Contents
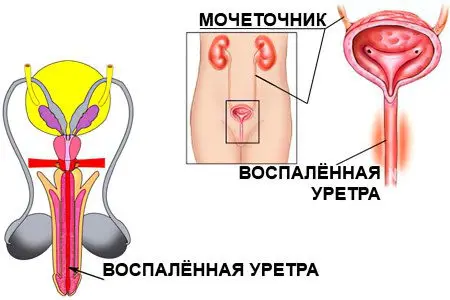
Urethritis is an inflammation of the walls of the urethra (urethra). It is one of the most frequently diagnosed pathologies in urological practice. Urethritis affects both men and women. The development of the disease is indicated by discomfort in the urethra, the pain is gaining intensity during urination, accompanied by cuts and a burning sensation. It will not be possible to ignore the symptoms of urethritis, as they significantly reduce the quality of life.
Lack of treatment leads to the spread of inflammation to neighboring organs. The pathological process includes: bladder, prostate, scrotum organs. The long course of the disease leads to changes in the walls of the urethra, they narrow, or are completely clogged with adhesions.
The most common cause of urethritis are bacteria: opportunistic and sexually transmitted. Sometimes the disease has a non-infectious nature, developing against the background of radiation therapy, allergies, or becomes the result of medical or diagnostic procedures associated with the placement of a catheter in the urethra.
Women suffer from urethritis less often than men, which is due to the peculiarity of the structure of their urethra. In women, it is thicker and shorter, so it is difficult for bacteria to fix on it. In men, the canal, on the contrary, is long, with expansions, narrowings and bends, which are predisposing factors for the reproduction of microbial flora.
Causes of urethritis
The causative agents of sexually transmitted diseases are among the most common provocateurs of infectious urethritis. Among them:
Gonococci;
Chlamydia;
Mycoplasma;
Trichomonas;
Ureaplasma.
Conditionally pathogenic flora, which can cause the development of urethritis:
Staphylococci;
Streptococci;
Proteus;
fungal flora;
E. coli.
In primary urethritis, the infection enters the urethra directly, for example, during intimacy with an infected partner. In secondary urethritis, bacteria enter the urethra from another source of inflammation, such as the prostate or bladder.
Risk Factors
Predisposing factors for the development of urethritis include:
Injury to the urethra during intercourse.
Prolonged catheterization of the bladder;
Passage of transurethral endoscopy;
Numerous sexual relations;
General decrease in immunity.
For women – entry into menopause or pregnancy (urethritis develops against a background of hormonal imbalance).
Atypical location of the external opening of the urethra – hypospadias (congenital anomaly).
Errors in observing the rules of personal hygiene.
Abuse of alcohol, sour, sweet and spicy foods that irritate the bladder and urethral walls.
Allergy. Urethritis can occur as a result of a local reaction to an allergen that has entered the body along with food.
Maintaining a sedentary lifestyle, which provokes the development of stagnation in the pelvic organs.
Symptoms of urethritis
The first symptom of urethritis is discomfort in the urethra.
The acute form of the disease is accompanied by the following manifestations:
Deterioration of general well-being.
Pain and burning at the beginning and at the end of intercourse.
Hyperemia and pain localized in the urethra.
Increased body temperature.
Swelling of the tissues of the genital organs.
Frequent urge to urinate without passing urine.
Pain in the lower abdomen.
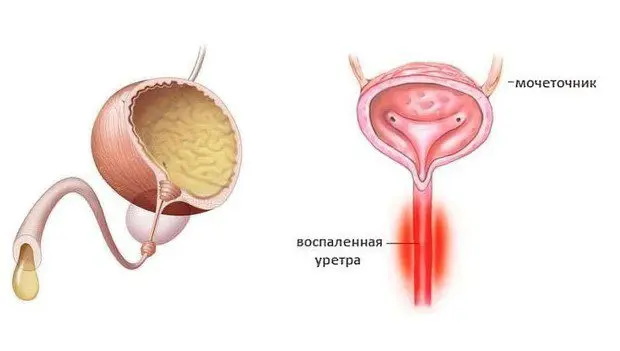
The chronic form of the disease is not accompanied by vivid symptoms. The patient is concerned about mild itching and burning when trying to empty the bladder. Mucous contents may be discharged from the urethra.
Symptoms of urethritis in men

Features of the course of the disease in men:
Retention of urine when trying to empty the bladder.
Weak stream of urine.
Intermittent urination.
Excretion of urine in small drops.
Acute retention of urine.
If it is not possible to empty the bladder, then it is necessary to urgently seek medical help. In such cases, surgery is always required.
Symptoms of urethritis in women

In women, the disease rarely occurs with complications. The clinical picture is often blurred. This is due to the fact that the causative agent of the disease does not have time to gain a foothold on the walls of the urethra, continue reproduction and provoke pronounced changes in the organ.
However, the danger of female urethritis is that the infection tends to spread along the ascending path, rising up the urethra to the bladder and kidneys.
Symptoms of urethritis in children

The disease can occur at any age, but severe clinical manifestations are rarely observed in children. In addition, it is difficult for a child to explain what exactly worries him.
Parents may suspect an infection based on the following signs:
Change in the nature of urine. It becomes cloudy, a sharp unpleasant odor emanates from it.
Crying during urination.
An increase in body temperature in the absence of signs of acute respiratory infections.
Itching in the genital area.
Anxiety.
The main danger of urethritis in childhood is the rapid involvement of nearby organs in the pathological process.
Diagnostics

With an external examination of the genital organs, the doctor notes hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membranes. When touched, the patient complains of pain. It is possible to detect pathological discharge.
Laboratory tests are required to confirm the diagnosis:
Urethral smear microscopy with Gram stain.
Analysis of the first portion of urine with sediment microscopy.
PCR study of scrapings from the urethra to determine the pathogen: chlamydia, gonococcus, mycoplasma, etc.
Nechyporenko test.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (according to indications).
If symptoms suggestive of urethritis appear, it is necessary to contact a urologist or gynecologist.
Urethritis treatment
Therapy of urethritis is reduced to taking antibacterial drugs. His choice depends on which microbe caused the inflammation.
Antifungal drugs are prescribed when the infection is caused by mycotic microorganisms. With nonspecific urethritis, drugs are prescribed to relieve inflammation, for example, NSAIDs. Vitamin and mineral complexes are used as a means to support immunity.
[Video] Dermatovenereologist Ovsepyan Zh.A. – what is urethritis, symptoms and treatment:









