Every year, several tens of millions of cases of infection with viral hepatitis E are recorded, of which more than 50 are fatal. The disease is widespread throughout the world, but the greatest risk of infection is noted in areas with a lack of clean drinking water. This problem is observed in African, Asian countries and Latin America.
Hepatitis E outbreaks often occur in conflict zones and other public emergencies. The spread of the virus is facilitated by poor sanitary and hygienic conditions, lack of clean water, and poor medical care.
Men between the ages of 20 and 40 are most susceptible to contracting hepatitis E. Women and children are much less likely to get sick. In the course of the research, the dependence of outbreaks of infection on the time of year was revealed. In southeast Asia, the disease is common during the rainy season, and in the central regions of this region, infection with hepatitis E occurs more often in the fall.
Causes of Hepatitis E
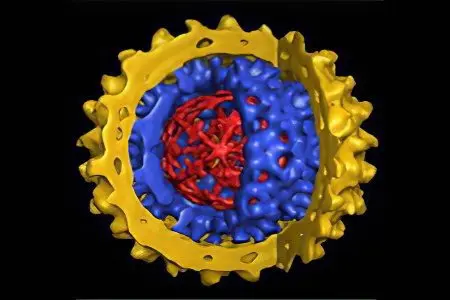
The causative agent of hepatitis E is a spherical-shaped virus, the genome of which is a single-stranded coding RNA. You can deal with it with the help of chlorine-containing disinfectants. After all, compared with the hepatitis A virus, this pathogen is less stable.
Main mode of transmission of hepatitis E virus – through unboiled contaminated water. This is how the infection spreads in Russia. It is also possible to transmit it by contact-household means, for example, through the use of the same dishes by a healthy person after a sick person. Hepatitis E is a zoonotic infection, since it is animals that contribute to the circulation of the virus in the environment. It has been found in the blood of wild boars, pigs and some bird species. For this reason, workers of livestock farms who are engaged in the primary processing of carcasses are largely susceptible to infection with hepatitis E.
Hepatitis E is not transmitted sexually, unlike some other similar infections.. It is also difficult to get infected by contact. However, the virus can be passed from mother to child in late pregnancy. In some cases, infection may occur through blood transfusion. To avoid hepatitis E, it is not recommended to eat raw shellfish, low-quality meat and raw tap water.
Symptoms of Hepatitis E
The symptoms of hepatitis E and the course of the disease are in many ways similar to hepatitis A. The development of infection in the body leads to damage to hepatocytes, impaired liver function and intoxication. The duration of the incubation period for hepatitis E ranges from several days to one and a half months. In the preicteric period, which takes about a week, the patient feels unwell, there is a general weakness of the body, nausea, turning into vomiting. A characteristic symptom, by which hepatitis E is often determined, is severe pain in the right hypochondrium. In some cases, patients have a slight fever.
During the icteric period, transaminase activity increases, the urine acquires a rich dark shade. The skin, like the sclera, is covered with characteristic yellow spots. Since hepatitis E mainly affects the liver, during the icteric period this organ increases significantly in size. At the same time, all the symptoms of the preicteric period remain: weakness, nausea, general malaise.
Heavy form hepatitis E is accompanied by hemoglobinuria (the appearance of hemoglobin in the urine). This complication is especially dangerous for pregnant women in the later stages. The development of hepatic encephalopathy can lead to the death of the patient. However, such cases are rare. Most often, the disease passes in a mild form, and with timely medical care, a full recovery occurs soon enough.
Diagnosis of hepatitis E
To determine the presence of hepatitis E in a patient allows a special type of analysis – polymerase chain reaction. During it, an antigen is detected in the biological material.
The greatest difficulty is the differential diagnosis. Hepatitis E is in many ways similar to other varieties of this disease. Therefore, doctors usually take into account not only external symptoms and test results, but also the possibility of the virus entering the body. For example, during the patient’s stay in dangerous areas such as the tropics or Asian countries. Marker diagnostics is used for suspected hepatitis E in pregnant women. Among this group of patients, the number of deaths is maximum, so it is very important to quickly and accurately determine the presence of the disease.
Hepatitis E treatment
Patients with severe hepatitis E, pregnant women are subject to immediate hospitalization. With mild to moderate severity of the disease, bed rest and diet can be dispensed with. In most cases, this is enough for recovery.
Fried, smoked foods, pickles and alcohol should be excluded from the diet. The body must receive a sufficient amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. The patient should drink a sufficient amount of liquid daily: pure water, tea, natural juice, compote.
Low-fat varieties of meat, fish, carbohydrates – honey, jam, white bread, oatmeal, pasta from durum wheat can act as a source of animal protein.
For moderate hepatitis E, drugs such as ursodeoxycholic acid, enterosorbents, fat-soluble vitamins E and A are used. Intravenous injections of glucose help to cope with nausea and vomiting.
If there is a severe form of hepatitis E, then intensive therapy is required. In this case, treatment involves the fight against hepatic encephalopathy and thrombohemorrhagic syndrome. The detection of hepatitis E during pregnancy is not a reason for its termination, but it is necessary to minimize the time of delivery and provide sufficient pain relief.
There is no vaccine against this disease yet, so the only possible way of prevention is to comply with hygienic and sanitary standards.









