Contents
Crop rotation of vegetable crops is the main rule for obtaining a rich harvest. It is he who allows you to use the soil without depletion, successfully resist diseases and pests in the garden.
What’s this
The optimally selected alternation of vegetable crops from year to year and their correct placement on the site next to each other is called vegetable rotation. Annual plants that occupied the garden bed last year largely determine this year’s harvest, it depends on them which plants should be planted, and which should not be planted in any case. For example, it is recommended to grow potatoes after cucumbers and cabbage, it is possible even after beets and carrots, but after tomatoes, peppers, eggplants it is strictly forbidden.
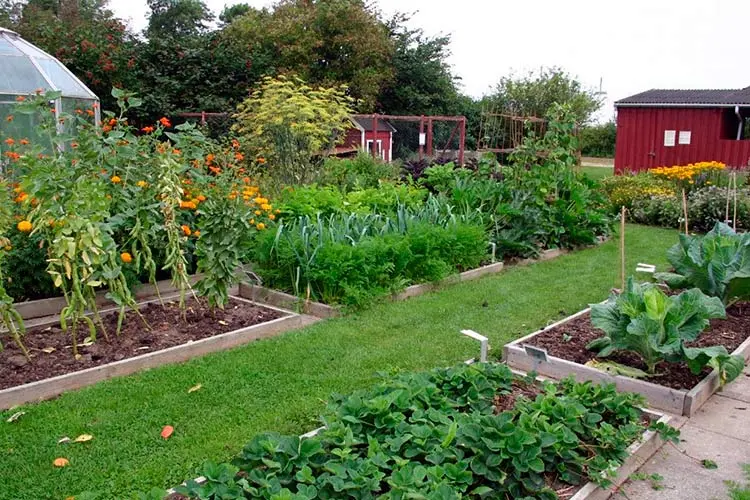

Tomatoes should be planted after cucumbers, carrots, cauliflower, and certainly not after potatoes. Plants belonging to the same family can be grown in the same place no less than 3-4 years later, some experts insist: the period should be 5 years. Therefore, crop rotation is planned for several years at once, and it is necessary to take into account not only the plants that grew there, but also soil fertilizer, as well as crops that will grow nearby.
It is necessary to take into account the influence that vegetables have on each other. So carrots will not grow well next to cabbages – the roots of cabbage secrete substances that inhibit the growth of carrots, but these substances are probably good for tomatoes. Having a small garden, it is difficult to adhere to such a strict frequency, and even if most of it is allocated for potatoes from year to year. Therefore, vegetable growers are trying, by combining all the conditions, to draw up their own crop rotation plan, at least partially close to the ideal. Is it really that important?
What is the importance of crop rotation

In order to successfully grow and bear fruit, different vegetables absorb different trace elements. So carrots, beets, potatoes need phosphorus in large quantities, but cabbage and all types of lettuce need nitrogen. Root crops reach the lower soil layers, extracting phosphorus and potassium, and leafy greens with their short roots will not reach there, it feeds in the upper layers. Tomato roots collect food at a depth of almost a meter, and corn roots reach 2 m in height.
If you plant the site from year to year with the same crops, they will deplete one layer of soil, which means that in a year or two the gardener will not see a good harvest on his site. In addition, a lot of plant residues remain in the ground, pathogens thrive in them, they will happily pounce on plants that they will not be able to resist them. All sorts of pests that have trodden the path to their favorite garden bed and settled offspring nearby will not leave the plants alone of their own free will. And the weeds will take root in such a way that they cannot be brought out. This is what can happen if you plant vegetables in one place all the time. And to prevent this from happening, you need a competent alternation of crops in the garden.
Video “We do crop rotation on our own”
How to organize
In order to plan a crop rotation of various crops in the garden, you first need to mark the beds, make a diagram of the entire plot. Write down what grew on which bed, what will grow next year, in a year, in two years. The table may look like this: Or you can do it in a completely different way, break the garden into 4 parts, think about which crops will need more fertilizer, which ones will need less.

Take the first plot for zucchini, cucumbers, cabbage, they will need a lot of fertilizer, so you need to add the required amount to the soil. It is enough to add half of this amount of fertilizer to the soil of the second plot for the tomatoes, eggplants, onions, and garlic planted there. The third plot should be given to root crops, the soil for them does not need to be fertilized (root crops cannot be planted where the soil was fertilized with manure this year, they can be twisted, damaged and bad in taste). Determine the fourth part of the garden with potatoes and apply very little fertilizer to the soil.
And in subsequent years, change these areas in a counterclockwise direction, as shown in the diagram: Such an organization of crop rotation of vegetables is beneficial in its simplicity, and also in that it provides protection from diseases and pests, weed control, even economical use of fertilizers. In order to make it easier to draw up a crop rotation scheme for your site, you can first compile (or take from the Internet, tested on someone else’s experience) a table of plants that can be grown after each other.
What cultures to combine
Vegetables, like people, affect each other when they are nearby. Some can release substances that are beneficial or harmful to neighbors, others can attract or repel insects, which will also somehow affect neighbors, and still others are so focused on themselves that they can even be planted between plants that are undesirable to each other. All these complex relationships have to be taken into account when compiling crop rotation tables.
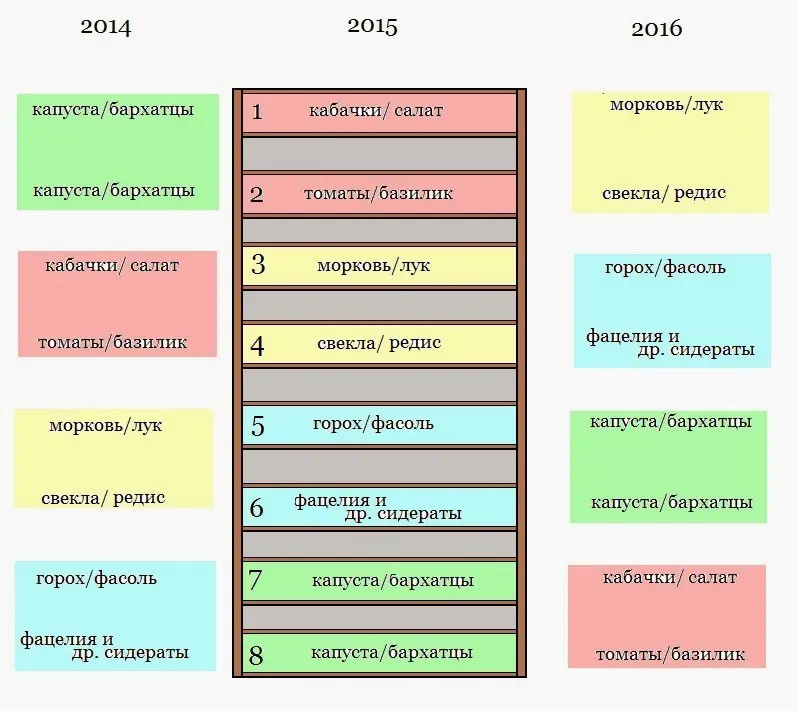
Crop rotation in the table for recent years
I must say that the correct combination of vegetable crops in the garden cannot replace the crop rotation process. They perfectly complement each other, not replace.
Lettuce, spinach, radish grow well next to cucumbers. Carrots feel protected next to onions, as their smell repels pests. And dill during flowering attracts lacewings that feed on aphids, which means that next to it there will be protection from aphids. It has long been noticed that onions and beets growing next to dill become tastier, parsley improves the taste of tomatoes. If celery and cabbage are planted side by side, the yield of both crops will be higher.
Potatoes get along well with beans, corn, cabbage, and tomatoes, cucumbers and pumpkins can ruin their crop. Cucumbers are good next to beans, corn, peas, and bad – with potatoes, parsley, tomatoes. Black radish with onions, carrots and cabbage cannot be planted side by side – they have a bad effect on each other, worsen the taste and reduce the yield. Cabbage has a bad effect on tomatoes and beans, although it is better for it from the neighborhood of beans – less pest threat. These are the complex relationships that occur in vegetable beds, but all of them must be taken into account in order to get good harvests on a small garden or summer cottage.
Video “What cultures are compatible with each other”
If you do not know how to properly rotate crops in your garden, then this video was created especially for you.









