Contents


Vitamin B1 is a water-soluble organic heterocyclic compound. The modern name of vitamin B1 is thiamine, and the outdated name is aneurin.
A feature of this substance is that it is not able to accumulate in the body. That is why its regular daily supplies from the outside are so important. Vitamin B1 is not afraid of high temperatures. It does not destroy when in an acidic environment, even if you bring it to 140 degrees. However, in neutral and alkaline concentrates, its ability to withstand heat is reduced.
It is difficult to overestimate the benefits of vitamin B1 for the body. It stimulates the brain, improves cognitive processes, so that any information is absorbed faster. Thiamine is essential for bone and muscle growth. It is especially needed by the elderly, people who abuse alcohol, smokers. It is taken for seasickness, as it eliminates its symptoms, prevents motion sickness. There is evidence that it makes toothache less intense. It is necessary for the normal functioning of the heart, organs of the digestive system.
Products-record holders for the content of vitamin B1
The main food sources of vitamin B1 are bran and rye bread, pork (especially fillets: 0,9 mg) and nuts. But most of all vitamin A is found in various cereals, sunflower seeds are the champion. Various bran – are a kind of concentrate of this vitamin. In vegetables, its content usually does not exceed 0,1 mg per 100 g.
When choosing a product, do not forget that vitamin B1 is resistant to high temperatures, up to 140 ° C.
 4,0 mg
4,0 mg 3,2 mg
3,2 mg 2,8 mg
2,8 mg 1,6 mg
1,6 mg Fresh: 1,5 mg Fried: 0,1 mg
Fresh: 1,5 mg Fried: 0,1 mg Seeds: 1,2 mg Flour: 2,7 mg
Seeds: 1,2 mg Flour: 2,7 mg Fresh: 1,2 mg Roasted: 0,7 mg
Fresh: 1,2 mg Roasted: 0,7 mg Fresh: 0,9 mg Fried: 0,7 mg
Fresh: 0,9 mg Fried: 0,7 mg 0,7 mg
0,7 mg 0,7 mg
0,7 mg Meat, liver, heart: 0,6 mg
Meat, liver, heart: 0,6 mg Fresh: 0,6 mg Roasted: 0,3 mg
Fresh: 0,6 mg Roasted: 0,3 mg Fresh: 0,6 mg Fried: 0,2 mg
Fresh: 0,6 mg Fried: 0,2 mg 0,6 mg
0,6 mg 0,6 mg
0,6 mg 0,5 mg
0,5 mg 0,4 mg
0,4 mg 0,4 mg
0,4 mg Fresh: 0,4 mg Roasted: 0,2 mg
Fresh: 0,4 mg Roasted: 0,2 mg 0,4 mg
0,4 mg+ 15 more foods rich in vitamin B1 | |||||
Pine nut | 0,4 | Trout | 0,4 | White beans | 0,2 |
Walnut | 0,3 | Salmon | 0,3 | Pancakes | 0,2 |
pumpkin seeds | 0,3 | Fried catfish | 0,3 | Almonds | 0,2 |
Green pea | 0,3 | Egg yolk | 0,2 | Garlic | 0,2 |
Chicken liver | 0,3 | Mackerel | 0,2 | bananas | 0,2 |
View the entire table of herbal products 250+ ➤
View the entire table of animal products 100+ ➤
Daily intake of vitamin B1 for women, men and children
The daily requirement of vitamin B1 differs depending on the age and sex of the person. The state of the body matters. For example, during pregnancy and lactation, the need for it increases. The norm indicators are presented in the table.
Categories of people | Daily requirement, mg | ME/IU |
0-6 months | 0,2 | 67 |
7-12 months | 0,3 | 100 |
1-3 years | 0,5 | 167 |
4-8 years | 0,6 | 200 |
9-13 years | 0,9 | 300 |
Men aged 14 and over | 1,2-2,5 | 400-833 |
Women 14-18 years old | 1,0 | 333 |
Women aged 19 and over | 1,1 | 367 |
Pregnancy | 1,5 | 500 |
Lactation | 1,7 | 567 |
During hard physical work | 2,5-3,0 | 833-1000 |
Elderly people | 1,2-1,4 | 400-467 |
When does the need for vitamin B1 increase?
There are conditions and lifestyle features in which the body’s need for vitamin B1 increases. These include:
Smoking, alcohol abuse.
The habit of drinking more than 2 cups of coffee a day. Caffeine leads to the destruction of vitamin B1 molecules.
Abuse of carbohydrate foods: pastries, pasta, sweets.
Therapy with antibacterial drugs and drugs aimed at reducing the acidity of gastric juice.
Bearing a fetus. The need for thiamine is especially high in the last 2 months of gestation.
Lactation. If a child receives less vitamin B1 from milk, the risk of developing cardiopathologies increases.
Taking contraceptives.
The absence in the diet of fresh products that have not been cooked. Heat and salt destroy vitamin B found in vegetables, grains and meats.
Conditions that reduce immunity: emotional overstrain, diseases of the digestive system, diabetes mellitus, disorders in the functioning of the thyroid gland, infections, surgery, burns, injuries.
Hard physical labor.
HIV. There is evidence that 25% of AIDS patients are deficient in vitamin B1, which leads to weight loss and neurological diseases.
Chronic fatigue syndrome with its characteristic symptoms: sleep problems, loss of strength, increased fatigue, depression.
Compliance with a diet.
Growth and development of the body. Children who eat a lot of pastries and sweets are in dire need of vitamin B1.
Elderly people. The older a person is, the worse his body absorbs any substances.
Living in hot climates and cold regions. Such boundary conditions lead to the fact that the need for vitamin B1 increases by 50%.
Diligent study or active career building. According to statistics, a lack of vitamin B1 is observed in 40% of young people.
Work in hazardous industries associated with toxic substances (arsenic, mercury, etc.).
Why does the body need vitamin B1?

Vitamin B1 performs many functions in the body. It is necessary for the proper functioning of the nervous and digestive systems. The brain, skin, blood cells, liver, gallbladder and more need it.
Energizes. The coenzyme of vitamin B1, which is called cocarboxylase, performs important functions in the body. It is responsible for the breakdown of carbohydrates to glucose, without which the normal functioning of the brain is impossible. Neurons cannot use any other nutrients as a source of nutrition, except for glucose. It is to maintain their normal functioning that up to half of the sugars involved in metabolism are spent. However, carbohydrates can become a source of energy for cells only if they have undergone the process of phosphorylation. Without thiamine, the attachment of phosphate residues to glucose is impossible.
Vitamin B1 neutralizes metabolic products, namely lactic and pyruvic acid. Their excess leads to rapid fatigue, decreased energy, loss of strength. Cocarboxylase converts acids into glucose, which acts as an “accumulator” for the body.
Vitamin B1 is a source of good mood, excellent appetite and energy boost.
Good for the liver and gallbladder. The biological role of vitamin B1 is to maintain the normal metabolism of amino acids. He takes part in the formation of fatty acids that can protect the hepatobiliary system from stones.
Necessary for the proper functioning of the nervous system. The main role in protecting the shell of neurons from destruction belongs to choline. In addition, this substance is responsible for lowering LDL levels. Choline is present in the formula of acetylcholine, which is responsible for signal transmission from the brain to the muscles. Acetylcholine prevents the destruction of neurons, maintains human cognitive abilities at the proper level.
The mechanism of action of vitamin B1 is such that it does not allow choline to be broken down. Moreover, without it, the normal production of acetylcholine is impossible.
Thiamine is involved in the control of the action of serotonin (the hormone of joy) and gamma-aminobutyric acid (a substance responsible for the functioning of the brain).
Good for digestion. Thiamine is prescribed to patients with stomach ulcers and other diseases of the digestive system. It helps to control the acidity of gastric juice, normalizes the contractility of the digestive tract.
Against skin diseases. Vitamin B1 has the ability to stop inflammation in various layers of the dermis, so it is used in the treatment of burns, wounds, psoriasis, eczema, lichen and neurodermatitis. Vitamin B1 is no less useful for mucous membranes. It is necessary for the skin, as it contributes to the production of substances that help fight infection, bacteria, as well as substances that enter the bloodstream during insect bites.
Essential for DNA. He is directly involved in the transfer of genetic material in the process of cell division.
Essential for pregnant and lactating women. Vitamin B1 is needed for the proper development of the fetus and newborn child, as well as for the normal functioning of the female body.
Relieves pain. Thiamine helps reduce the intensity of toothache. It is used as a remedy for motion sickness in land, air and water transport.
Participates in hematopoiesis. Without this vitamin, the normal production of blood cells is impossible. Its lack in the body can cause anemia.
Antioxidant. Vitamin B1 acts as an antioxidant, preventing cells from aging and dying.
Physicochemical characteristics
Vitamin B1 is a substance with high biological activity. It is represented by a water-soluble crystalline powder with a yeasty odor. When heated, some of the beneficial properties of vitamin B1 disappear.
Chemical properties that vitamin B1 has:
It is soluble in water, but insoluble in fats and alcohol. The synthetic analogue of thiamine, binfotiamine, dissolves in fats.
Vitamin B1 cannot be produced in the human body in sufficient quantities, so it must come from outside.
Thiamine is absorbed in the intestine. The body absorbs 2-5 mg of vitamin B1 for knocking (no more than 15 mg). In diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, this indicator decreases.
The coenzyme of vitamin B1 is cocarboxylase. From the intestine, the thiamine molecule enters the liver, where it combines with phosphoric acid molecules and, due to the influence of magnesium, is transformed into the coenzyme thiamine diphosphate. In this form, it goes to the organs and tissues. Due to its high activity, the coenzyme is absorbed better than thiamine.
Muscles contain 50-60% of vitamin B1. Its remaining part is distributed among the internal organs. It is present in the brain, liver, heart, kidneys, adrenal glands.
It occurs in the body in 4 forms:
Thiamine is not phosphorylated.
Thiamine monophosphate.
Thiamine diphosphate (thiamine pyrophosphate – cocarboxylase, TPP, TDP). This form is more active than the others.
TTF thiamine triphosphate.
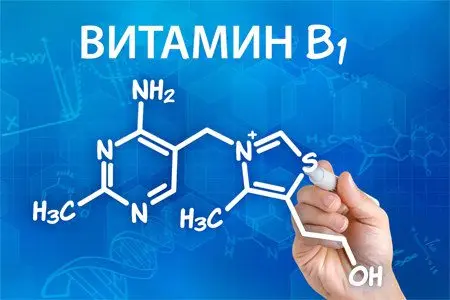
The chemical formula of vitamin B1 is C12H17N4OS.
Lack of vitamin B1 in food leads to diseases

Vitamin B1 deficiency in food leads to the following health problems:
Decreased appetite, anorexia. Vitamin B1 is necessary for the brain, in particular, the hypothalamus, in which the center responsible for saturation is located. In studies with rodents, it was found that the lack of foods in their diet – sources of vitamin B1, leads to a decrease in the amount of food they consume by 69-74%. However, after bringing the level of thiamine in the body of rats to the initial level, the appetite returned to normal. [1, 2]
Increased fatigue.
Irritability.
Decreased knee jerk, deterioration of the innervation of the triceps and ankles. With the progression of vitamin B1 deficiency, a person may lose the ability to move normally.
Paresthesia, manifested in the form of a burning sensation, tingling and crawling. In studies with rodents, it was found that a lack of vitamin B1 leads to damage to the peripheral nerves. [3, 4]
Chronic muscle weakness.
Visual impairment up to the development of edema of the optic nerve, neuropathy and even blindness.
Nausea and vomiting.
Slow heart rate. This has been proven in a number of animal studies. [5, 6]
Shortness of breath caused by heart problems.
Impairment of consciousness, memory loss, byrd, hallucinations. These symptoms are characteristic of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, which develops against the background of alcoholism and vitamin B1 deficiency.
[Video] Dr. Berg – Vitamin B1 deficiency: what is it for?









