Contents
- Groups of birth control pills
- How to choose good birth control pills?
- How to take hormonal oral contraceptives correctly?
- Side effects of birth control pills
- Absolute contraindications to oral contraceptives
- Can you get pregnant while taking birth control?
- Can I take contraceptives when I’m already pregnant?
- Is it possible to take hormonal pills after 35?
- Emergency and non-hormonal contraception
- Benefits of using hormonal birth control pills
- Cons of using birth control pills

The article is devoted to the analysis of the positive and negative aspects of the use of contraceptive pills and the assessment of their potential harm to women’s health:
The first part of the article contains information about the classification, contraindications, side effects and advantages of taking hormonal oral contraceptives.
The second part analyzes the potential risk of long-term effects from taking drugs for perfectly healthy women.
Women should be attentive to the prospective forecasting of their own health. It is worth considering the following factor – each intervention in the delicate and sensitive mechanism of natural processes occurring in the female body can result in both minor and tragic consequences.
Every woman should weigh her decision to take or refuse birth control pills after consulting a gynecologist. You should not recklessly refuse these drugs, but you should definitely analyze all the risks of long-term contraception using oral contraceptives.
Groups of birth control pills
Among all other forms of a wide range of contraceptives offered to consumers by the pharmaceutical industry, hormonal birth control pills are leaders in consumer demand. Unfortunately, many women “prescribe” them to themselves on their own, without thinking about side effects and contraindications to taking these drugs. Correction of the term for the use of tablets, and, most importantly, their choice is carried out exclusively by a gynecologist based on a study of the woman’s history and the results of laboratory tests.
Types of oral contraceptives:
COCs (combined oral contraceptives),
Mini-pili.
The main active ingredient of COCs is one of the progestogens (norethisterone, norgestrel, desogestrel, gestodene, etc.) and ethinylestradiol (an analogue of the hormone estrogen).
Types of COCs depending on the ratio of hormones:
Monophasic drugs
Biphasic drugs
triphasic preparations
Monophasic drugs In each tablet of drugs in this group, the percentage of the progestogen and estrogen components is unchanged |
Desogestrel and ethinylestradiol:
|
Ethinylestradiol and dienogest:
|
Gestodene and ethinylestradiol:
|
|
|
| |
Biphasic drugs The dose of estrogen in all tablets is the same, the dose of progestogen varies depending on the period of the menstrual cycle |
|
| |
triphasic preparations Doses of estrogen and progestogen change three times depending on the period of the menstrual cycle |
|
|
|
The mechanism of action of combined oral contraceptives is to block the formation of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) in the pituitary gland, resulting in inhibition of ovulation. At the same time, the functioning of the ovaries and the structure of the endometrium change. The glandular regression of the mucous membrane makes it impossible for a fertilized egg to attach to the wall of the uterus. The mucus in the cervical canal becomes thicker, so the passage of sperm into the uterus is difficult.
Classification of COCs according to the degree of concentration of active components:
Microdosed oral contraceptives. The content of hormones is minimal, the drugs are recommended for those who use COCs for the first time, as well as for young women under 25 years old. Monophasic drugs of this group: Zoeli, Jess, Miniziston, Dimia, Novinet, Logest, Miniziston, Mercilon, three-phase drug Qlaira.
Low dose oral contraceptives. The drugs have an antiandrogenic effect, when they are used, the growth of unwanted hair, greasiness of the skin of the face and head, seborrhea, and acne are reduced. Recommended for young and middle-aged women who have given birth, as well as for those for whom microdosed preparations are not suitable, as there are spotting in the middle of the menstrual cycle. Preparations of this group: Diana, Jeanine, Miniziston, Rigevidon, Yarina (Midiana), Tri-Merci, Regulon, Belara, Femoden, Lindinet, Marvelon, Chloe, Silest, Demulen, Microgynon.
High-dose oral contraceptives. The content of hormones in the preparations of this group is quite high, they are prescribed for the treatment of hormonal disorders or pathologies of the female genital area (endometriosis) exclusively on prescription. Preparations: Non-ovlon, Triseston, Triquilar, Tri-regol, Ovidon.
Mini-pili. Preparations of this group contain only progestogen, act on limited areas of the female genital organs. The active substance of the minipill changes the composition and amount of mucus in the cervical canal, which prevents the movement of spermatozoa into the uterus. As a result of taking drugs, the morphology and biochemistry of the endometrium changes, thereby creating the impossibility of implantation of the egg. Half of the women who use mini pills for contraception? ovulation does not occur. Preparations of this group with linestrenol as an active ingredient (Orgametril, Exluton, Microlut), with desogestrel (Charozetta, Lactinet).
|
|
|
|
Charozetta (800 rubles) desogestrel | Lactinet (530 rubles) desogestrel | Orgametril (1100 rubles) linestrenol | Exluton (1250 rubles) linestrenol |
How to choose good birth control pills?
The choice of oral contraceptives should not be trusted by friends or a pharmacy pharmacist, appoint them yourself. To choose pills for contraception, you need to visit a gynecologist. The doctor will analyze the patient’s history, genetic predisposition to the main diseases of the risk group, and evaluate possible contraindications.
As a result of a medical examination, the following indicators are evaluated:
Weight, blood pressure;
The condition of the skin, the presence of excessive hair growth on the body;
Signs of an overabundance of androgens;
The state of the mammary glands (by palpation);
Analysis of blood biochemistry, blood sugar, liver enzymes, hormonal levels;
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and mammary glands (mammography);
Analysis of smears from the vagina and cervical canal;
The state of the pelvic organs (examination in the mirrors);
Assessment of the state of the organs of vision (examination by an ophthalmologist).
The choice of birth control pills is based on the type of woman’s constitution.
Parameters of the constitutional-biological type:
Growth, features of appearance;
The volume of the mammary glands;
Type of pubic hair;
Skin and hair condition;
Features of menstruation and premenstrual symptoms;
Amenorrhea or menstrual irregularities;
Existing somatic pathologies.
Female phenotypes and most suitable oral contraceptives:
The predominance of estrogens
Phenotype – feminine, with dry skin and hair, having a short and medium height, long periods with a large loss of blood, a menstrual cycle of more than 4 weeks. Women with a predominance of estrogens are recommended contraceptives with a high and medium dose of hormones: Rigevidon, Triziston, Milvane, etc.
|
|
|
Milvane (ethinylestradiol and gestodene):
| Ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel:
| |
The same amount of estrogens and androgens
The phenotype is feminine, with developed mammary glands of medium size, medium height, oily skin and hair is normal, PMS is absent, the menstrual cycle lasts 4 weeks, menstruation is 5 days. New generation drugs are recommended: Microgynon, Silest, Femoden, Marvelon, Lindinet-30 and others.
|
|
|
|
Ethinylestradiol and desogestrel:
| Ethinylestradiol and Norgestimate:
| Eethinylestradiol and Gestodene (Milvane):
| Ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel:
|
The predominance of androgens (gestagens)
Phenotype – high growth, underdeveloped mammary glands, oily skin and hair above normal, PMS in the form of depression and pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, scanty menstruation with a short cycle of less than 28 days. Recommended drugs: Jess, Janine, Yarina, Diane-35.
|
|
|
|
Ethinylestradiol and drospirenone:
| Ethinylestradiol and drospirenone:
| Ethinylestradiol and drospirenone:
| Nomegestrol and Estradiol:
|
|
|
|
|
Ethinylestradiol and dienogest:
| Ethinylestradiol and cyproterone:
| ||
How to take hormonal oral contraceptives correctly?

The standard blister with contraceptive pills, designed for one cycle, contains 21 pcs. Exceptions: Jess (a new generation drug designed for young women) – 24 tablets, Qlaira (a modern drug for women over 35) – 28 tablets.
Rules for taking oral contraceptives:
Reception begins on the first day of menstruation, it is continued daily at the same hour chosen for this.
The rule for the forgetful is to put a blister with pills where it will constantly catch your eye (attach with a magnet to the refrigerator door, put in a cosmetic bag, to a glass with a toothbrush).
Take 1 tablet daily until the end of them in a blister, then take a break for 7 days, during which bleeding will occur according to the type of menstruation.
After seven days, you need to start a new blister with contraceptives, regardless of whether the bleeding has ended or not.
If vomiting occurs, the pill should be taken out of turn.
If the next pill was missed, it should be resumed immediately.
When vomiting and skipping the drug, it is advisable to protect yourself by other means for 1-2 days.
A similar tactic of additional contraception is used in the first 2 weeks of taking oral contraceptives, if this happened for the first time in life.
Bloody discharge in the middle of the cycle is not a reason to stop taking COCs. Most likely, they are associated with the restructuring of the hormonal background of the body, and will last no longer than 2-3 months.
After an artificial termination of pregnancy, birth control pills are started either on the day of the abortion, or a month after it, on the day of the first menstruation.
There are drugs, with the simultaneous use of which the contraceptive effect of tablets is reduced. An example is Rifampicin, which stimulates the production of liver enzymes. In the case of systematic treatment of somatic diseases, you should carefully study the instructions for the drugs, inform the doctor about the regular use of oral contraceptives. If such drugs have to be taken, it is necessary to provide methods of barrier contraception for the duration of treatment (condom).
As for the mini-pills, there is no break for menstruation during their intake. Tablets are taken for 28 days, at the same time. Lactation is not a contraindication for taking mini-pill, breastfeeding can not be interrupted. If a woman is not breastfeeding, she is shown low-dose contraceptives. They are allowed to be used from 3-4 weeks after childbirth.
Side effects of birth control pills
Side effects are manifested when using oral contraceptive pills.
Minor side effects:
| Serious side effects:
|
Women taking oral contraceptives should periodically assess their current state of health in order to notice side effects in time.
Necessary activities:
Blood pressure monitoring – every six months;
Physical examination (state of the mammary glands, liver, gynecological examination of the pelvic organs), urinalysis – annually;
Self-examination of the mammary glands – monthly.
There is a world practice for the distribution of oral contraceptives. These are programs for countries with a low level of medical development. For this reason, access to regular check-ups for these women is almost impossible. They have an increased risk of side effects.
Absolute contraindications to oral contraceptives
There are diseases for which birth control pills are not prescribed. These are congenital hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert’s syndrome), multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, thalassemia, bronchial asthma, thyrotoxicosis, sarcoidosis, the need for renal dialysis, rheumatoid arthritis, Hodgkin’s disease, retinitis pigmentosa.
Absolute contraindications to combined OK:
| Absolute contraindications to taking pure progestins:
|
The danger from the use of oral contraceptives should not be underestimated even by seemingly completely healthy women. It is possible that neither the patient nor the attending physician is aware of the hidden diseases from the list of contraindications. Therefore, the risk of developing oncological diseases, pulmonary thromboembolism cannot be completely excluded.
Can you get pregnant while taking birth control?

There is such a possibility, but its probability against the background of the use of birth control pills is minimal.
Conditions for the occurrence of an unwanted pregnancy while taking OK:
Violation of the rules for taking the drug – the use of expired tablets with an expired shelf life, omissions or irregular intake at different times of the day.
Vomiting in case of poisoning immediately after taking OK or taking pills in conjunction with other drugs that reduce the contraceptive effect.
Can I take contraceptives when I’m already pregnant?
Of course not. Taking OCs during pregnancy will greatly affect the fetus. The medication should be stopped immediately.
Is it possible to take hormonal pills after 35?
In countries with a high level of medical development, approximately 50% of couples prefer sterilization as a method of contraception. Women after 35 years of age are not recommended to take hormones with a combination of diseases of the cardiovascular system with smoking, or a high risk of oncological diseases.
After 40-45 years, it is advisable to take drugs from the mini-pill group. They have proven themselves in endometrial hyperplasia, uterine myoma, endometriosis.
Emergency and non-hormonal contraception
Emergency contraception
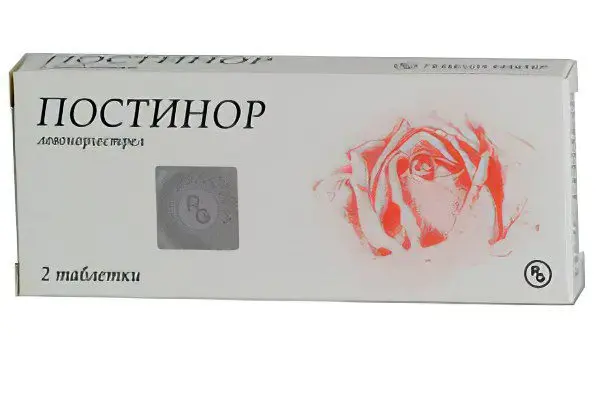
To prevent unwanted pregnancy during unprotected intercourse, a woman can use emergency contraception. The most famous drugs from this group are Postinor and Escapel. Postinor is used no later than 72 hours after sexual intercourse without contraception.
First, a woman should take 1 tablet, after 12 hours the second. Conventional oral contraceptives (COCs) can also be used as emergency contraception. It is important that the tablet contains at least 0,25 micrograms of levonorgestrel and at least 50 micrograms of ethinyl estradiol. Immediately after sexual intercourse, you should take 2 tablets of an oral contraceptive, after 12 hours, repeat the intake in the same dose.
Non-hormonal contraception
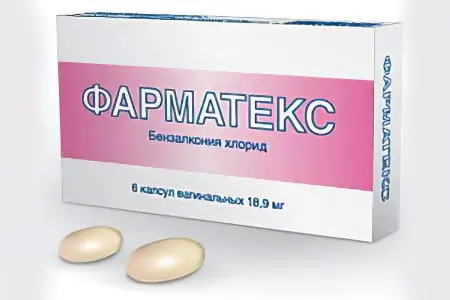 Non-hormonal contraceptive pills are spermicides intended for topical use for contraception. The main active ingredient of these contraceptives serves as a kind of barrier for the penetration of spermatozoa into the uterine cavity. An additional effect of non-hormonal contraceptives is an anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect. Method of application – the introduction of the drug intravaginally 10-15 minutes before the intended sexual intercourse. Preparations of this group: Pharmatex, Patentex Oval, Benatex and others. |
Benefits of using hormonal birth control pills

If we compare barrier contraceptives and modern new generation contraceptive pills, then all the advantages will be on the side of the latter.
Pros of using oral contraceptives taken on the recommendation of a gynecologist:
Almost 100% effective contraceptive method;
Available for use by women at any age;
Against their background, the menstrual cycle becomes regular, menorrhagia disappears;
There is a cosmetic effect – hirsutism, acne, seborrhea of the hairline are reduced;
A woman acquires psychological comfort, as the fear of unwanted pregnancy disappears;
It becomes possible to regulate the time of the onset of menstruation;
Presumably, there is a therapeutic effect in mastopathy, ovarian cysts, endometriosis, uterine myoma (this question remains open, since most studies are funded by OC manufacturers);
Fertility does not suffer, the ability to bear children is restored after 2-6 cycles, a maximum of a year.
To obtain an objective picture, it is necessary to analyze the arguments against taking oral contraceptives. In any case, a woman must make a decision armed with knowledge of the benefits and dangers of long-term drug use.
Cons of using birth control pills

The modern production of medicines is the same business as construction, trade and any other sectors of the economy. The more often you have to take drugs, the greater the benefit of their production brings manufacturers. You can imagine how profitable it is to produce birth control pills that should be taken daily by millions of women around the world. Over the past decade, independent experts from the United States have conducted several studies, the results of which may be shocking.
The consequences of taking oral contraceptives in nulliparous women (according to studies):
risk of breast cancer;
Increased risk of liver cancer, cervical cancer;
Increased blood sugar levels;
Alopecia (hair loss);
migraine attacks;
Development of osteoporosis;
bouts of depression;
The appearance of pigmentation on the skin of the face and body.
The centers of hormonal regulation – the pituitary and hypothalamus, associated with peripheral glands that produce hormones (ovaries, adrenal glands, thyroid gland), perform the functions intended by nature in the human body. The ovaries with the help of this system interact with all the organs of a woman. Every cycle, the uterus prepares to receive a fertilized egg, and this delicate balance can be disturbed by any interference from outside.
Doses of hormones given daily with birth control pills alter the function of the uterus and ovaries. Oral contraceptives suppress ovulation and ovarian activity, and egg production is disrupted. These violations are reflected in the work of the higher regulatory centers of the hormonal system. Over the years and even decades of taking contraceptive drugs, the uterine endometrium changes. Its uneven rejection is manifested by bleeding and dark discharge in the middle of the cycle. The transformation of the upper layer of the endometrium is dangerous with the appearance of cancer during menopause.
The lack of demand for hormones produced by the ovaries leads to a reduction in their number, malnutrition and ovarian size. Hormonal “shake” at the beginning of taking contraceptives and during their withdrawal is a stress for the woman’s reproductive system. That is why fertility is restored for so long (up to a year), and in some cases it is not restored at all.
Negative consequences of taking birth control pills:

In the presence of serious contraindications, women are prohibited from taking oral contraceptives in order to avoid vein thrombosis with a fatal outcome, the development of an oncological process;
Accelerates the excretion of B vitamins2, b6, which leads to skin diseases, damage to the nervous system (irritability, insomnia, weakness, fatigue);
The body’s receipt of folic acid, which is necessary for conception and pregnancy, is disrupted, the marketing move of pharmaceutical companies about its inclusion in hormonal preparations is most often not confirmed in practice;
With prolonged use of birth control pills, the risk of developing glaucoma doubles, according to studies by the University of California, among 3500 women who took ok, glaucoma occurs more often than in those who do not take such drugs;
Increased risk of osteoporosis, increasing after age 40;
3 times the risk of developing Crohn’s disease in women who have taken oral contraceptives for 5 years or more (according to a study conducted with 230 thousand women);
An increase in the risk of developing brain tumors by 1,5-3 times with prolonged use of OK (according to scientists from Denmark);
Increased thrombus formation in the vessels of the brain, cardiac and pulmonary arteries, which increases the risk of stroke and premature death from thromboembolism, which is more likely to affect women who smoke, patients with hypertension and a genetic predisposition;
The appearance of venous insufficiency – vascular “asterisks”, swelling of the legs, a feeling of heaviness, pain and cramps, varicose veins, the appearance of trophic ulcers;
Increased risk of inflammatory diseases of the cervical canal, breast tumors;
Violations of the ability to bear children, problems with conception and gestation;
Inability to protect against sexually transmitted diseases;
The appearance of pigmentation on the skin of the face and body;
Increased risk of multiple sclerosis by 35% (according to a study by scientists from the USA);
Hair loss;
Development of transient hypothyroidism (decreased thyroid function);
development of depression;
Decreased sex drive;
The possibility of skipping the reception time, errors in use, the need for self-control;
The need to visit a gynecologist;
The high cost of birth control pills.

According to statistics provided by WHO, about 100 million women worldwide use oral contraceptives. This huge market brings huge profits, so the truth about the dangers of OK harms the interests of manufacturers.
Public organizations create their own lobby, the purpose of which is to draw the attention of women to the dangers of oral contraceptives, as well as to ban especially dangerous drugs. The result of this is the recommendations of gynecologists in America and Europe to use condoms to protect against unwanted pregnancy and sexual infections. The same role can be played by a hormonal patch and an ectopic device.
Promotion of the dangers of contraceptive pills, a number of deaths and lawsuits in the US and Europe led to the prohibition of the drug Diane-35. According to surveys, 67% of Europeans aged 16 to 64 use condoms for contraception, 16% use a hormonal patch, and 7% use a spiral. Only about 10% of respondents use oral contraceptives.
In Russia, gynecologists still recommend the use of OCs to women from adolescence. Most doctors do not provide women with complete information about the true picture of the dangers of contraceptives to health.