Contents
- How is urea different from uric acid?
- Why is urea produced?
- Normal indicators of urea in the blood (table)
- When should I take a blood urea test?
- What types of tests need to be done?
- Preparing for a blood test
- What diseases does a strong increase in urea in the blood indicate?
- At what indicators of urea should I go to the doctor?
- Medications that lower urea levels
- Is it possible to reduce urea with folk remedies?
- Other treatments
- Risk of complications


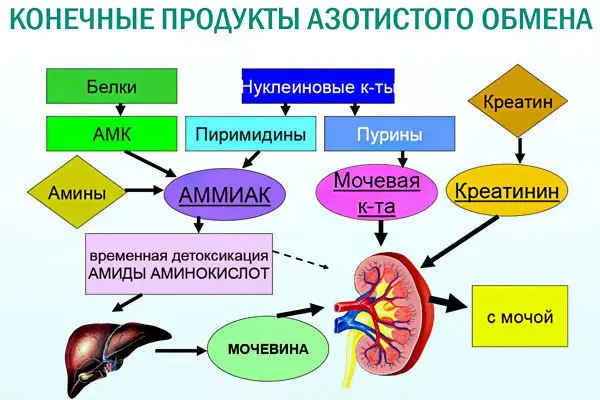
Is urea a by-product of protein breakdown? produced by the liver from ammonia and is involved in the process of concentrating urine. The main function of urea is the neutralization of ammonia, a toxic substance.
Urea is excreted by the kidneys, therefore, if the norm of urea differs upwards, this means kidney disease.
The norm of urea in children under 14 years old is 1,8-6 mmol / l, in adults – 2,6-7,3 mmol / l. In people over 50 years of age, the norm is 3,0–9,2 mmol / l.
A high concentration of urea compounds indicates a severe lesion of the excretory system, namely the kidneys. A healthy body excretes urea in the urine, its release into the blood occurs in a minimum concentration. Excess urea indicates serious kidney damage, kidney failure.
How is urea different from uric acid?
Uric acid and urea are substances that have nothing in common. The essential difference between them is in the metabolic processes. Uric acid is a component of urine, which is formed as a result of the breakdown of nucleic acids. The mechanism of its formation involves the blood, liver and brain. The whole process is aimed at neutralizing ammonia. The excretion of uric acid occurs with urine and sweat. Violation of the formation and metabolism of uric acid leads to the development of gout, the deposition of salts in the tissues of internal organs.
Urea is a nitrogen-containing compound that is formed during protein metabolism, the breakdown of amino acids. In a small amount, it is present in the general circulation, while the main part is excreted from the body with urine. The presence of urea indicates the development of certain diseases, however, a small amount of it is not harmful to the body.
Why is urea produced?
Increased urea production is associated with the presence of protein-rich foods in the daily diet, but subject to impaired renal function.
Development takes place in several stages:
Eating protein foods.
Breakdown, further absorption of proteins and other nutrients by active enzymes, gastric juice.
The final step in the breakdown of proteins in the liver, the transformation of nitrogenous elements into urea.
Transfer of urea into the bloodstream, further filtration in the renal structures.
Removal of the formed biochemical substance with urine.
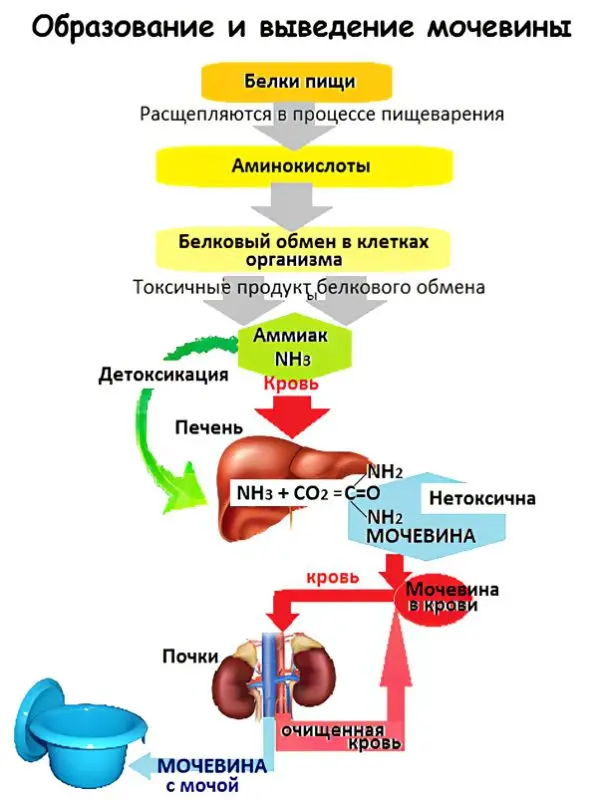
Normally, urea contains about 46% nitrogen. With prolonged abstinence from protein foods, a low urea content is observed, both in blood serum and in urine.
Normal indicators of urea in the blood (table)
For children, adult men and women, there are norms for the concentration of nitrogen-containing compounds in the blood.
Urea indicators for different ages are presented in the table.
Age gender | Reference values | |
1,8 – 6 mmol / l | ||
4 – 14 years | 2,5 – 6 mmol / l | |
14-20 years | 2,9 – 7,5 mmol / l | |
20 – 50 years | male | 3,2 – 7,3 mmol / l |
female | 2,6 – 6,7 mmol / l | |
> 50 years | male | 3 – 9,2 mmol / l |
female | 3,5 – 7,2 mmol / l | |
Indicators that do not correspond to the norm indicate the development of an acute or already chronic disease of the genitourinary system, gastrointestinal tract or kidneys. To find out the root cause of the deviations, a more accurate diagnosis is required.
Video: Sergei Baiko Chief Freelance Nephrologist of the Health Committee of the Minsk City Executive Committee, Ph.D. talk about the causes and treatment:
When should I take a blood urea test?
How much urea in the blood is increased is determined by determining the amount of protein breakdown products in diseases associated with metabolic disorders, pathologies of the excretory system, and digestion. The expediency of conducting a study on the level of urea in the blood serum is determined by the attending physician.
The reason for conducting an appropriate analysis may be the following complaints of the patient:
Frequent urge to urinate with discolored urine.
Frequent headaches, bouts of nausea, vomiting.
Disorder of the heart rhythm, feeling of suffocation.
The appearance on the skin of the scalp, the body of a salt coating.
Decreased or complete lack of appetite.
Loose stools not caused by food intoxication or intestinal disease.
Severe swelling in the eyes, face, lower extremities.
The smell of urine or acetone from the mouth. In severe cases, with a high concentration of urea in the blood, a characteristic smell of ammonia appears from the patient’s skin.
In the absence of an established underlying cause of these symptoms, the patient should consult a therapist. In the case when the underlying disease is diagnosed, the patient is treated by specialized specialists – nephrologists, hematologists. Their task is to conduct a detailed diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
What types of tests need to be done?

Self-diagnosis in the event of the appearance of certain symptoms is impossible. Be sure to consult with your doctor. The therapist collects a detailed history, clarifies the patient’s complaints, and conducts an examination in order to identify specific symptoms.
Based on the information received during the reception, he appoints the delivery of tests and some types of diagnostics:
Blood test for biochemistry. It is carried out by taking venous blood and further determining the level of urea, traces of nitrogenous substances, total protein, creatinine, bilirubin.
Analysis of urine. Sets the concentration of urea, protein.
Urinalysis according to the Nechiporenko method. Allows you to establish the prevalence of the inflammatory process in the renal structures and throughout the urinary system.
Urinalysis according to Zimnitsky. Urine collection is carried out within 24 hours. The doctor analyzes the volume of urine received, taking into account the fluid consumed during the same time.
Ultrasound examination of the liver. Allows you to establish hepatitis, cirrhosis, the presence of malignant tumors that affect the metabolism of nitrogenous compounds and the production of urea.
Gastroscopy of the stomach, endoscopic examination of the intestine. It will be needed in case of identified diseases of the digestive system that affect the normal digestion and absorption of proteins.
Ultrasound examination of the kidneys. It is necessary to establish the cause of impaired renal function: the presence of neoplasms, calculi, the localization of foci of inflammation, the fact of blockage of the ducts.
First of all, a biochemical blood test is performed. This is the main method for determining the level of urea in the blood. The remaining diagnostic measures are additional. They can help identify the underlying cause affecting blood nitrogen levels.
Preparing for a blood test

Proper preparation before taking blood to determine the level of urea allows you to get the most accurate data.
When prescribing this type of study, the doctor explains to the patient what recommendations should be followed:
Tell your doctor if you are taking any medications. The active components of pharmacological agents can affect the levels of urea in the blood.
For three days before the delivery of biological material, you should refrain from taking meat, fried, fatty, smoked dishes.
Two days before the study – do not visit the sauna, bath.
Give up alcoholic beverages for 48 hours.
Blood for biochemistry is taken on an empty stomach. The last meal should be no later than 8-12 hours.
The evening meal on the eve of the study should consist of light cereal porridge, vegetables. Portions should be small to avoid overeating.
Patients who smoke on the eve of the study can smoke their last cigarette one hour before blood sampling.
During the day, it is not recommended to engage in sports training, to perform hard physical work.
On the day before the study, avoid psycho-emotional stress and anxiety.
Venous blood donation takes place in the morning until 9.00, always on an empty stomach.
Immediately before the manipulation of venous blood sampling, it is recommended to sit, rest, take a few deep breaths to restore breathing.
The required volume of blood to obtain accurate diagnostic results is from 2 to 5 ml. In the conditions of a state medical institution, the analysis is carried out free of charge. A biochemical blood test in a private clinic costs about 850 rubles. The analysis time in the laboratory takes from 3 to 5 hours.
What diseases does a strong increase in urea in the blood indicate?
The determination of normal or deviating from physiological indicators of the level of urea occurs on the basis of the tabular data that we discussed above. Higher or lower values of a nitrogen-containing compound in the blood indicate the development of pathological processes.
An increase in urea values uXNUMXbuXNUMXbcan be observed under the following conditions:
Acute or chronic form of renal failure.
Narrowing of the lumen of the ureters.
Prostate hypertrophy in men.
Urolithiasis, formed calculi.
Obstruction of the urinary tract.
Low levels of urea are fixed during the development of a number of diseases:
Damage to the liver, leading to destruction, necrosis of its tissues, a decrease in its functions, for example, cirrhosis, fibrosis, hemochromatosis.
A disorder of the water-salt balance associated with the accumulation of excess fluid in the body.
protein deficiency.
Violation of the processes of digestion, absorption of nutrients in the small intestine.
If, when deciphering a blood test for urea, its sharp increase or decrease is revealed, first of all, you should think about the development of a serious somatic pathology. To clarify the diagnosis, consultations of specialized specialists, a comprehensive laboratory and hardware examination are necessary.
At what indicators of urea should I go to the doctor?
The profile doctor conducts a full examination of the patient, finds out the presence of complaints, studies the results of previous studies. For the purpose of clarification, additional tests, hardware diagnostics may be prescribed. The data of all examinations make it possible to establish the root cause of biochemical disturbances in the blood count, a breakdown in the mechanism of the breakdown of nitrogenous substances and subsequent excretion from the body through the excretory system.
Medications that lower urea levels
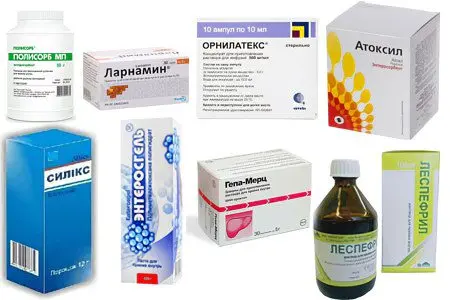
If urea in the blood is elevated, an integrated approach is needed to normalize its indicators. Combined treatment includes the appointment of certain drugs, the performance of artificial blood purification in order to remove toxic decay products.
The following drugs are most often prescribed to reduce the level of urea:
Polysorb – a preparation of the group of enterosorbents for oral administration in the form of a suspension. One tablespoon of the product is dissolved in a glass of clean water without gas. The prepared solution is taken 3-4 times a day one hour before meals. The course of treatment is from 10 to 15 days. The cost of the drug is approximately 240 rubles.
Atoxyl – sorbent with intense absorbing properties, which has antibacterial, disinfectant and wound healing effects. The drug is able to remove toxic substances from the body, eliminate the symptoms of poisoning. To prepare the solution, it is necessary to thoroughly stir 1-2 sachets of the product in 200 ml of slightly warmed water. Take Atoxil as symptoms develop. The price of the sorbent is about 150 rubles.
Enterosgel – an absorbent preparation in the form of a jelly-like paste. The remedy is taken 1 tablespoon 3 times a day for 1,5 – 2 hours before or after a meal. The course of therapy is designed for 7 – 14 days. The price of the drug is about 230 rubles.
Silix — multipurpose intestinal sorbent in the form of a powder. To prepare the solution, you need to dissolve 12 grams of the product in a glass of warm boiled water. The amount received is calculated per day. It is divided into several steps. The drug is taken within 14 days. The cost is about 190 rubles.
Lespenepril – antiazotemic, diuretic agent in the form of a solution for oral administration. The drug activates filtration, reduces the level of urea and removes nitrogenous compounds. A single dose is 1-2 teaspoons dissolved in ? glass of water. The treatment course is 3-4 weeks. The cost of the drug is about 195 rubles.
Gepa-merz – a drug to reduce the concentration of ammonia in the blood. The active substance contributes to the production of somatotropin, its own insulin. Favorably influences functions of a liver. The drug is administered by intravenous drip infusion. To prepare a medicinal cocktail in 500 ml of sodium chloride solution, 40 – 60 ml of Hepa-Merz are injected. The price of one ampoule of the product is about 630 rubles.
Ornilatex – refers to the hypoazotemic group of pharmaceuticals. The tool promotes the removal of excess urea, the synthesis of its own hormones. The required amount of the drug is administered in 500 ml of saline sodium chloride or Ringer’s solution, administered intravenously. The price for 10 ampoules of Ornilatex starts from 1470 rubles.
Ornicetyl – a detoxifying agent that helps reduce the level of urea in the blood, restore liver function. Produced in the form of a powder for the preparation of a solution for oral administration. The drug is taken 2-3 times a day, after dissolving the contents of the sachet in 200 ml of water. The daily dosage usually does not exceed 20 grams per day. The price starts from 500 rubles for 10 bags.
Larnamine – a drug of the hypoammoniemic group. It is able to reduce blood urea levels, restore the structure of liver tissues, and improve protein metabolism in the body. Can be used orally or by intravenous infusion. For oral solution, the contents of the sachet are mixed in one glass of water or juice. Take 3 times a day with meals. For intravenous drip infusions, the contents of the ampoules (from 4 to 8 pieces) are injected into a vial of physiological sodium chloride solution (500 ml). The price of the drug in the form of a powder is from 2400 rubles per package, in ampoules – from 1800 rubles for 10 pieces.
Under the influence of drugs, the concentration of urea in the body decreases, the decay products of nitrogen-containing compounds are eliminated. The appointment of medicines is carried out by the attending physician on the basis of laboratory data, after a detailed analysis of the results of ultrasound diagnostics.
Is it possible to reduce urea with folk remedies?
The preparation and use of decoctions, tinctures or herbal teas cannot be the main method of lowering blood urea levels. First of all, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease and restore normal functions of the liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract.

The use of folk remedies is permissible only after approval by the attending physician. In some cases, experts even recommend the use of herbal decoctions or infusions as part of complex therapy:
Decoction of licorice root. Pour 1 tablespoons of vegetable raw materials into 2 liter of water, boil for 2-3 minutes. Next, the broth is cooled. Take 1/2 cup twice daily before meals.
Bearberry infusion. 2 tablespoons of raw materials are poured into 0,5 liters of boiling water and infused for 4-5 hours. Infusion take 1 tablespoon before meals, three times a day.
A decoction of horsetail and hernia. A tablespoon of the herbal mixture is poured into 500 ml of water, boiled over low heat for 7 minutes, cooled. Ready broth is taken before each meal for 1/2 cup.
Rosehip tea stimulates urination, but may be contraindicated in some kidney disorders. Raw materials can be harvested independently or purchased ready-made in a pharmacy.
Infusion of black currant leaves. For cooking, you need to take young blackcurrant leaves, dry them in natural conditions in the sun for several days. For infusion, you need 7-9 large leaves, pour 1 liter of water, leave for about 5 days. Take the finished product 250 ml twice a day. The course of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
Other treatments
In some cases, there is a rapid increase in urea in the blood, which is accompanied by the rapid development of symptoms of intoxication. Too high a concentration of nitrogenous compounds may not be reduced by sorbents or hypoazotemic drugs.
If a high level of urea is established, the patient has signs of uremia, they resort to hemodialysis. The patient is connected to an artificial kidney machine. The procedure takes place in a hospital in a specialized department using disposable consumables. During the entire session of hemodialysis, the patient is under the supervision of qualified medical staff.
The patient is helped to lie down on a special chair-couch and the device is connected to the circulatory system. The device removes urea and toxic substances from the blood due to an acetate or bicarbonate solution. The hemodialysis procedure is carried out under sterile conditions.
If the violation of the functions of the liver, kidneys is temporary or happened for the first time, hemodialysis can be performed only once. Such measures are sufficient to normalize the patient’s condition and restore normal biochemical parameters of the blood. In the case of chronic or acute renal failure, a hemodialysis procedure can become life-saving. In severe cases, patients need it several times a week.
Risk of complications
In the case of an increase in the level of urea in the blood, it is necessary to take timely medical measures. Doctors make every effort to quickly remove it.
If the patient does not receive adequate care, does not undergo the necessary complex treatment, there is a risk of developing a number of serious complications:
Uremia with a severe course and a high probability of developing a coma.
Poisoning of the whole organism with damage to all organs and systems.
Cardiovascular insufficiency.
The development of a hypertensive crisis, the likelihood of a stroke.
Cardiac ischemia.
Liver damage in the form of hepatitis, cirrhosis.
The need to undergo hemodialysis throughout life, at least once a week.
The death of the patient.
The rapid establishment of the causes contributes to the urgent adoption of measures to eliminate the increased concentration of urea in the blood without disturbing the mechanisms of general metabolism. Most often, a high level of nitrogenous compounds indicates the development of severe somatic pathologies, disruption of the normal functioning of the kidneys and liver.









