Contents
Gourds are loved by adults and children for their sweet, rich taste. Reviews of the Vietnamese melon The gift of Ho Chi Minh’s grandfather is positive, but sometimes gardeners are upset by poor yields associated with improper care. Growing fruits, watering, feeding, shaping are described in the article.
Description of Vietnamese melon Gift from grandfather Ho Chi Minh
The plant belongs to the Cucurbitaceae family, and Vietnam is indeed the birthplace of the variety. Initially, the culture was widespread in Central Asia, Asia Minor, then spread to other regions. Vietnamese melon variety Gift of Ho Chi Minh Grandpa is an early maturing variety for cultivation in open ground and greenhouse conditions.
Long and abundant fruiting allows you to get from each bush up to 30 medium-sized specimens of an oval, occasionally rounded shape, each weighing 100 – 200 g. called pineapple. Ripe fruits are dark orange or brown in color with light yellow stripes evenly scattered throughout the peel.
The appearance of the fruit can be estimated from the photo of the Vietnamese melon:

Pros and cons of the variety
Among the shortcomings, only the size of the fruit is distinguished. The advantages of the Vietnamese melon Gift from grandfather Ho Chi Minh City are more:
- ease of care: all processes are well known to gardeners;
- high taste qualities;
- decorative appearance;
- good yield;
- short growing season;
- resistance to temperature extremes;
- immunity to many diseases.
How to grow Vietnamese melon
A small-fruited sugar plant loves well-lit places. If you choose the right landing site, the yield will increase significantly even with temperature changes. This is also facilitated by self-pollination of female flowers of the Vietnamese melon Gift from grandfather Ho Chi Minh City. For this, a male flower is plucked, the petals are torn off, and dust particles are leaned against the pestle.
To prevent the fruits from rotting, boards, pieces of plastic or other objects are placed under them that will prevent pouring melons from touching the soil surface. Further touching the fruit is not recommended to avoid damage. Grown in a greenhouse, Vietnamese melon Gift from Ho Chi Minh’s grandfather will be the same as in the open field.
Seed preparation
One-year seed is not recommended to choose – it will give few female flowers, which will affect the number of ovaries, yield. Three-year-old seeds are the most suitable – they are sorted, the largest are selected. For a good harvest, gardeners recommend treating the seed with microelements.

In regions with a cold climate, it is not recommended to plant non-hardened Vietnamese milk melon seeds. To acquire resistance to temperature extremes, they must be placed in a bright, cool place for 2 to 3 days before soaking. Seeds of the Gift of Grandpa Ho Chi Minh variety are poured with a weak solution of potassium permanganate to protect against pests, swell, and also identify bad specimens. In the liquid, the seed should stay for at least a day.
Preparation of seedlings
Vietnamese melon Grandpa Ho Chi Minh’s Gift, like any other variety of this plant, does not respond well to transplants, so it is recommended to germinate the seeds in peat pots: such containers can be planted in the ground along with seedlings.
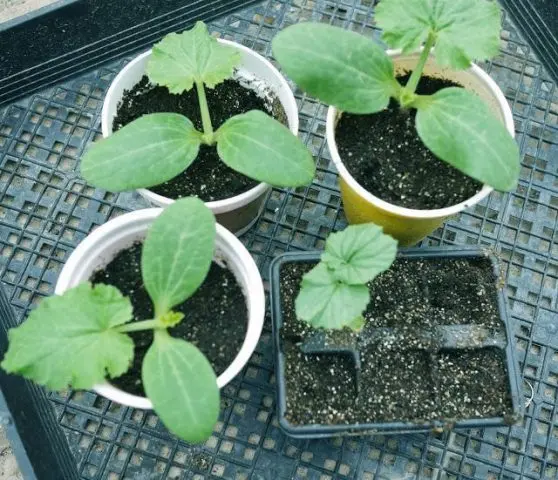

In the soil mixture, holes are made 2–4 cm deep, into which 2–3 seeds are placed. Until the sprouts of the Vietnamese melon appear Gift of the grandfather of Ho Chi Minh, it is recommended to maintain the temperature in the room within 23 – 25 oC. As soon as the first two leaves open, reduce to 20 oC to prevent seedlings from pulling out. Therefore, growing Vietnamese melons at home is difficult.
Feed the variety with complex fertilizers at the time the first leaf appears and repeat after 14 days. This will allow the seedlings of the Vietnamese melon Gift of the grandfather of Ho Chi Minh City to gain strength. When the 3rd leaf appears, pinching will be required to allow the side shoots to emerge.
Selection and preparation of the landing site
Sandy, loamy soil is great for growing melon Gift from Ho Chi Minh City’s grandfather, but the variety is undemanding to the composition of the soil, so it can grow anywhere. The quality of the autumn preparation of the land directly affects the yield – it must be dug up and fertilized with manure. The plant prefers well-lit places without drafts.
Rules of landing
When the 4th full-fledged leaf appeared on the seedlings of the Vietnamese melon, it is ready for planting. Holes for planting material are dug at a distance of 70 cm from each other and with the same spacing between rows. In greenhouses, you can plant thicker – 50×50 cm.
A weak solution of potassium permanganate is poured into each well for disinfection, then a peat pot is placed there. Sprinkle with earth carefully so that the root neck remains above the surface. Scatter rotted manure around the holes, you can do mulching.
Watering and top dressing
To increase the yield of the variety, the fertilizer application regimen should be observed. 14 days after planting in open ground, Vietnamese melon sprouts The gift of Ho Chi Minh’s grandfather should be fed with nitrogen-containing fertilizers – it can be diluted mullein, saltpeter.
The second time fertilizers are applied at the moment the ovaries reach the size of a walnut: the same solutions can be used. Further feeding of the Vietnamese melon is carried out regularly at intervals of two weeks. Nitrogen and potash fertilizers are applied during the flowering period of the Gift of Grandpa Ho Chi Minh variety. Phosphorus, ammonia supplements are needed when the ovaries are formed.
The Vietnamese melon A gift from Grandpa Ho Chi Minh City is watered with warm water under the root in the morning, avoiding its contact with the leaves, so that the soil has time to warm up by evening. Irrigation during fruit pouring should be regular. To improve the palatability of melons Gift of Grandpa Ho Chi Minh City, watering is stopped 20 days before full ripening. The plant does not respond well to high humidity, so spraying is not required.
Formation
This is an important technique for improving fruiting. The main thing for the Gift of Grandpa Ho Chi Minh variety is to pinch the plant in time and correctly, which will also affect the taste of the melon.
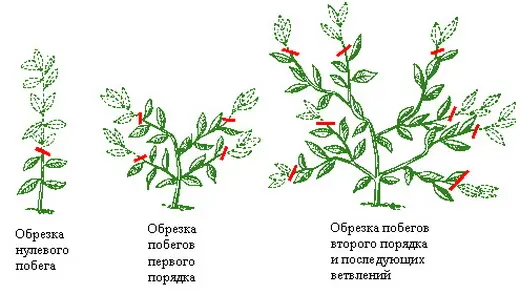
- When the 5th sheet appears, pinch over the third. On the main stem, only barren flowers are formed – male flowers, so it is shortened.
- After the first reception, 3 lashes of the second order begin to form. The lower process is removed, the remaining two are pinched after 6 leaves.
- Leaving 2 – 3 ovaries, pinch the apical shoot: you get 6 lashes.
- After 14 – 16 days, the growing point is removed to speed up the formation of melons.
Harvesting
Until the Vietnamese melon is fully ripe, it is not recommended to touch it with your hands. Even a slight mechanical damage to the peel will inevitably lead to rotting of the entire fruit. Ripeness is determined by the color, which turns bright orange, and also by the tail: it must dry out.
Diseases and pests
Vietnamese melon Ho Chi Minh Grandpa’s gift damage:
- melon aphid;
- wireworm;
- nibbling owls;
- spider mite;
- melon fly.
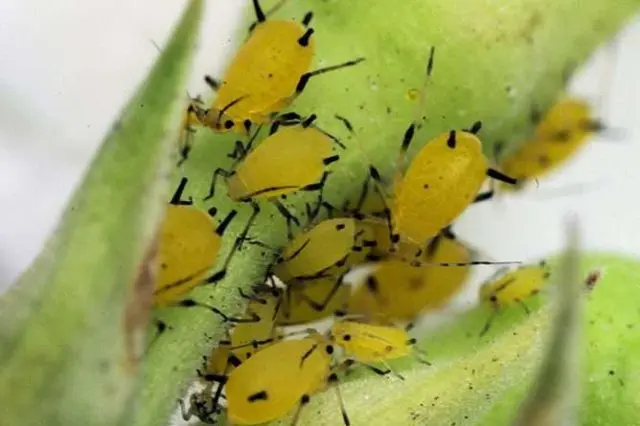
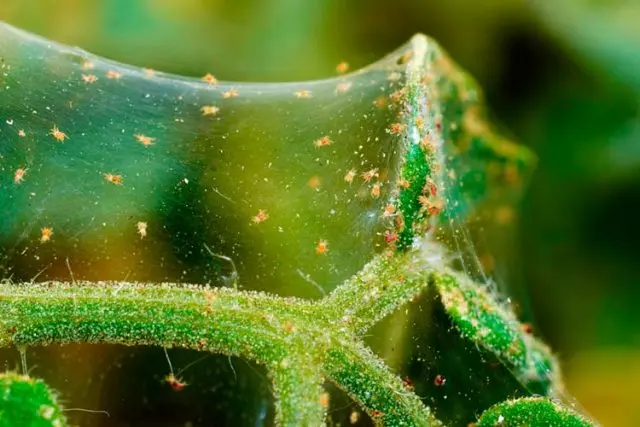
Melon Caviar feeds on plant sap, multiplies rapidly. Occurs on the stem, lower part of the leaf. The result of the appearance of aphids will be yellowing of leaves, flowers, their shedding. You can fight the pest by regularly weeding weeds, treating plants with 10% karbosof, and also with soapy water: 10-12 g of soap is mixed in 10 liters of water.

spider mite weaves thin cobwebs that can be found in the axils of the leaves. They live under leaves and feed on sap. To combat the pest, they observe the correct crop rotation, weed regularly, and in the fall they dig the soil well.

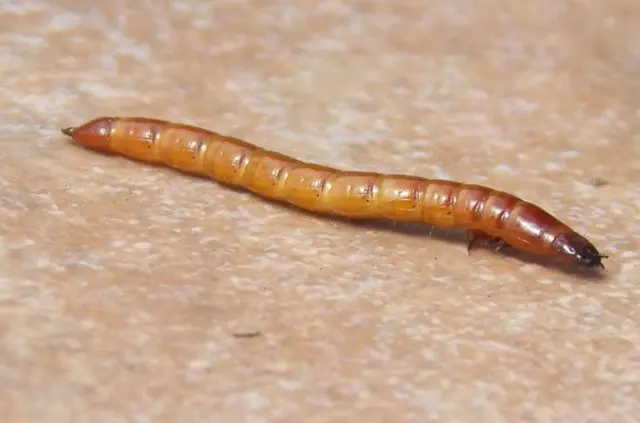
Wireworm – a small yellow worm. It gnaws at the stems, causing the entire plant Ho Chi Minh Grandfather’s Gift to wither. It is necessary to fight such a pest with regular weeding, loosening, cleaning the remnants of weeds from the site.

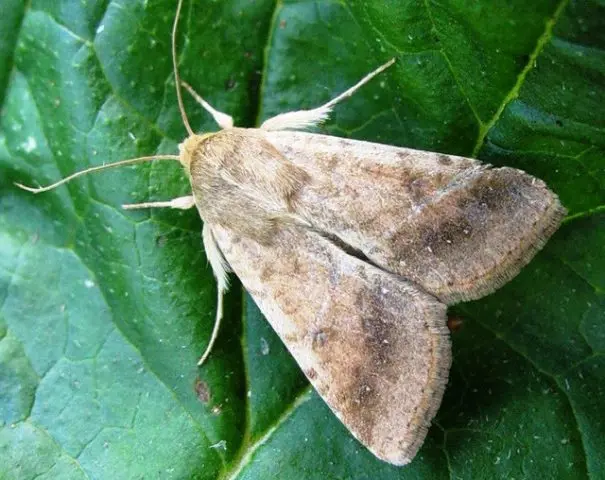
Gnawing scoops live in the ground or on its surface. They feed on plant sap, damage the stem. To prevent it, it is necessary to observe the correct crop rotation, in the fall it is good to dig up the soil, weed regularly.

melon fly pierces the peel of the fruit, lays the larvae inside, which leads to decay. To combat the pest, chemical agents are used – solutions of “Rapier”, “Kemifos”. They are diluted at the rate of 10 ml for every 10 liters of water.

Vietnamese melon Gift of Grandpa Ho Chi Minh is resistant to most diseases, due to the short vegetative period. It can only be damaged by:
- downy mildew;
- powdery mildew;
- fusarium wilt;
- anthracnose;
- root rot.
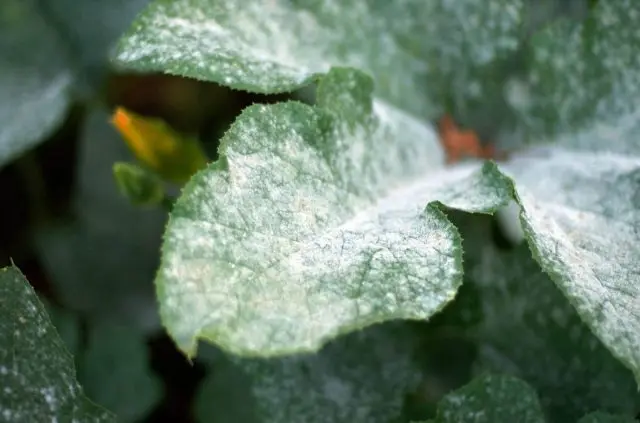
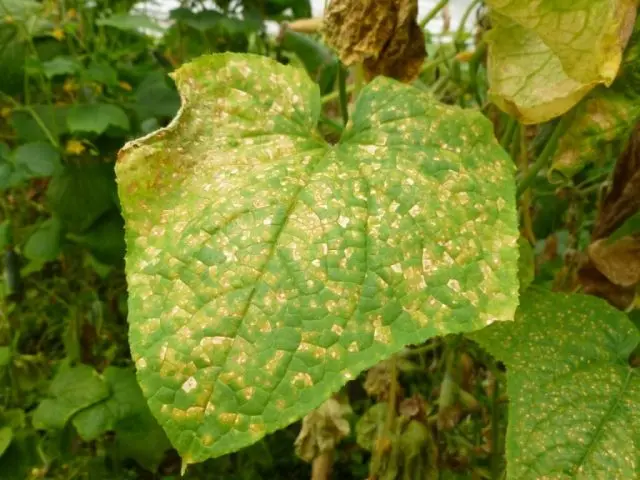
Mučnistaâ rosa forms a whitish bloom on the green part of the plant. At first small, the spots soon grow, which leads to gradual wilting, drying out of the leaves. To combat the disease, it is necessary to remove the affected areas, treat healthy plants with colloidal sulfur – 50g per 10l.

Fusarium wilt affects sprouts, occasionally adult plants, is manifested by a change in the color of the leaves. Plants die after 10 days, so the fight against the disease must begin immediately. The affected sprouts are burned, the rest are treated with a solution of potassium chloride.
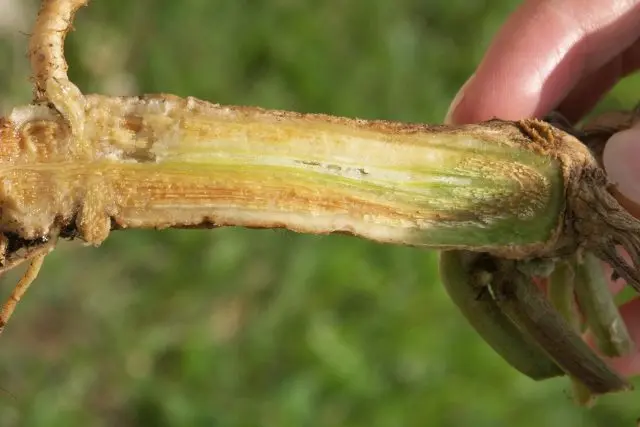

Antraknoz manifested by pink, gradually growing spots. The disease can affect fruits. To eliminate the disease, it is necessary to loosen the soil, treat the plants with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture.
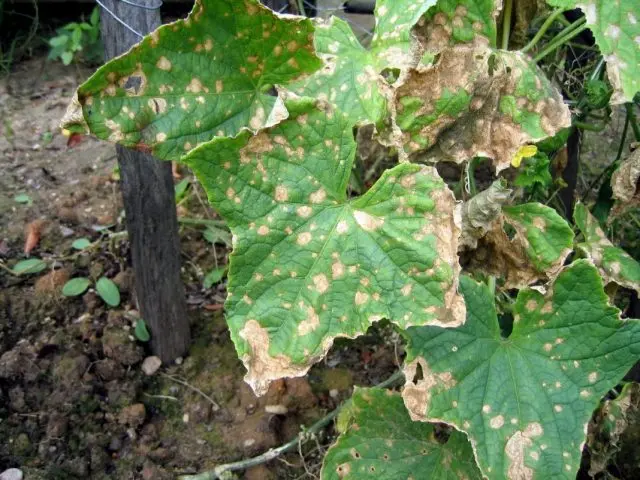

Peronosporosis, or downy mildew, forms yellowish spots. The heating of the seeds in warm water will be protected by treatment with a solution of potassium permanganate. To combat the disease, it is necessary to remove the affected plants, treat the rest with urea: 1 g per 1 liter every 10 days.

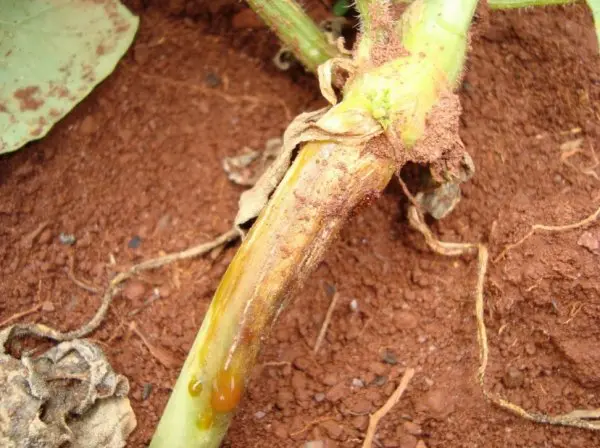
When root rot appeared, it’s too late to save the plant. For prevention, it is necessary to pickle the seeds before planting in a 40% formalin solution. Timely loosening, proper watering, and removal of weak plants will also help.

Vietnamese milk melon reviews
Conclusion
Reviews of the Vietnamese melon A gift from Ho Chi Minh’s grandfather say that the variety is really early, high-yielding. The first fruits can be enjoyed already in July. Caution should be observed in patients with diabetes mellitus, nursing mothers. You should not eat melon with dairy products or alcohol – this will lead to indigestion.









