Contents
Anemia characterizes the state of the body, in which the level of hemoglobin in red blood cells is significantly reduced. Hemoglobin provides a substance that contains iron, and erythrocytes are red blood cells. There are several types of anemia, each of which is accompanied by a number of specific symptoms and develops for different reasons. Anemia is a pathology that equally affects adults and children. Anemia can accompany other diseases.
To detect this violation, it is required to conduct laboratory tests. Often anemia acts only as a concomitant symptom of a serious illness in the body. The deterioration of the quality characteristics of blood leads to the fact that the functioning of the whole organism as a whole suffers.
Anemia: symptoms and causes

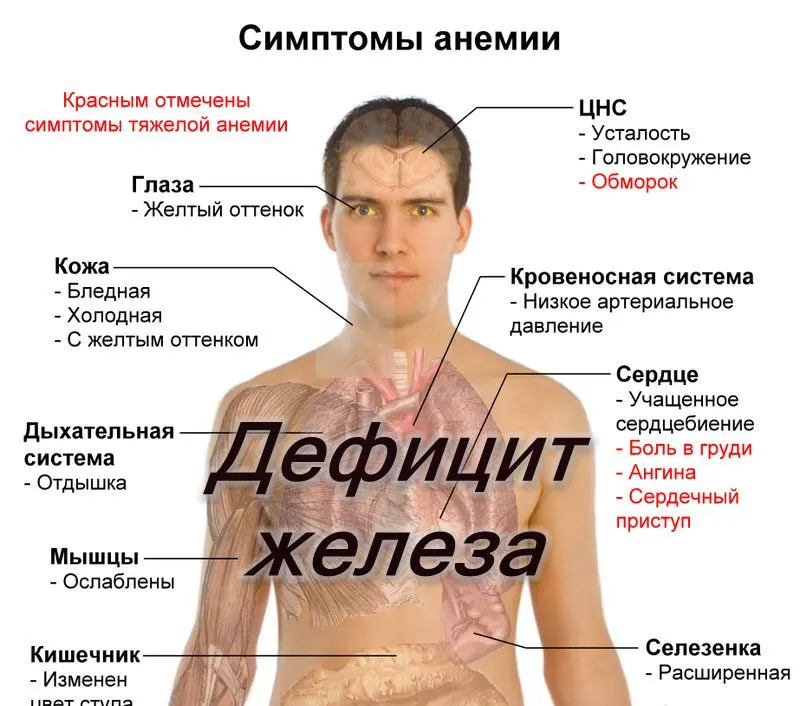
The symptoms of anemia, regardless of its type, will be determined by the severity of the disease and the general health of the person.
Anemia leads to hypoxia of internal organs and tissues, which causes disturbances in their work.
The most common symptoms of anemia include:
Paleness of the skin and mucous membranes. Sometimes they can give yellowness.
The person feels tired all the time.
Sleepiness increases during the daytime, despite the fact that a person gets enough sleep at night.
With regular intervals, the patient is disturbed by dizziness, which can end in fainting.
Blood pressure decreases.
The person often experiences headaches.
Even with slight physical effort, shortness of breath appears.
The pulse is quickened, as is the heartbeat.
Immunity is reduced, which leads to frequent colds.
The condition of nails and hair worsens.
As for the reasons that lead to the development of anemia, they can be very diverse. There are anemia that is inherited, as well as anemia acquired during life.
Factors that can provoke the development of anemia: bleeding (acute and chronic), diseases (acute and chronic), nutritional errors, etc. If a person suspects that he is developing anemia, then you need to contact a doctor. The doctor will prescribe the appropriate studies that will confirm the diagnosis. The basic method is to perform a clinical blood test.
There are the following types of anemia:
Acute iron deficiency anemia and chronic posthemorrhagic anemia with iron deficiency in the body.
B12 deficiency anemia.
Anemia associated with folic acid deficiency.
Hemolytic anemia.
Aplastic anemia.
Iron deficiency anemia
Causes that can provoke the development of iron deficiency anemia:
Certain periods in a woman’s life, such as pregnancy and breastfeeding.
In childhood, anemia often develops in babies born prematurely.
Diseases of the digestive system can lead to anemia.
The cause of iron deficiency in the body is often chronic bleeding.
Iron deficiency anemia is indicated by laboratory data such as a decrease in the level of red blood cells, hemoglobin and serum iron in the blood.
One of the signs of iron deficiency in the body is the deterioration of the hair and nails, as well as peeling of the skin. Teeth can be affected by caries.
To get rid of iron deficiency anemia, the patient will need to take iron supplements and follow a special diet. The doctor should help determine the specific drug. The doctor selects the dose of the drug, and also controls its effectiveness. If the patient does not tolerate the drug well, then it should be replaced. Provided that iron deficiency anemia has a severe course, the patient is hospitalized.
B12 deficiency anemia

B12 deficiency anemia develops when the body does not get enough vitamin B12. This disease is often observed in vegetarians, in people who are on diets. In addition, B12-deficiency anemia can manifest against the background of impaired absorption of this vitamin in the stomach and intestines.
Pregnant women, nursing mothers, the elderly, cancer patients – all these categories of citizens are at risk for developing B12-deficiency anemia.
In a blood test, it will be possible to see red blood cells that are large in size. Anemia of this type is indicated by symptoms such as: numbness of the hands and feet, deterioration of their sensitivity, inflammation of the tongue, problems with swallowing food, an increase in the size of the liver and spleen.
Treatment of anemia involves diet correction with the inclusion of animal products in the menu. You should also act on the cause that led to the deficiency of vitamin B12.
folate deficiency anemia
When there is a lack of vitamin B9 (folic acid) in the body, a person develops folate deficiency anemia. Often a similar problem occurs in pregnant and lactating mothers, in premature babies, in patients with oncology, in alcoholics and drug addicts.
Common symptoms of folate deficiency anemia are: increased weakness, increased fatigue, pale skin with a slight yellowish tint, and frequent dizziness.
The body cannot produce vitamin B9 on its own, it gets it from food. However, at high temperatures, this vitamin is rapidly destroyed. To get rid of folate deficiency anemia, you will need to include foods rich in folic acid in the menu. You may need medication to correct the pathology.
Hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia is characterized by mass death of red blood cells, which leads to the development of jaundice. Yellowing of the skin occurs due to an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood. Often, hemolytic anemia is observed in newborn children, when the Rhesus conflict with the mother becomes a provoking factor.
Hemolytic anemia can be inherited from blood relatives, or it can develop during life. Most often, this pathology is still congenital. Risk factors that can provoke the development of anemia in an adult are: blood transfusion, therapy with a number of drugs, burn disease, bacterial infection, vitamin E deficiency.
The main signs of anemia are: fever, chills, dizziness, enlargement of the spleen in size. Treatment is carried out under strict medical supervision.
Aplastic anemia
Aplastic anemia is a disease rarely diagnosed, but extremely severe. In this case, there is a decrease in the activity of bone marrow cells, which later cease to divide themselves and die, being replaced by adipose tissue.
Aplastic anemia develops against the background of exposure to toxic chemicals, viral infections, and alcoholism. Also, pathology can be hereditary in nature.
Symptoms of aplastic anemia include: fever, increased weakness, bleeding from the gums, heavy menstruation, a tendency to nosebleeds.
Aplastic anemia does not tolerate delay in treatment. The therapy is carried out in a hospital setting.
So, anemia is a rather serious violation in the hematopoietic system. There are many varieties of pathology, therefore, in order to make the correct diagnosis, you need to contact a doctor.









