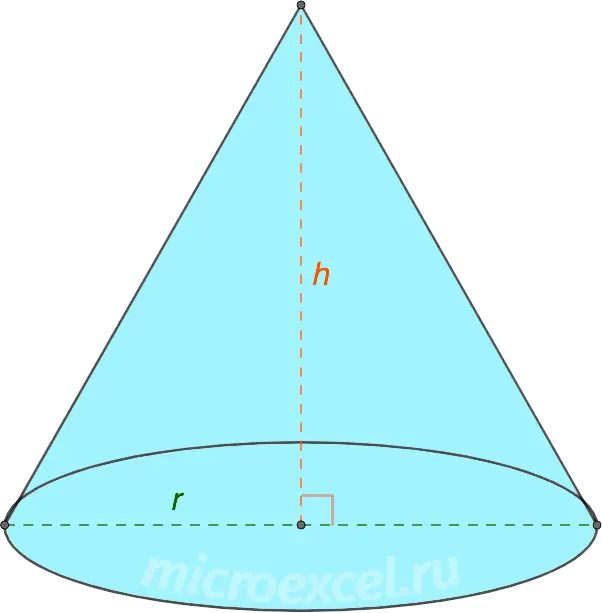
So, straight circular cone – This is a three-dimensional geometric figure obtained by rotating a right triangle around one of its legs, which in this case will be the axis of the figure. In view of this, sometimes such a cone is called cone of revolution.
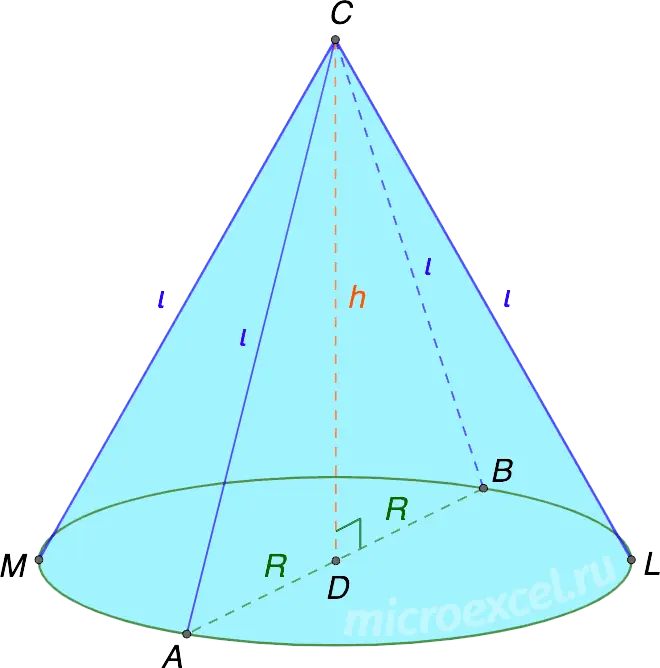
The cone in the figure above is obtained as a result of the rotation of a right triangle ACD (or BCD) around the leg CD.
The main elements of the cone
- R is the radius of the circle that is cone base. The center of the circle is a point D, diameter – segment AB.
- h (CD) – the height of the cone, which is both the axis of the figure and the leg of right triangles ACD or BCD.
- Point C – the top of the cone.
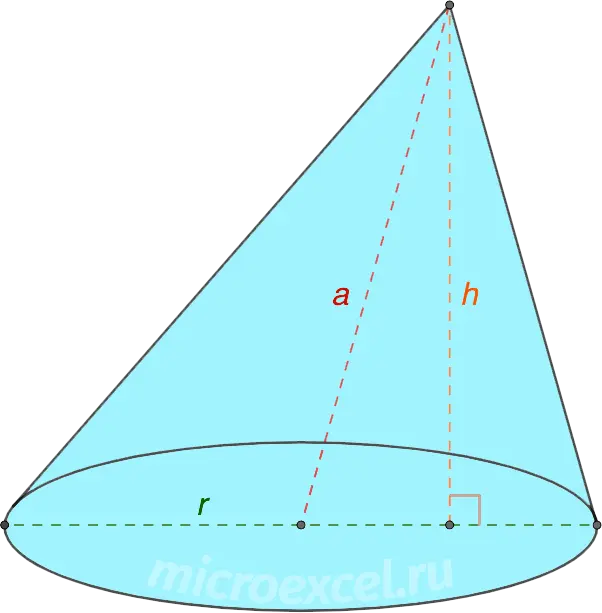
- l (CA, CB, CL и CM) are generators of the cone; these are segments connecting the top of the cone with points on the circumference of its base.
- Axial section of the cone is an isosceles triangle ABC, which is formed as a result of the intersection of the cone by a plane passing through its axis.
- Cone surface – consists of its lateral surface and base. Formulas for calculating , as well as a right circular cone are presented in separate publications.
There is a relationship between the generatrix of the cone, its height and the radius of the base (according to):
l2 =h2 + R2
Scanning cone – the lateral surface of the cone, deployed in a plane; is a circular sector.
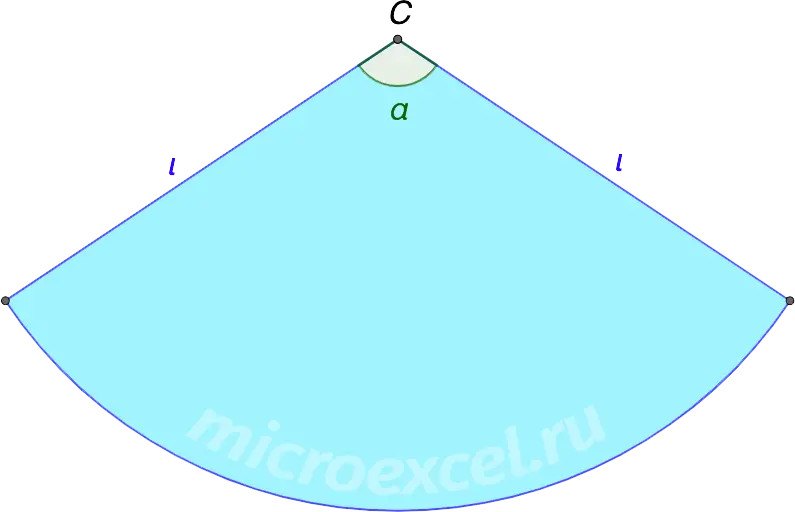
- equals the circumference of the base of the cone (i.e. 2πR);
- α – sweep angle (or central angle);
- l is the sector radius.
Note: We reviewed the main ones in a separate publication.
Types of cones
- straight cone – has a symmetrical base. The orthogonal projection of the top of this figure onto the base plane coincides with the center of this base.

- Oblique (oblique) cone – the orthogonal projection of the top of the figure on its base does not coincide with the center of this base.

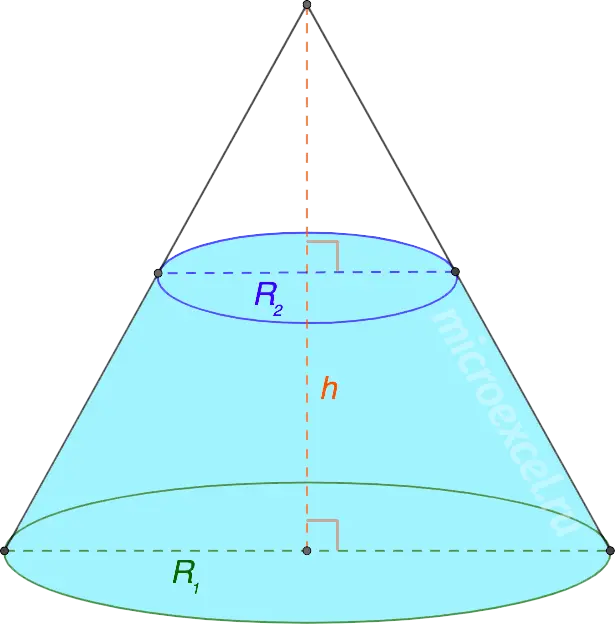
- (conical layer) – the part of the cone that remains between its base and a cutting plane parallel to the given base.

- circular cone The base of the figure is a circle. There are also: elliptic, parabolic and hyperbolic cones.
- equilateral cone – a straight cone, the generatrix of which is equal to the diameter of its base.