Contents
Vygotsky is a pedagogue psychologist born in 1896 in the Russian Empire (now Belarus). He became known around the world for his work in developmental psychology and his historical-cultural theory of the psyche at the start of the 20th century. He explained that socialization affects an individual’s learning process, through their awareness and sensitivity.
Vygotsky became famous for a theory called “theory of social development” or “socio-cultural theory of cognitive development”. Russian psychologist and educator, Vygotsky poses in this theory the contribution and contributions of society on individual development and learning. Thus, he suggests that human learning is largely a social process, further mentioning the influence of interactions between people and the culture in which they live.
This theory of social development is deepened by looking at how adults and peers will influence individual learning, just as cultural beliefs and attitudes will influence the way of teaching.
The role of the community
Community, according to Vygotsky, would therefore give meaning to the learning process. Child learners are far from being passive receivers, but build their knowledge and their own patterns from the information they are given, but also from cultural influences and from collective consciousness and sensitivity. Vygotsky is thus a precursor of social constructivism, translating these same ideas.
According to this psychologist, there are then two factors that can influence learning:
- the social environment;
- the personal environment.
Indeed, from birth, human beings are social and destined to live in society.
We then need other people to develop us and to elevate us intellectually. Even from a very young age, a child is built step by step thanks to the interaction that he nurtures with his parents and then with other people in his immediate environment. Influenced by others, he will then in turn influence the actions and behaviors of the people around him.
This theory includes three main concepts:
- the role of social interaction in cognitive development;
- others better informed;
- the zone of proximal development.
According to Vygotsky, it is social interactions that decisively influence the process of cognitive development, in other words, learning.
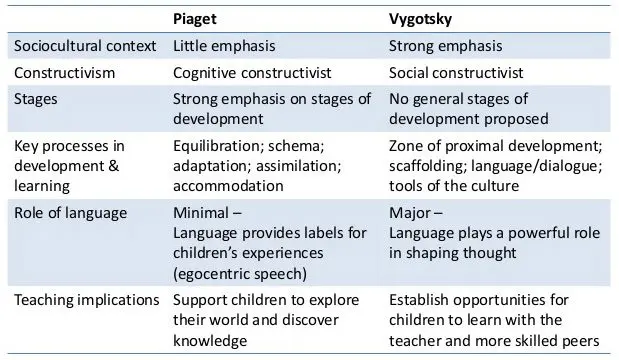
He is thus opposed to Jean Piaget, Swiss biologist, psychologist and epistemologist, who made himself famous for his work on social development.
Piaget argued that learning comes after building an individual. Vygotsky asserted the opposite: social learning would take place upstream of development.
According to him, the cultural development of a child occurs first on the social level (called interpsychological) and then on the individual or personal level (called intrapsychological). It thus appears clear that all the cognitive functions of a child appear thanks to the interaction with other people.
For Vygotsky, there are two types of mental functions:
- Lower : these are the functions with which we were born. They are innate to us. They are therefore determined biologically.
- Superior : these are the mental functions acquired and developed through social interaction.
Better informed others
In order to transmit information to a learner (child or young adult), the theory suggests that it is therefore necessary to rely on a person with superior skills compared to the learner in the task invoked, in the process or the concept.
We will name this person AMI or Other Better Informed. This person can be a teacher, a parent, an expert or even an elderly person, but it can also be friends or younger people, or even robotic devices (computers, talking robots, etc.).
For example, a teacher who will teach a young child his multiplication table is a FRIEND, a father who will teach his daughter to ski is still a FRIEND. A computer that is asked for information is also an AMI.
Proximal Development Zone (ZDP)
Finally, the last concept developed by Vygotsky in his theory is the zone of proximal development: it is the space between the tasks that the child can perform on his own and those that he manages to perform with the help. of someone more advanced in this field. This area therefore corresponds to everything that the learner can master when given external and appropriate help.
In this “zone”, the learner or the child can learn, being guided and encouraged by another informed person (other better informed, FRIEND). But this ability, according to this theory, is reduced to nothing without an AMI.
In this area, therefore, learning takes place: the child can then develop his higher cognitive functions.
Psychological tools
All psychology tools aim to order information externally, they are as follows:
- the symbols ;
- writing ;
- art ;
- the drawings ;
- language.
This last tool, language and speech, are the most important, because the child or the learner will communicate via this tool mainly with his social environment. The more this tool is developed, the more its ability to increase its higher cognitive functions will be high.










ano ibig ng culture Kay vygotsky ?