Contents
The female orgasm is the peak of enjoyment that occurs as a result of sexual arousal and the stimulation of an erogenous zone such as the clitoris or the G-spot. In parallel, the body secretes adrenaline, oxytocin and dopamine which further boost the pleasurable sensations. But does this intense pleasure manifest itself in the same way in men and in women?
It seems that falling in love is an unearthly feeling that is difficult to explain in the language of science. In fact, what we experience during love and intimacy can be explained in terms of the chemical processes that take place in the brain.
The Healthy-Food tells what happens in the mind of men and women before, during and after sex in terms of hormones and neurotransmitters.
Wish
Sexual desire arises spontaneously or in response to a stimulus, which can be a partner or various events: touching, watching an erotic film and pictures. Desire is largely influenced by external events, such as stress or the state of the body.

Spontaneous desire most often occurs with a new partner during the period of falling in love. In a long-term relationship, attraction often begins with an erotic stimulus or a desire to be physically and emotionally closer to a partner.
The choice of a partner depends on various factors: the structure of society, the influence of culture, economic conditions, and even a set of genes . Of course, we do not walk around with a pocket device for DNA analysis, but we do it unconsciously.
According to the smell and physical attractiveness of a partner, we give preference to those people whose genes responsible for the functioning of the immune system are as different as possible from ours.
The structure of olfactory receptors depends on genetics, and determines the perception of odors. How a person perceives certain odors depends on the sensitivity of the receptors.
It is not yet clear how contraceptive use affects women’s sexual desire. A review of the studies found mixed results: most women felt no change or experienced an increase in libido, with some reporting a decrease in desire.
Excitation
Arousal and desire are difficult to distinguish, but researchers prefer to separate them.
Most often, excitation is understood as the physiological response of the body. For example, changes in the genitals due to exposure to sexual stimulus. And arousal can occur even if a person initially had no desire to have sex.
The peripheral nervous system during touches, kisses and other stimuli receives a signal and sends it to the brain. The hypothalamus, the region of the brain that controls hormones throughout the body, responds to arousal. It transmits a signal to increase testosterone production.
In men, arousal is influenced by the secretion of vasopressin, the hormone of aggression, memories and concentration in both sexes.
However, in women, an increase in vasopressin, which is accompanied by anger and anger (for example, due to trouble and stress), on the contrary, discourages the desire to have sex. Vasopressin also constricts blood vessels, which is why it has such a name: vaso – vessel, press – to press.
In the female body, arousal is positively affected by luteinizing hormone , the peak of which occurs at ovulation – the period when the egg is ready for conception.
Some studies claim that a woman’s gait, voice, and even body odor change before ovulation. For example, researchers at the University of New Mexico have proven that strippers get more tips when they are ovulating.
Why do we want to have sex? Procreation is the evolutionary strategy of any species. And for a person to have sex, it is enough to reward him with a feeling of pleasure during and after this process, which is what the neurotransmitter dopamine does.
Excitation leads to the release of nitric oxide and norepinephrine. These substances increase blood flow to the genitals – starts an erection in men, the release of lubrication and enlargement of the labia in women.

Plateau
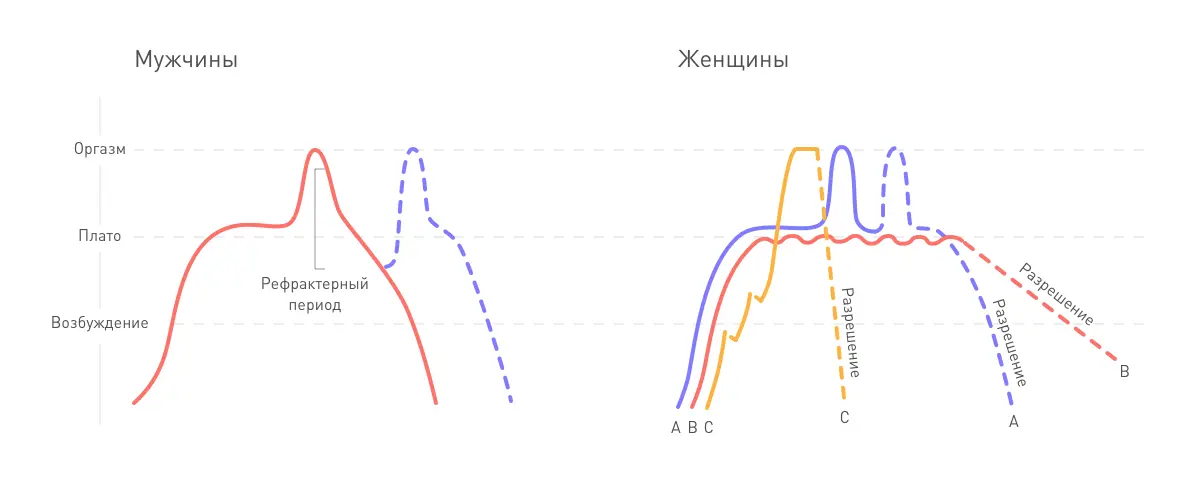
The plateau phase is what happens between arousal and orgasm. If there is no orgasm, after the plateau comes resolution. In another way, the plateau phase can be called the highest degree of excitation.
At this stage, the pulse and breathing continue to increase, pressure and muscle tension increase, the clitoris becomes more sensitive, and the Bartholin glands in the vagina secrete more lubrication.
The activity of different areas of the brain increases. One of them is the tonsil. It is responsible for the perception of visual images and emotions. During the plateau phase, activity decreases in the area of the brain where memory is stored. This is probably because at this moment we do not care at all about memories and the emotions associated with them.
Orgasm
The most pleasant and the shortest phase. Women are a little more fortunate, they tend to have orgasms longer than men’s, and they can have multiple orgasms while men don’t. But men have another advantage: it is easier for them to get an orgasm than for girls.
During orgasm, the hormone oxytocin is released, which leads to rhythmic muscle contraction and ejaculation. And the stronger the orgasm, the greater the release of oxytocin in the body. After that, the nucleus accumbens in the brain rewards us with a good dose of dopamine – and we experience pleasure.
The stronger the orgasm, the greater the release of the “happiness” hormone, oxytocin, will be in the body.
An MRI of the brain showed that during orgasm, different areas of the brain turn on one after another:
- amygdala – memory and emotions,
- hypothalamus – unconscious control of the body,
- anterior cingulate cortex – impulsiveness and empathy,
- nucleus accumbens – a feeling of euphoria.
In total, about 30 areas of the brain are involved in orgasm.
Sex can be considered a pain reliever.
According to research, during vaginal stimulation and orgasm, sensitivity to pain decreases. Scientists claim that this mechanism facilitates childbirth.
Immediately after ejaculation, men need time ( the refractory period ) to experience orgasm again. During this period, neurons are simply not able to release the required amount of neurotransmitters. Women do not have to wait, they can experience an orgasm many times in a row.
Permission
Muscles relax, heart rate and breathing return to normal, and pleasant fatigue spreads through the body.
After orgasm and ejaculation, a man needs to rest first. Someone can be excited in a couple of minutes, someone may need several hours or a day. It depends on various factors.
It is known that the stronger the release of oxytocin and prolactin during orgasm, the longer the body will recover.
The release of oxytocin creates a sense of trust and makes us miss our partner. However, people with high testosterone levels may not feel close, as this hormone inhibits the action of oxytocin.
Disclaimer!
Sex research has a number of limitations. First, even among scientists, stereotypes about the difference in sexual responses between men and women are common, which makes it difficult to obtain objective results. Secondly, studying sex life and brain function is difficult and expensive, so there are not many high-quality works on this topic. We have tried to collect in the article objective information from the currently available studies.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WDetHC86Dgo&t=144s
How to achieve female orgasm?
Research work carried out by two American sexologists, William Howell Maser and Virginia Eshelman Johnson, has made it possible to establish an orgasmic cycle divided into 5 phases common to both sexes:
- Desire: the urge to make love or masturbate begins under the main control of the brain;
- Arousal: the sexual organs become hypersensitive, the penis becomes erect, the clitoris swells and the lubrication of the vagina is activated;
- The plateau phase: the sexual organs are stimulated manually or during sexual intercourse;
- Orgasm: muscle tension is at its peak, breathing accelerates and the explosion of pleasure appears, most often manifested in men by ejaculation and in women by a retraction of the clitoris;
- Appeasement also called “little death”: the body relaxes to return to its natural state after about 30 minutes. The penis returns to normal size and the clitoris shrinks.
What are the differences between female orgasm and male orgasm?
A study conducted by the University of Quebec in Montreal reveals that, from a physiological point of view, orgasm seems to manifest itself in the same way in both sexes. Men and women describe a sensation of rhythmic contractions (every 0,6 to 0,8 seconds) in the perineal belt. If some evoke a more intense orgasm in women, no study has come to prove this assertion.
On the other hand, it has been shown that orgasm is longer in women, between 10 and 15 seconds, against 4 to 10 seconds in men for physiological reasons. Indeed, vasocongestion, that is to say the increased blood flow into the tissues extends to the entire pelvic area in women and is limited to the sexual organs in men.
The possibility of a multiple orgasm in women
It is possible for a woman to have several orgasms in a row and the intensity can vary. Indeed, according to a study conducted by the University of Geneva, it is estimated that 17 to 20% of the female population are multi-orgasmic. A phenomenon made possible in particular because the woman does not experience a refractory phase after orgasm unlike the man, for whom it will be impossible to obtain a new erection before this break time.
What is the role of the brain on female orgasm?
Thanks to MRI observations carried out by researchers in New Jersey, we know that when you come, your brain boils. Nerve stimulation from the genital area is sent to our brain system. The hypogastric nerve, the pudendal nerve and the vagus nerve are notably responsible for the nervous transfer of orgasm. The pleasure and well-being hormones are released and a feeling of ultimate well-being is added to the intense pleasure. Conversely, the parts of the brain linked to stress and fear are extinguished.









