Contents
What is a dislocation?
Dislocation is a violation of the articulation of the articular surfaces of bones (congruence), which occurs as a result of destructive processes in the joints (arthrosis, arthritis) or injuries. In case of injuries under the action of mechanical forces, a forced displacement of the ends of the bones from their normal position occurs.
Even during uterine development, a person can get injured, which will cause a dislocation. This type of damage accompanies people at all life stages.
During a dislocation, there is a violation of the integrity and functionality of the joint. In severe cases, there may be a rupture of the joint capsule and damage to the ligaments, arteries and nerve nodes. Such a disease requires the intervention of specialists who will provide first aid to patients and prescribe constructive treatment.
Most often, dislocations occur during bumps and falls. A special risk group is made up of athletes in contact sports (football, hockey, volleyball, etc.) or people involved in sports that involve frequent falls (skiing, skating).
The dislocated joint is temporarily deformed and immobilized. The typical symptoms are severe pain and swelling. The dislocation must be corrected, returning the displaced joint to its original place.
Types of dislocations
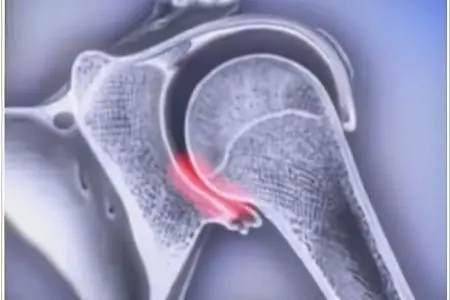
Dislocations are classified by the degree of displacement, by origin and by the size of the joint that was displaced.
According to the degree of displacement, the dislocation can be complete, i.e., one that is accompanied by a complete divergence of the ends of the joints, or incomplete (subluxation) – when the surfaces of the joints are partially in contact. A dislocated joint is one that is further away from the body. Exceptions are the vertebrae (a vertebra located above is considered dislocated), collarbones, shoulder (dislocation can be anterior and posterior).
Depending on the origin, dislocations can be congenital or acquired. Congenital arise as a result of a violation of the intrauterine development of the child. A common pathology is a dislocation of the hip joint (dysplasia), less common is a dislocation of the knee joint. Acquired dislocations are the result of injuries or various diseases (arthritis, arthrosis, osteomyelitis, poliomyelitis, etc.)
Also, dislocations can be open and closed. Closed dislocations occur without tearing the skin and tissues above the joint, while open dislocations occur with the formation of a wound. Damage to muscles, blood vessels, bones, tendons, or nerves makes dislocation complicated. They speak of habitual dislocation in situations where, due to poor treatment, dislocation can occur again even with a slight impact. Pathological dislocation, characteristic mainly of the hip and shoulder joints, occurs if the pathological process destroys the surfaces of the joints.
If the muscles surrounding the joint are subject to paralysis or paresis, they speak of a paralytic dislocation.
In addition, modern medicine identifies more than ten types of dislocations that can affect the following joints in the following parts of the body:
Ankle dislocation
Dislocated ankle
Dislocation of the shoulder joint
Dislocation of the leg
Dislocation of the neck (cervical vertebra)
Dislocation of fingers and toes
hip dislocation
Dislocation of the arm
Dislocation of the jaw
Symptoms of dislocations

The symptoms of a dislocation depend on its type. For example, congenital dislocation of the hip joint is manifested by gait disturbances, since leg abduction is limited, gluteal folds are asymmetrical, over time one leg becomes shorter than the other, which is fraught with lameness. If the hip dislocation is bilateral, the gait becomes “duck”.
Congenital dislocation of the knee joint is accompanied by severe pain, gait disturbances; the joint is inflamed and immobile. Traumatic dislocations are manifested by swelling, immobility and pain in the joint.
But if we talk about general symptoms, then the following symptoms are observed:
redness appears in the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe damaged joint;
there is a strong pain syndrome, which increases with any movement of the limb;
in the victim, the deformation of the joint is visually determined, since due to dislocation it changes not only its size, but also its shape;
severe edema appears in the area of dislocation;
some patients lose sensation in the limbs (with nerve damage);
impaired motor function;
temperature increase;
fever followed by chills, etc.
Causes of dislocations
In most cases, dislocations occur due to indirect injuries, that is, those in which the injury site is distant from the damaged joint. For example, falling on the outstretched hand, a person is most likely to dislocate the shoulder joint. Also, traumatic dislocation can occur with sudden movements that exceed the norm of joint mobility. Dislocations from direct trauma to the joint are much less common.
Many people are diagnosed with dislocation of the joints against the background of previous diseases, such as:
any injury during which the joint is fixed for a while;
tuberculosis;
osteomyelitis;
arthrosis, arthritis, etc.
This type of joint damage can be not only acquired, but also congenital, developing as a result of improper formation of the musculoskeletal system in a person even in the period of intrauterine development.
First aid for dislocation

With dislocations, you can not self-medicate, as you can cause irreparable harm to the damaged joint.
People around you can provide first aid to the victim as follows:
immobilize the injured joint and fix it in this position, using either a medical splint or any available means for this purpose;
if there is damage to the skin in the joint area, then they should be treated with alcohol or hydrogen peroxide;
apply a cold compress to the damaged area, which will help reduce swelling;
give the victim a medication that will relieve severe pain;
call an ambulance or independently transport the patient to the nearest medical facility (no later than 2-3 hours after the injury).
If a person is injured in the upper extremities, he should be transported to a medical facility in a sitting position. In the event that the victim has injuries to the lower extremities, it is necessary to deliver him to the hospital in a horizontal position.
Diagnostics
During the examination, the traumatologist (surgeon) will palpate the damaged areas of the body, after which he will refer the patient to a hardware examination. X-rays can determine the extent and exact location of damage. Once the preliminary diagnosis has been confirmed by X-ray, the patient is treated for the dislocation.
Treatment
The essence of any method of treatment of dislocation is to reduce the articular limbs and return them to their usual physiological position. All therapeutic measures in this category of patients should be carried out under local or general anesthesia. The choice of the type of anesthesia directly depends on the location of the dislocation and its complexity.
The specialist starts the reduction of the joint only after the complete immobilization of the damaged limb. The reduction process must be done very carefully. The doctor should not make any sudden movements that can aggravate the situation. The joint will fall into place in parallel with the characteristic sound – a click.
Treatment of traumatic dislocation after reduction of the joint consists in physiotherapeutic manipulations (massage, therapeutic exercises, acupuncture). Pathological dislocations sometimes require surgery to restore function to the joint. It is also imperative to treat the underlying disease if the dislocation of the joint is its consequence.
Usually, it takes a person one month to fully restore the functions of an injured limb. During this period, it is recommended to reduce the load on the joint as much as possible. In the second month, you can start physical activity, gradually increasing it.
Congenital dislocations are treated differently. Therapy should be started as early as possible, the optimal age is up to two years. Otherwise, you will need the imposition of special splints, wearing orthopedic shoes, or even surgery.
Rehabilitation
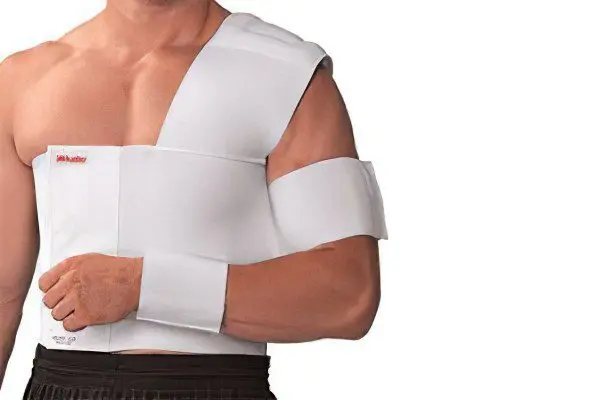

After removing the plaster bandage, patients must undergo rehabilitation, due to which the motor function of the joints will be fully restored.
Everyone, without exception, is recommended:
undergo a course of physiotherapy procedures;
engage in physical therapy;
visit the pool;
take walks in the fresh air, etc.
Prevention
In order to prevent dislocations, you must first take care of your health. Everyone should avoid falls and other types of injuries that can cause dislocations. Regular exercise will strengthen the joints and make the ligaments more elastic. Do not forget about proper nutrition, the use of vitamin and mineral complexes, which include the components necessary for the full functioning of the joints.









