Contents
To date, there is no simpler and safer, but at the same time highly informative diagnostic method than ultrasound. It is this technique that allows you to determine the structure, structure and location of the thyroid gland. In the primary diagnosis of diseases of this organ, the ultrasound procedure plays a key role.
More serious and expensive diagnostic methods (CT, MRI) can be used only if a more thorough examination is necessary, as well as in cases where the location of the gland (retrosternal) is difficult to reach for ultrasound waves.
For diagnostics using the ultrasound method, modern devices equipped with additional features (Doppler sonography) are used. High-precision sensors allow you to maximize the detail and effectively assess the state of the thyroid gland and its surrounding anatomical structures (muscles, blood vessels). The Doppler ultrasound method allows you to absolutely accurately determine the level of blood flow in the gland itself, as well as nearby lymph nodes. Against the background of drug therapy, the Doppler method will allow to track the effectiveness of treatment according to the dynamics of the pathological process.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the thyroid gland
This study does not require special preliminary preparation due to the convenient location of the thyroid gland itself.
However, if you want to get additional information (assessment of the level of blood flow), you should follow some rules:
On the eve of the procedure, you should refrain from taking medications that affect the level of blood pressure and cardiac output;
Completely exclude alcohol 3 days before the procedure;
Elderly people should pay attention to the fact that it is better to conduct the study on an empty stomach, given the possible appearance of a gag reflex when the ultrasound probe is pressed on the gland area.
During the procedure itself, the patient takes a horizontal position on his back, and to improve the conductivity of ultrasonic waves, a specialized gel is applied to the study site. The duration of the diagnostic process is no more than 15 minutes, depending on the goals and objectives of the study. A transcript of the results obtained can be obtained immediately after the end of the ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
It is advisable to have a paper towel with you to remove the remaining gel.
Evaluation of research results
To understand the overall clinical picture, as well as to make a probable diagnosis, the doctor performing the thyroid ultrasound should determine the following parameters:
Location of the gland. If the gland is located within the anatomical norm, this position is called typical. With the development of the pathological process, the location of the gland will be aberrant. The most common aberrant location is the root of the tongue. Perhaps the appearance of ectopic areas of the thyroid gland, which border on the main tissue of the organ;
The structure of the gland. Anatomical norms suggest the presence of a pair of lobes and a small isthmus. There are frequent cases of the formation of another (pyramidal) lobe and tissue outgrowths, which are located in the region of the lower poles of the lobes and descend to the thymus (its horns). As a result of a violation of the intrauterine formation of the thyroid gland, its location may be one-sided (instead of a normal bifurcation). This condition is called “agenesis of the thyroid lobe”. In the case of complete underdevelopment of the organ, the pathology is called “aplasia of the thyroid gland”;
Contours of the gland. This parameter is quite informative in terms of diagnosing the inflammatory and tumor process. By their nature, the contours of the thyroid gland can be clear and fuzzy. It is the presence of fuzzy contours that gives grounds for confirming the presence of a pathological process;
gland size. This parameter is valuable in diagnosing hyperplasia and hypoplasia of organ tissues. In order to determine the size of the isthmus, its thickness is measured in the direction from front to back. To obtain data on the volume of the gland, three linear parameters are measured in perpendicular planes;
The structure of the gland. In the absence of any pathology, the structure of the gland is homogeneous with the presence of specific granularity. Under the condition of the inflammatory process, the structure of the gland may lose its homogeneity;
Echogenicity of the thyroid gland. The term “echogenicity” refers to the contrast of the color of the gland when it is displayed on the screen of the ultrasound machine;
Focal formations. It is mandatory to carry out a description of the detected focal formations. By them are meant all kinds of nodes, cysts and calcifications;
The structure of the regional cervical lymph nodes. A prerequisite is the determination of their size, general structure, the presence of pathological formations. The malignant process is characterized by the loss of the internal structure of the lymph nodes, the absence of a clear picture of the “gate” of the lymph node (the area where the lymphatic vessel enters the node). The most serious indicators include the presence of calcifications, an increase in blood flow in the lymph nodes, as well as the appearance of cystic transformation. All these signs indicate the development of the tumor process.
According to the results of the ultrasound of the thyroid gland, an appropriate conclusion is drawn up. It should provide correct information regarding ultrasonic features. For example, the wording of the results should not look like “Adenoma of the left lobe of the thyroid gland” but “Signs of the presence of a node of the left lobe of the thyroid gland.”
Do not confuse the results of thyroid ultrasound with the final and reliable diagnosis. Attempts by the doctor conducting the diagnosis to independently make a diagnosis based on the results of an ultrasound examination go far beyond his competence and are erroneous.
Normal ultrasound of the thyroid gland
After an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, the patient’s natural desire is to get a transcript of the results. The main formulations used by doctors, as well as their detailed explanation, will be outlined below.
The most valuable in terms of information for a specialist conducting ultrasound of the thyroid gland are the following parameters:
Homogeneity of the structure of the gland;
The intensity of the blood supply to the gland;
The clarity of the contours of the gland;
Change in the echogenicity of the gland;
The presence of structural and organic changes in the tissue of the gland (cysts, nodes, calcifications).
Along with the thyroid gland itself, the monitoring and assessment of the condition of nearby regional lymph nodes is carried out.
So, let’s go directly to the assessment and decoding of the main parameters of the study:
Contours of the thyroid gland may have varying degrees of clarity. Absolutely clear contours are considered an indicator of the norm. A deviation from the norm, as well as an indicator of the presence of an inflammatory and tumor process, are fuzzy contours of the thyroid gland. It is the exit of the malignant process beyond the boundaries of the gland itself that gives a blurred picture of the contours;
Fabric structure is another important indicator, it can be both homogeneous and heterogeneous. The thyroid gland normally can only have a homogeneous structure with the presence of a characteristic granularity. The heterogeneity of the structure indicates the development of the pathological process. Inflammatory diseases of the thyroid gland of an autoimmune nature can occur against the background of structural heterogeneity. Then the tissue of the thyroid gland may resemble a honeycomb. In medical practice, there are two types of description of the heterogeneity of the thyroid tissue structure: “pronounced heterogeneous” and “moderately heterogeneous”. In the first case, we can talk about pathological changes, but the second option can be considered a variant of the norm. Moderate heterogeneity is not uncommon in completely healthy people, and it is caused by an increase in the level of antibodies to thyroglobulins;
Echogenicity of thyroid tissue is determined by the image that shows the monitor screen of the ultrasound machine. It should be taken into account that the screen image is formed by computer processing of incoming ultrasonic signals. The term “echogenicity” refers to the light gray color in which the thyroid gland is represented on the monitor screen. An indicator of the norm is the absolute correspondence of the echogenicity of the parotid salivary gland and the thyroid gland. As a result of the development of the inflammatory process, the echogenicity of the thyroid gland tends to decrease, but with a severe form of the course, it may increase. A decrease in echogenicity is evidenced by an increase in the tone of the thyroid gland compared to the tone of adjacent muscles. A change in this indicator is a serious signal for an ultrasound doctor. Normal echogenicity values may vary slightly, but, as a rule, the gland has a lighter tone compared to the surrounding vessels and muscles;
Focal changes (nodes) cannot be contained in a healthy thyroid gland. Permissible deviations from the norm are considered small cystic formations, the diameter of which does not exceed 4 mm. On the screen of the ultrasound machine, these formations have a homogeneous structure and are absolutely black in color (there is no echogenicity). These are ordinary follicles filled with a colloid (a hormone-containing jelly-like component). When detecting objects of large diameter and significantly different in their echogenicity from the tissues of the thyroid gland, we can confidently speak of the presence of nodes.
Nodes are usually classified in the following order:
Isoechoic, not differing in the level of their echogenicity from the tissues of the thyroid gland;
Hypoechoic, characterized by a decrease in the level of echogenicity compared to the surrounding tissues of the gland (dark in color);
Hyperechoic, characterized by an increase in the level of echogenicity compared to the surrounding tissues of the thyroid gland (light);
Anechogenic, which are characterized by a completely black color, and this may indicate the presence of a cavity that is filled with fluid (cysts).
The appearance of nodes in the thyroid gland in any case cannot be considered a variant of the norm. The normal state of the organ is evidenced by the uniformity of the structure and the absence of any nodes.
If a node is detected, the ultrasound doctor must draw up its characteristics, which include the following parameters:
Clarity of contours;
The presence or absence of a halo rim, which is located on the periphery of the node;
The degree of echogenicity of the node;
The presence or absence of foci of calcification (based on the acoustic shadow);
Linear dimensions (three main parameters are taken into account, allowing you to measure the volume of the node);
Presence or absence of cystic transformation.
Blood supply to thyroid tissue, or rather, its intensity, is determined using a Doppler study. An indicator of the norm is the presence of single signals on the surface of the thyroid gland. When an inflammatory process is formed, the blood flow in the gland increases several times, so the organ on the monitor screen looks like an object burning with fire.
Regional lymph nodes of the neck in the normal state are not enlarged. Normally, they have clear and even contours, the length prevails over the width, pronounced “gates” can be traced in the structure. The blood flow in the lymph nodes should not be increased. The presence of cysts is not a variant of the norm, and may indicate the development of a malignant pathology.
Ultrasound signs of thyroid disease
In the process of analyzing the results of ultrasound of the thyroid gland, the doctor needs to characterize a whole list of parameters that are of the most important general clinical and diagnostic significance. The characteristic of general indicators allows diagnosing a number of diseases of the thyroid gland. For example, an increase in the size of an organ in combination with a decrease in its echogenicity and a lack of homogeneity of the structure may indicate an autoimmune thyroiditis of a hypertrophic type, or a diffuse toxic goiter. To confirm these diagnoses, it is necessary to conduct a study of the hormone-forming function of the gland itself.
But there are also a number of rather specific indicators, when detected on ultrasound of the thyroid gland, one can confidently speak about the development of a particular pathology. Let’s consider the most characteristic of them.
The absence of the thyroid gland in a typical place and below it, provided there have been no previous operations on the neck, may indicate intrauterine underdevelopment of the gland (agenesis) or its atypical location (lingual goiter). People suffering from agenesis know about their diagnosis from the very moment it is made, so they must inform the doctor before performing an ultrasound of the thyroid gland. In the case of an atypical location of the organ, people are often not aware of this, since the function of the gland is not impaired, and nothing bothers the person.
When the gland is located at the level of the root of the tongue, an incomplete overlap of the lumen of the pharynx occurs, which entails a violation of the act of swallowing and creates a feeling of a “lump in the throat”. It is this defect that is the most common complaint of people suffering from thyroid pathologies.
In the case of an atypical location of the thyroid gland, as well as in the absence of information about insufficient production of hormones, it is mandatory to conduct an additional research method, such as computed tomography of the neck and chest area, in order to determine the true location of the thyroid gland.
The presence of a cystic formation in the midline of the neck above the isthmus of the thyroid gland, located close to the hyoid bone, indicates a median cyst of the neck. This pathological formation begins its formation during the period of intrauterine development. Diagnosis is not particularly difficult. Patients with a median cyst complain of the periodic appearance of a kind of mound in the neck. There are frequent cases of the development of a purulent process in the cavity of the cyst itself. The characteristic signs of the development of a purulent process are reddening of the skin on the neck, the presence of characteristic soreness during touch, and a local increase in temperature.
This problem is solved exclusively through surgical intervention to remove the cyst. Before making a final diagnosis, the doctor must take into account that such a cystic formation may be the result of metastasis of thyroid cancer. Surgical intervention in the presence of metastasis is carried out in order to completely remove the entire thyroid gland with a nearby fatty tissue. Only the total removal of the gland will protect a person from the occurrence of relapses of the disease.
If a median cyst of the neck is found, a histological examination of its cellular composition should be carried out by taking a biopsy. Histological analysis will allow to exclude or confirm a malignant pathology.
A thyroid nodule with uneven fuzzy contours, a pronounced decrease in echogenicity and microcalcifications is a pathognomonic sign of a malignant pathology. The complete absence of the halo rim indicates the spread of the tumor process beyond the thyroid tissue. The presence of microcalcifications indicates the development of papillary thyroid cancer. In some cases, during an ultrasound using the Doppler method, it is possible to detect increased blood flow in the thyroid gland, which indicates active tumor growth.
In case of detection of alarming signs on ultrasound, it is necessary to conduct a fine-needle biopsy of the node. Only taking into account the obtained data of histological examination, the question of the expediency of surgical intervention is decided. It is possible that there are doubtful signs in non-malignant nodes that have changed their structure during long-term existence.
Enlarged cervical lymph nodes with the formation of cysts and microcalcifications in them or the appearance of increased blood flow are quite serious signs that may indicate metastasis of a thyroid tumor to the region of the lymph node. Increased blood flow in the area of the lymph node may signal the presence of another tumor process, for example, metastasis from the tumor focus to other organs.
The detection of any of the above signs should entail a mandatory histological examination of the lymph node biopsy, as well as the study of swabs taken from the puncture needle in order to determine the level of calcitonin and thyroglobulin. It is important to remember that taking a biopsy of the thyroid gland and lymph nodes should be accompanied by ultrasound guidance of the needle.
Below are images obtained during ultrasound examination of a pathologically altered thyroid gland:
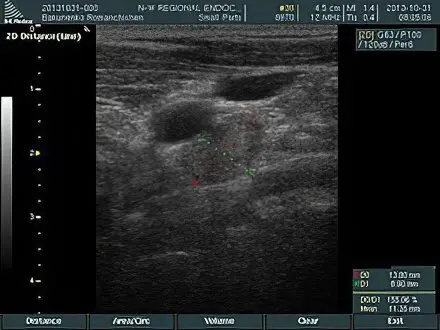 | 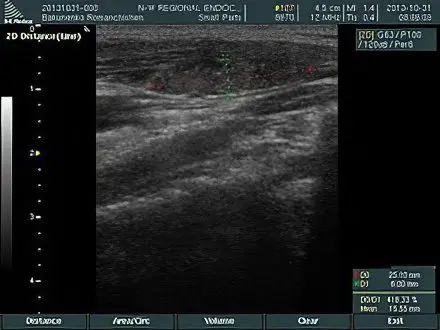 |
| Damage to the jugular cervical lymph node by metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer – an ultrasound picture | The disappearance of the internal structure of the cervical lymph node on ultrasound in case of metastasis of papillary cancer |
It must be remembered that even the presence of dubious signs revealed during an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland is not an indication for the appointment of any treatment. To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out a number of additional diagnostic measures, for example, measuring the level of the corresponding hormones, determining the oncomarker (calcitonin), and conducting a histological examination by taking a biopsy.
General Notes on Thyroid Ultrasound
Study Frequency
Pretty relevant question for a lot of people. The recommended frequency of thyroid ultrasound is 1 time per year in the absence of any complaints, and at least 1 time per six months in the presence of complaints. Given the alarming results of laboratory and clinical studies, the frequency of ultrasound can be increased to several times a week.
Indications for conduction
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland can be performed as the next preventive examination, or as one of the most informative diagnostic studies in the presence of certain indications.
Preventive Research
The ultrasound diagnostic procedure, as a rule, is included in the general list of preventive measures, and is not the result of any complaints of malaise. Preventive studies in people who have previously had thyroid diseases are considered quite justified. The purpose of ultrasound in this case is to assess the dynamics of the state of the organ, determine possible relapses, and also assess the likelihood of complications.
Diagnostic study
There are situations when ultrasound of the thyroid gland is a mandatory measure for making an accurate diagnosis.
An ultrasound examination is appropriate if a person presents the following complaints:
Visual enlargement of the gland or the presence of any compacted formation in the corresponding area;
Soreness in the neck during touch and pressure;
Swelling and redness of the lateral or anterior surface of the neck;
The formation of a hoarse voice, difficulty breathing, the appearance of problems with the act of swallowing;
Development of tremor (trembling) of the limbs;
The presence of arrhythmia, tachycardia, bradycardia;
The development of edema in different parts of the body;
Sweating, fever, feeling hot or cold on the skin;
Hair loss;
Excessive drowsiness, general weakness, depression, excessive irritability.
The main advantages of the method
If there is a need to choose the most appropriate and informative method for examining the state of the thyroid gland, then it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the advantages of ultrasound diagnostics.
The main advantages of this method include:
Complete absence of ionizing radiation;
Non-invasive (the integrity of the skin is not violated);
Elimination of the possibility of infection;
In pregnant women, the absence of any effect on the fetus.
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland has no contraindications and is absolutely harmless. This ensures its widespread use among pregnant and lactating women, as well as children and the elderly. An important advantage of the method is its relatively low cost, availability and rather high information content.
Topicality
An extremely important condition is the timely and regular passage of ultrasound of the thyroid gland. The impetus for its implementation should not be the appearance of certain complaints. Regular assessment of the state of the thyroid gland allows you to prevent and diagnose the presence of serious diseases, such as benign and malignant neoplasms, the presence of metastasis.
Timely detection of a benign tumor process allows you to choose the most appropriate treatment tactics in order to reduce the risk of malignant degeneration of the tumor. Particular attention should be paid to this method for pregnant women, as well as those who have previously suffered gynecological diseases. For example, the presence of hypothyroidism can adversely affect the development of the fetus. It is better if the disease is detected and treated before pregnancy.
Conclusion
Considering all the variety of positive aspects, the possibilities of the ultrasound method for examining the thyroid gland are far from limitless. For example, according to the results of ultrasound, it is impossible to determine the level of secretion of thyroid hormones, as well as the severity of the autoimmune process. To clarify such details, it is necessary to conduct a laboratory blood test.
Using ultrasound, it is impossible to determine the presence of malignant degeneration in the tissues of the thyroid nodule. For these purposes, a histological examination of a previously taken biopsy specimen is carried out.
In any case, if a visual increase in the size of the thyroid gland is detected, as well as if other symptoms described above appear, you should immediately contact an endocrinologist for advice and undergo an ultrasound procedure. Their outcome and the likelihood of complications depend on the timeliness of diagnosing diseases.









