Contents


Vitamin A or retinol refers to the substances necessary for the human body to maintain normal life. It enhances defenses, improves the ability of the immune system to resist viral, bacterial, fungal flora and allergen attacks. Acting as an antioxidant, vitamin A prevents the harmful effects of toxins on the body. Its lack threatens the development of iron deficiency anemia, since it is directly involved in the synthesis of blood cells.
Without vitamin A, the normal functioning of the nervous system is impossible, its lack leads to chronic fatigue syndrome.
Vitamin A comes in 4 forms:
Retinol acetate or retinol (A1).
Dehydroretinol (A2).
Retinal is the active form of A1.
Retinoic acid.
The single name for all of these forms of vitamin A is retinol. In this form, it is present in animal products. The human body does not have to expend effort on the absorption of retinol, it is absorbed very quickly in the gastrointestinal tract.
In plant foods, the vitamin is usually found in the form of carotene (provitamin A). In the intestines, it is transformed into retinol and only after that it is absorbed into the blood.
What foods contain vitamin A?
The liver contains a large amount of vitamin A. Depending on the animal, the amount of retinol in it varies greatly, but it is always present in large excess. But the main source of vitamin A for humans is not only fish oil, liver and carrots, but also kefir, whole milk (330 micrograms per liter), eggs, sour cream, greens.
 30 mcg
30 mcg Duck 11 mcg Turkey 984 mcg Beef 10 mcg Goose 751 mcg Pork 9 mcg Chicken 442 mcg
Duck 11 mcg Turkey 984 mcg Beef 10 mcg Goose 751 mcg Pork 9 mcg Chicken 442 mcg 4 mcg
4 mcg 1 mcg
1 mcg 1 mcg
1 mcg 840 μg
840 μg 835 μg
835 μg 709 μg
709 μg 500 μg
500 μg 469 μg
469 μg 426 μg
426 μg 421 μg
421 μg ~200-400 mcg
~200-400 mcg 386 μg
386 μg 381 μg
381 μg 180 μg
180 μg 171 μg
171 μg 157 μg
157 μg 90 μg
90 μgView the entire table of animal products 130+ ➤
View the entire table of herbal products 200+ ➤
Vegetables-record holders for the content of vitamin A
Rating | Vegetables (100 g) | Vitamin A, mcg | Beta-carotene, mcg | Alpha-carotene, mcg |
1 | Carrots | 835 | 8 285 | 3 477 |
2 | Sweet potato | 709 | 8 509 | 7 |
3 | Cabbage kale | 500 | 5 927 | 54 |
4 | Pumpkin | 426 | 3 100 | 4 016 |
5 | Bulgarian red pepper | 157 | 1 624 | 20 |
6 | Broccoli (pickled) | 77 | 929 | 0 |
7 | Red cabbage | 56 | 670 | 0 |
8 | squash | 56 | 670 | 0 |
9 | Tomatoes | 42 | 449 | 101 |
10 | Green beans | 32 | 380 | 0 |
Fruits-record holders for the content of vitamin A
Rating | Fruit (100 g) | Vitamin A, mcg | Beta-carotene, mcg |
1 | Mushmula | 76 | 0 |
2 | Cherry | 64 | 770 |
3 | Passion fruit | 64 | 743 |
4 | grapefruit | 58 | 686 |
5 | Mango | 54 | 640 |
6 | Fizalis | 36 | 0 |
7 | Tangerines | 34 | 155 |
8 | Guava | 31 | 374 |
9 | Watermelon | 28 | 303 |
10 | Plum | 17 | 190 |
The record holder for the content of beta-carotene is red palm oil, containing 52 mcg, that is, as much as 500 mg of provitamin A in 2,6 teaspoon. Even with 1/1 RAE absorption, you get 2 mcg of retinol, which is more than enough.
Daily Value of Vitamin A for Women, Men and Children
The daily amount of vitamin A recommended by scientists is calculated based on the fact that the body not only covers its daily needs, but can also ensure its replenishment in the depot for several months in advance. Only under the condition of a sufficient amount of retinol in the liver, the normal functioning of the immune and reproductive systems, the organs of vision, and even the activity of genes is possible.
Below in the table is information about the daily requirement for retinol. For your convenience, the figures are presented in mcg, ME, IU. In addition, the upper limit of consumption is given, when vitamin A becomes toxic.
Categories of people | Daily requirement, mcg | ME/IU | Excess, mcg |
0-6 months | 400 | 1333 | 600 |
7-12 months | 500 | 1667 | 600 |
1-3 years | 300 | 1000 | 600 |
4-8 years | 400 | 1333 | 900 |
9-13 years | 600 | 2000 | 1700 |
Men from 14 years old | 900 | 3000 | 3000 |
Women from 14 years old | 700 | 2333 | 2800 |
Pregnancy | 770 | 2566 | 3000 |
Lactation | 1300 | 4333 | 3000 |
Daily doses recommended by the German Nutrition Society (DGE) and other European nutrition committees.
1 mcg = 1 mcg RE = 3,333 IU = 3,333 IU = 12 mcg beta-carotene (without fat) = 2 mcg beta-carotene (in fat)
Keep the table for yourself, and always be guided by these data when buying vitamins.
Reasons for increasing the body’s need for vitamin A:
Body weight gain.
Hard physical work.
The need to work at night.
Sports at a professional level.
Emotional turmoil.
Sunlight deficiency.
The load on the organs of vision, for example, when working at a computer.
Pregnancy and lactation.
Diseases of the digestive system.
Viral infections.
Metabolism in the body
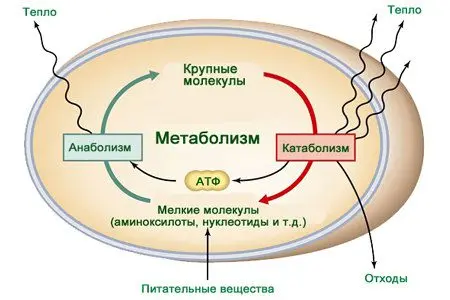
Regardless of the form, retinol is absorbed by 50-90% of the total. Once in the systemic circulation, its molecules bind to blood proteins and reach the liver. It is this organ that acts as a depot for the vitamin. If too little of it comes from the outside, then the liver blocks the needs of the body. Its reserves are impressive, they are enough for about a year. From the liver with the bloodstream, vitamin A enters various organs. Their cells have receptors that capture retinol molecules, deliver them inside, where they are consumed.
Vitamin A enters the body from the liver on a regular basis, due to which its stable level of 0,7 µmol / l is maintained in the blood. Once in the gastrointestinal tract, it is first sent to the depot to replenish depleted reserves, and unused retinol circulates in the systemic circulation.
In the cells of the internal organs, vitamin A is found in the form of retinal and retinoic acid. Therefore, in the blood, these two forms are determined in an amount of not more than 0,35 µmol / l. With a decrease in their content in various biological structures, they lose their ability to perform life-supporting functions, which is why a person develops various diseases.
In order for the body to better absorb vitamin A, it must be supplied together with zinc and vitamin E.
How to improve the absorption of vitamin A?
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble substance, so you need to consume it with oily or fat-containing foods. To a greater extent, this applies to carotene from plant foods. In order for carrots, dill or parsley to become a source of provitamin A, a salad with them must be seasoned with oil. You can enhance the effect by regular walks in the sun.
The best vitamin A supplement is vitamin E (tocopherol). In this combination, it is absorbed much faster, but the dose must be controlled.
It is also often prescribed in conjunction with vitamin C. This combination improves iron absorption, which is very important in the fight against anemia.
Antioxidant vitamin-mineral complexes containing vitamin A have been developed. Selenium, ascorbic acid, tocopherol, zinc, and iron are often found in their composition. Such drugs are prescribed by doctors to correct deficient conditions, as well as for various diseases.
In the course of scientific research, it was found that the activity of carotenoids is 2 times lower than previously thought. In this regard, the US Institute of Medicine in 2001 proposed a new unit as the equivalent of retinol activity – RAE. As a result, the following values were obtained:
1 mcg of retinol = 1 RAE.
2 micrograms of beta-carotene dissolved in fat = 1 RAE.
12 micrograms of beta-carotene from food = 1 RAE.
24 micrograms of other multivitamins A = 1 RAE.
In order for vegetables to give the body the maximum amount of vitamin A they contain, it is recommended to fry them in a pan with a small amount of oil for 2-3 minutes. Fiber softens and it is easier for the intestines to “extract” useful substances from it. Other heat treatment acts similarly on products.
Meat is best steamed or grilled. So it will retain more vitamin A.
Functions and biological role of vitamin A in the human body

The value of vitamin A for the human body:
Regulation of the synthesis of steroid hormones and proteins.
Activation of spermatogenesis.
Antitumor activity.
Normalization of metabolism.
Formation of lipids and bone tissue.
Improving skin condition, accelerating cell regeneration.
Improving the quality of nails and hair. Vitamin A makes them stronger, enhances their ability to withstand destructive factors.
Neutralization of free radicals.
Strengthening the immune system.
Help the body fight infectious diseases.
Promotes proper growth and development of the embryo.
Improving the function of twilight vision by stimulating the formation of rhodopsin.
Prevention of inflammatory diseases of the cornea.
[Video] Briefly about the main functions of vitamin A and its role in the human body:
Contraindications and cautions

Consuming excess amounts of vitamin A can be hazardous to health. With a balanced diet, the daily dose is easy to dial without the use of specific additives, from ordinary products. For adults, the upper daily limit is 3000 micrograms (10 IU). Very high doses can cause severe poisoning and even death.
Symptoms of overdose:
Deterioration of visual function.
Joint pain, bone pain.
Lack of desire to eat.
Nausea and vomiting.
Photosensitization.
Baldness.
Headache.
Dryness of the skin.
Lesion of the liver.
Yellowing of the skin.
Retarded growth.
Dizziness.
Itching itch.
Too much vitamin A is dangerous during pregnancy. Overdose carries a risk to the health of the mother and fetus. There is evidence that vitamin A hypervitaminosis increases the risk of lung cancer in smokers. Therefore, you need to take retinol supplements carefully, strictly observing the dosage.
Signs of severe vitamin A deficiency
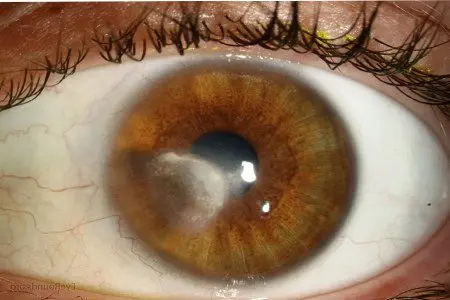
Vitamin A deficiency develops if a person consumes few foods containing this substance. The situation is aggravated by alcoholism and malabsorption. You can understand that the body is experiencing a lack of vitamin A by the following signs:
Chicken blindness. This is the first signal of existing hypovitaminosis.
Corneal ulcers. With severe vitamin A deficiency, vision can be completely lost.
Immunodeficiency.
Frequent respiratory infections. Among children with beriberi, there is a higher mortality from measles.
Diarrhea.
Violation of the growth and formation of bones.
COPD, emphysema. Obstruction most often develops in smokers.
Signs of too much vitamin A

Symptoms of acute vitamin A hypervitaminosis:
Nausea.
Headache.
Decreased performance.
Loss of appetite.
Dizziness.
Dryness of the skin.
Edema of the brain.
Chronic hypervitaminosis of vitamin A can cause the development of osteoporosis, as well as birth defects in the fetus. In this regard, retinol derivatives are especially dangerous, so it is better for pregnant women to prescribe beta-carotene.
For a long time, people with an increased risk of lung cancer, smokers, and people whose body is exposed to asbestos should not take vitamin A supplements.
Interaction with other medicinal products
With a lack of vitamin E, vitamin A in the body is quickly destroyed. It is also not deposited in the depot if there is a deficiency of choline.
Antibacterial drugs reduce its effectiveness. However, vitamin A itself enhances the side effects of isotretinoin treatment when taken together.









