Contents
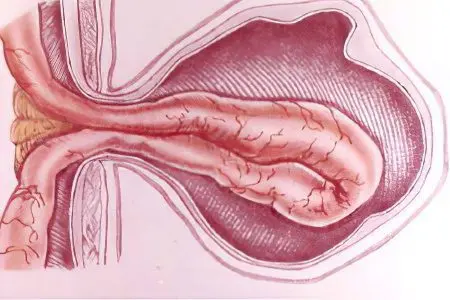
Ventral hernia – This is a postoperative defect in the muscles and tendons of the abdominal wall. It is formed in the area of the scar that remains after surgery. This type of protrusion refers to post-traumatic.
As for the statistics, ventral hernia is formed in 11-19% of patients who underwent surgery. 50% of patients find a protrusion already in the first year after the intervention. In the remaining 50%, a hernia appears within a five-year period after surgery. It happens that the protrusion appears after surgery to remove the hernia. In this case, we are talking about recurrent ventral hernia. The risk of its occurrence is higher if the operation was unplanned and carried out urgently.
The functions of the anterior wall of the peritoneum are diverse, it has several layers. The protrusion appears in the most durable, but not elastic layer – in the muscle-tendon.
The ventral type of protrusion, like other hernias, has a gate, a bag and the contents of the bag. Most often they are formed after surgical interventions to get rid of uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, intestinal obstruction, stomach ulcers, appendicitis, cholecystitis, umbilical hernia and some others.
Causes of ventral hernia
The fact of heredity. Systemic dysplasia or impaired development of connective tissue is a genetically determined pathology that can lead to the formation of a hernia. If the patient who has undergone surgery has a congenital weakness of the connective tissue, tendons and ligaments, then the risk of forming a ventral protrusion increases significantly. The fact that the patient has hereditary dysplasia can be indirectly indicated by thin skin, on which stretch marks are easily formed, high growth, hernias in other areas, increased joint mobility and asthenic body type. If a patient has two or more signs indicating dysplasia, then hernia treatment will be effective only with the imposition of a synthetic prosthesis.
Non-compliance with the regimen prescribed to the patient after surgery. Failure to comply with medical recommendations leads to the formation of a hernia. It must be understood that the postoperative suture is not only an external defect. The healing of a skin wound does not mean a complete recovery and the ability to start full-fledged physical labor. The tendon plate (aponeurotic part of the wound), which is responsible for the integrity of the peritoneal wall, will be fused for the longest time. If in young patients this period takes up to 4 months, then the elderly can wait for healing only after six months or more. If a person has concomitant diseases, then the process of complete scarring can take up to a year. That is why it is so important to follow all the recommendations of the surgeon, and, if necessary, wear a bandage.
Failure of the postoperative wound healing process. It happens that even under conditions of the strictest sterility, infection of the wound occurs. As a result, the process of suppuration starts, which affects the healing time and the formation of a full-fledged scar. As a result, it becomes not as strong as it should be. An infection that has entered the wound does not indicate the indispensable formation of a hernia, but significantly increases the risk of its formation. In some cases, there is an individual intolerance to the material used for suturing. As a result, its rejection occurs and the unfused edges diverge.
Presence of comorbidities. Any disease that provokes an increase in intra-abdominal pressure is capable of increasing the risk of protrusion formation. These are bronchitis, asthma, chronic constipation. In addition, excess weight, prostate adenoma and other diseases have an impact. As a result, the edges of the postoperative wound are constantly subjected to tension. Their blood circulation is disturbed, the supply of nerves – as a result, a loose scar is formed. In addition, normal blood supply can be affected by: atherosclerosis, hypertension, ischemia, diabetes mellitus.
Moreover, the risks increase even in the presence of one of these diseases. To reduce them, you should try to get rid of existing problems before the start of the operation. If the diseases are chronic, then it is necessary to wait for their stable remission.
Excess weight is dangerous in terms of hernia formation. If the protrusion has been operated on repeatedly, if it has an impressive size, then the body weight should be reduced and only after that surgical intervention should be performed.
Doctor’s mistake in terms of performing the suturing technique. This reason is the least common. However, sometimes the surgeon chooses an inappropriate technique and method of suturing the wound, sometimes too tightly or too weakly tightening its edges. As a result, a defect is formed.
Symptoms of a ventral hernia

A protrusion that forms in the area of the postoperative wound on the anterior wall of the peritoneum. It is localized along the line of the existing scar.
If a hernia has appeared recently, then it can be corrected, a person does not experience pain in the early stages.
Pain in the protrusion area appears as the pathology progresses. They can occur when lifting weights, when straining and making sudden movements.
If the hernia is not treated, the pain becomes constant, its character is cramping.
If a hernia is formed in the suprapubic region, then violations of the process of urination are possible.
Hyperemia of the skin, fever, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (nausea, vomiting, increased gas formation), the appearance of blood in the stool – these symptoms appear when the ventral protrusion is infringed or with the development of other complications.
Diagnosis of ventral hernia
Difficulties in terms of identifying pathology in diagnosticians do not arise. As a rule, a visual examination of the patient is sufficient to see the ventral hernia protrusion. The patient is asked to strain or cough to assess the true size of the hernia.
Ultrasound examination allows you to assess the size and shape of the protrusion, as well as the presence of adhesions.
Various variations of the X-ray examination allow us to evaluate the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, determine the presence of adhesions and the ratio of internal organs to the resulting protrusion.
To clarify the parameters important for the doctor, the patient is sometimes referred for MSCT or MRI. In some cases, a colonoscopy is performed.
Treatment of ventral hernia
Without surgical intervention, it will not be possible to get rid of the protrusion of the ventral hernia. It will require treatment and correction of the peritoneal wall with the removal of the resulting bag and subsequent plastic surgery.
Tension plastic
The protrusion is sutured with threads. It is possible to perform this procedure only in young patients, whose hernia size is small. In addition, the absence of comorbidities is important. The fact is that this method of intervention has a high percentage of relapses, which reaches 30%.
Of the advantages of the tension method:
ease of implementation from a technical point of view;
low price for materials and equipment used.
Of the disadvantages of the tension method:
risk of recurrence up to 30%;
respiratory dysfunction due to too much tension on the wound;
the occurrence of pain due to strong tension.
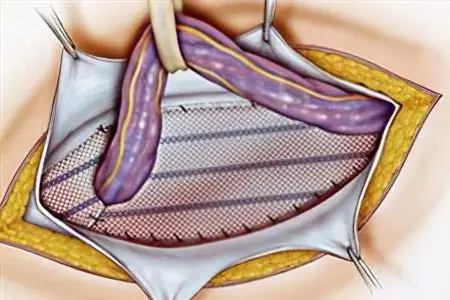
Tension-free hernioplasty
The place where there was a protrusion is closed with a synthetic prosthesis. It is made of polypropylene mesh and is inserted directly under the skin or along the fascia.
Of the advantages of this technique:
Low relapse rate.
The absence of pain after surgery or its slight severity.
No respiratory problems.
When the tension-free method is supplemented with abdominoplasty, it becomes possible to plastically restore the peritoneal wall even with a giant protrusion.
Of the minuses of the tension-free method:
High price category of the operation.
Increased risk of complications – seroma, hematoma, suppuration.
In theory – rejection of the implanted mesh, the appearance of a feeling of the presence of a foreign body.
If adhesions occur between the mesh and the intestine, intestinal obstruction may develop. (Read also: Causes and symptoms of intestinal obstruction)
Prosthetic hernioplasty using a laparoscope
This method of surgical intervention is the least traumatic and the most modern. A mesh implant is also inserted into the abdominal cavity, but this does not require incisions in the area of the hernia itself. As a result, there is no risk of suppuration.
Of the advantages of this method:
The abdominal cavity of the patient is practically not injured.
Pain is absent or minimal.
Extremely low relapse rate.
No wound complications.
A short recovery period and an early opportunity to return to work.
Of the disadvantages of the method:
The cost of the operation is extremely high.
The process of training surgeons is laborious and lengthy.
It is required to equip a medical institution with expensive equipment, which is not always possible.
Conclusions on the treatment of ventral hernia
It is possible to make a choice in favor of one or another method of surgical intervention only taking into account the recommendations of the attending doctor. To do this, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination with obtaining complete data on the patient’s condition.
In addition, the choice of technique is carried out taking into account the patient’s ability to endure general anesthesia.
As for conservative therapy, it is possible only if there are serious contraindications to the operation. In this case, the patient is recommended to adhere to a dietary diet, give up physical activity, prevent constipation and flatulence, and wear an individually selected bandage.
To avoid the risk of relapse or minimize it, the patient will need to strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations, adhere to proper nutrition, normalize weight and achieve regular bowel movements.









