In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
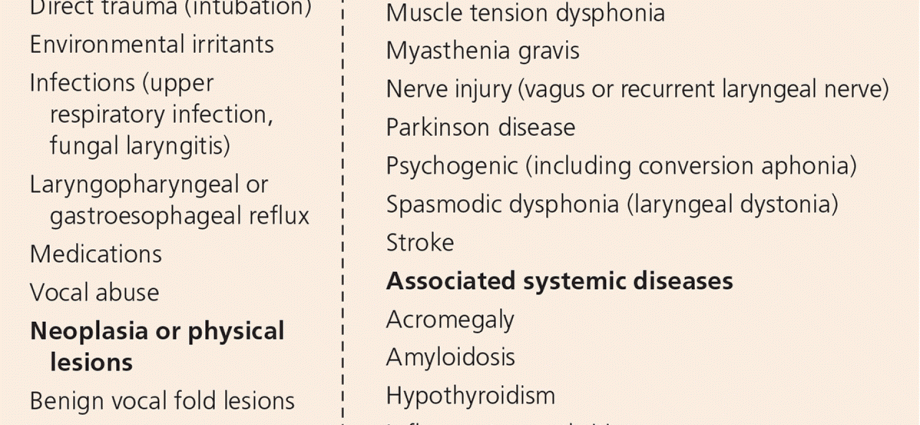
Voice problems, changes in voice, hoarseness, and discoloration can be a symptom of many diseases. A complete loss of voice or a change in timbre is called dysphonia. The change of voice may be caused by overloading of the vocal cords caused, for example, by their abuse, infection of the upper respiratory tract. The symptoms include, first of all, discomfort and even pain when speaking, the voice loses its quality.
Each long-lasting change of voice should disturb and induce the patient to a control visit to the ENT specialist. The cause of dysphonia can be diverse, therefore the diagnosis and course of treatment depend on the factors and, of course, the symptoms of the ailments.
Voice change – what is dysphonia?
A change of voice, or dysphonia, is any long-lasting anomaly in the timbre of the voice, its intensity, frequency of sounds or their length. The change of voice may be caused by prolonged overload of the vocal cords, frequent inflammation of the larynx. Functional dysphonia is not associated with abnormalities in the structure and function of the larynx.
The change of voice may be caused by physiological or anatomical changes in the larynx, because the emerging cysts, nodules, polyps, inflammations or ulcers will significantly affect our voice. There is a long list of diseases that make our voice change:
- gastro-oesophageal reflux
- pharyngitis
- laryngitis
- epiglottitis
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- Hypothyroidism
- gout
With a hoarse voice that does not go away after a few weeks and is not related to an upper respiratory tract infection, an ENT specialist is necessary, as this type of voice change may be caused by a developing cancer, e.g. larynx. In such cases, specialized tests using a laryngoscope are ordered. When should a voice change concern us?
- our voice becomes a few tones lower
- we constantly feel dry throat, pressure and burning
- the voice becomes hoarse
- we feel discomfort in the throat and the need to constantly cough up
- the conversation becomes an effort for us
Voice change – reasons
Symptoms that accompany a hoarse may include dysphagia and pain when speaking. The neoplasm shows not only a change of voice, but also shortness of breath, hemoptysis, and a palpable lump in the neck area. Other conditions that result in voice alteration are the most common laryngitis. It is a disease caused by viruses that cause swelling on the vocal cords, among other things. The ailment that causes dysphonia is acid reflux, i.e. the regurgitation of stomach contents into the larynx. With gastroesophageal reflux, not only a hoarseness may appear, but also a sore throat, a feeling of a lump in the throat, problems with swallowing. Voice change is also a side effect of the continued use of corticosteroids, so people with asthma may notice changes in their voice.
The change of voice may be the result of ailments of a neurological nature, but also related to the weakening of the thyroid gland. Dysphonia is common in hypothyroidism or after thyroid surgery. It happens that the vocal cords are weakened due to damage to the laryngeal nerves, and in this case there is also a change in voice. Any longer lasting changes in the sound, volume or quality of our voice should be consulted with a specialist doctor. Earlier detection of laryngeal cancer and a quick biopsy of the tissue changed by the disease make it possible to introduce a larynx-sparing treatment.