The larynx is an organ of the upper respiratory tract located between the pharynx and the trachea. This organ performs a respiratory function and forms a voice. The vocal cords are located in the larynx, they are transversely stretched and there is a gap between them. The voice is formed during the period of vibration of the vocal cords, when air passes through the glottis.
The muscular apparatus of the larynx carries out its work through nerve impulses, in the event of inflammation or damage to the nerves that transmit impulses to the muscles, paresis of the vocal cords occurs. Paresis is a partial loss of function of the vocal cords, it can occur with unilateral or bilateral lesions of the recurrent nerve, most often occurs during operations on the thyroid gland, neck vessels or spine.
This pathology of the vocal cords can be observed with tumors, when the organs of the mediastinum and esophagus are compressed, with protrusion of the aortic wall, enlargement of the lower chambers of the heart, and neck injuries. Symptoms of paresis – hoarseness, rattling, fatigue during communication, loss of voice, heavy breathing, lowering the pitch of the voice, due to the vibration of the vocal cords at two different frequencies, the simultaneous formation of two tones of different pitches is possible.
In medicine, several types of paresis are defined:
Myopathic paresis caused by laryngitis, hemorrhages with excessive voice tension, they occur during puberty.
Neuropathic paresis means weakness of the internal laryngeal muscles associated with impaired innervation.
Organic paresis occurs when the vagus nerve and its branches are damaged. Functional paresis – caused by a disorder in the relationship between the processes of inhibition and excitation in the cerebral cortex, functional neuroses, neurasthenia.
How to solve the problem?
Diagnosis is carried out on the basis of complaints and the results of laryngoscopy. Tomography of the throat area is also performed, checking the condition of the larynx using a flexible optical probe. A modern research method called stroboscopy is used, which allows you to observe the functional work of the vocal cords in slow motion.
The smallest deviations and pathologies in the vocal cords are determined by a computer acoustic method, during which a digital voice recording is performed. Various computer programs help to determine the frequency range, the stability of the sound extraction force, the stability of the speech frequency. Treatment of paresis of the larynx is prescribed depending on the etiology of the disease.
In the infectious-inflammatory nature of the paresis of the vocal cords, antibacterial and antiviral therapy is recommended. The detection of neuritis involves the use of neuroprotective drugs and vitamins of group B. The myopathic form of paresis is effectively treated with biogenic stimulants, such as ATP, aloe, prozerin, an activator of muscle activity.
As a remedy for functional paresis, neuroleptics, antidepressants, tranquilizers and sedative drugs will be exchanged. Today, there are several improved methods of treatment, but the problem of voice restoration in patients with unilateral paralysis of the larynx still remains one of the most difficult and relevant in laryngology.
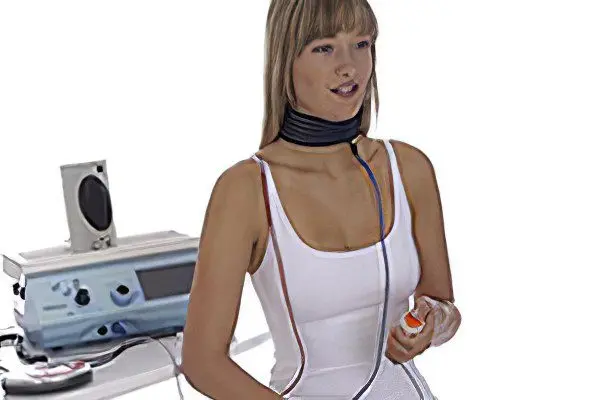
For the treatment of such patients, a phonopedic method, acupuncture is used. Excellent results that affect the rapid recovery of ligaments are provided by electrical stimulation with diadynamic currents of the neuromuscular apparatus of the larynx. In the fight against inflammation, fluctuating currents of resorptive and regenerative properties work well.
Modern medicine has an excellent method, which consists in heat treatment, causing vasodilation. This not only improves microcirculation, but also enhances metabolic processes. Surgical methods turned out to be ineffective, since they cause injury, injectable implants introduced into the vocal folds, made of various synthetic materials and biopolymers without toxic substances, showed themselves better.









