Contents
What is a hip fracture?
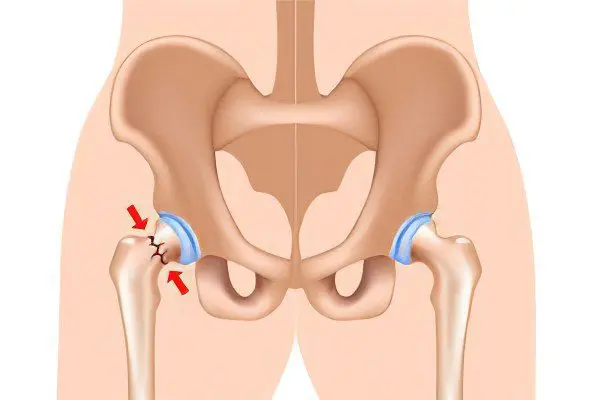
A hip fracture is an injury to the integrity of the femur. The injury is localized in its thinnest part, which is called the neck and connects the body of the bone and its head.
For many people, such a diagnosis is perceived as a sentence. Such an attitude to trauma is due to the severity of recovery and the need for surgery in most cases. The hip joint is large and powerful, in the human body, it takes the brunt of the load when walking.
Both the neck itself and the femoral head are injured, and sometimes the greater trochanter suffers. In the cervical zone, fractures are divided into lateral or lateral, as well as intra-articular. Medial fractures are recognized as the most dangerous, since the bone inside the joint is difficult to restore.
This type of injury is extremely common and accounts for 6% of the total number of fractures. The main category of affected people are pensioners who have crossed the line of 65 years. More often, women turn to doctors with such a problem. This is due to changes in their body after menopause. In a person with osteoporosis, a fracture can occur even as a result of a minor blow. Although sometimes young people also suffer from such an injury, they get a fracture after falling from a height, during an accident or at work.
Symptoms of a hip fracture
Such injuries are well studied and manifest themselves in the following:
Prolonged persistent pain, which is localized in the groin. At the same time, it is not pronounced, a person can endure it for some time without urgently seeking medical help. Most people take pain as a sign of another joint disease, such as arthrosis or osteoporosis. Over time, discomfort intensifies, especially when trying to make active movements and when focusing on the heel of the diseased limb.
External rotation of the foot, that is, turning it outward. This can be identified by carefully examining the position of the foot relative to the knee.
Shortening of the injured leg, but not much, no more than 4 cm, so this symptom is also often ignored. The reason for the shortening lies in the contraction of the muscles of the limb, inside which the fracture occurred. They seem to be pulled closer to the injured joint. This symptom is characteristic of varus fractures.
A symptom referred to by doctors as “stuck heel”. It manifests itself in the fact that when the patient holds the leg on weight, it slides off the horizontal surface, but the limb retains the ability to bend and unbend.
The occurrence of a crunch when the patient tries to turn the leg in a horizontal position.
Pain on palpation of the injured area.
Sometimes too intense pulsation of the femoral artery is noticeable.
Due to the displacement of the greater trochanter, the Shemaker line is violated.
With some fractures, the function of the leg is completely impaired and the person cannot not only walk, but also stand.
When pressing or tapping on the heel of the victim, there are unpleasant, sometimes very painful sensations.
The appearance of a hematoma, which may not form immediately. The delay is due to the fact that the vessels are damaged deep in the tissues, next to the joint. And only after some time the hemorrhage becomes visible.
Types of hip fractures
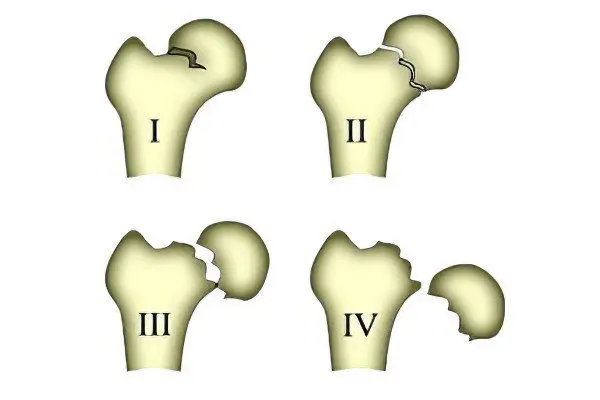
There are several classifications of species, they are based on different features:
Depending on the area of localization of the injury: in the region of the greater trochanter, in the region of the neck or head of the femur.
From the fracture site: median (medial), lateral (trochanteric, lateral).
From the level of location: subcapital (the most dangerous), cervical and basiccervical.
From the type of displacement: varus fracture (the head is displaced down and inwards), valgus fracture (the head is displaced up and outwards), impacted fracture (a fragment is inside another).
From the nature of the injury: open and closed fracture.
Each of them has characteristic features and its own symptoms. The most difficult and dangerous is considered to be an impacted intra-articular fracture, which, with inadequate therapy, can turn into a non-impacted one and require surgical intervention.
Displaced pertrochanteric fracture of the femur
Pertrochanteric fractures of the femur is an injury involving the area from the base of the neck to the subtrochanteric line. Most often, the reason for obtaining such a fracture lies in the fall on the greater trochanter, but sometimes the injury is also formed as a result of twisting of the limb. Retirement age is an additional risk of a displaced pertrochanteric fracture. Sometimes it is accompanied by a fracture of the ilium.
Characteristic features of pertrochanteric fracture:
A clear deterioration in the general condition of the victim.
Big blood loss.
There is a shift of the femoral neck, without destroying the spongy structure of the trochanter. There is a risk of displacement of fragments of the damaged bone.
Extensive tissue damage.
Swelling of the thigh.
Extensive hematoma.
Intense pain, with pronounced rotation of the limb.
For the treatment of a pertrochanteric fracture, it is urgent to immobilize the limb by fixing it and stretching it. After the patient is taken to the emergency room, a plaster cast will be applied to him. But in most cases, patients of retirement age cannot withstand its load for a long time, so they need surgery. This procedure needs careful preparation and is performed under general or local anesthesia, only in the orthopedic department. After it is carried out, the patient will need to wear a derotation boot for some time. When the bone fragments are securely fastened, it will be possible to move around without crutches.
Impacted fracture of the femoral neck
It occurs more often inside the joint; in people of retirement age, a fracture can form even as a result of intensive walking, increased load on the limb and a slight push, without falling. Since the pain is not too intense, and the functions of the leg are unlimited, a person can continue to lead a normal life without seeking medical help. The thought of a fracture can arise only because the pain, although not expressed, is chronic.
A particular danger of an impacted femoral fracture lies in its latent course. Due to the fact that the injury remains undetected, further displacement of one or more bone fragments occurs. This is fraught with the transition of an impacted fracture to a non-impacted one. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will need an x-ray taken in two projections – axial and anteroposterior.
A distinctive feature of an impacted fracture is a favorable prognosis for a complete cure, which is not typical for other types of trauma to the femoral neck. But it is important to start therapy on time, which will consist of skeletal traction, immobilization of the limb with a plaster cast, taking medications and exercise therapy.
Comminuted fracture of the femoral neck
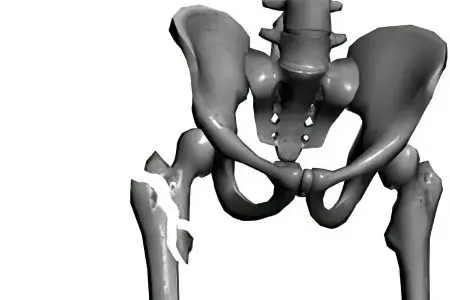
This type is characterized by the following features:
Pain of moderate intensity.
Swelling of the damaged area.
Extensive bruising in the joint area, more often in the left third of the thigh.
Inability to step on the heel.
Dizziness and general malaise.
Treatment consists of surgical intervention. It consists in the imposition of skeletal traction, which aims at the reposition of fragments, as well as the insertion of a pin into the corresponding section of the bone. After the operation, therapy with antibiotics and anticoagulants is carried out, after about 10 days the stitches are removed. Rehabilitation includes mandatory exercise therapy. The prognosis is favorable.
Open fracture of the femoral neck
This is the worst injury. Its main feature is the rupture of soft tissues with access to the external environment. Most often, such fractures are observed with a gunshot wound. They are characterized by high blood loss and severe pain. The victim must be taken to the hospital as soon as possible. Most often, such injuries are accompanied by damage to other internal organs.
Closed fracture of the femoral neck
A closed fracture is the result of a fall or a direct blow to the thigh. In this case, displacement of fragments is often observed. As in other cases, people of retirement age are most often affected.
A closed fracture with a displacement of two condyles, having a direction up and to the side, requires special attention. The fracture line runs along the entire joint, which is why hemarthrosis is formed. Blood is poured into the joint from the damaged area.
A closed hip fracture is accompanied by the following symptoms:
With a lower fracture, pain is characteristic in that part of the thigh, which is located closer to the knee. Movement of the limb is impossible, flexion and extension of the leg is painful.
If the fracture occurs directly inside the joint, then the pain will not be too intense, swelling and hematoma may appear.
The treatment consists in the implementation of a puncture of the joint, in order to suck out stagnant blood. If the separation of the fragments did not occur, which will be seen after the X-ray examination, then a plaster cast is applied to the injured limb.
The terms of wearing it are individual and depend on the intensity of the restoration of the damaged bone, but not less than a month. If fragments were found, then it is necessary to reposition them, and only after that it is possible to apply plaster. When matching of the broken parts of the joint is not possible, its complete replacement is required. If possible, doctors try not to do traction for older people, as this leads to a long rehabilitation period and bed rest, which is fraught with the development of other diseases.
Recovery time after fracture
The recovery time cannot be accurately calculated, since everything depends on its severity, nature, age of the patient and other factors. But on average they are at least six months. Only after this time has passed, a person will be able to stand on the injured limb, fully transferring the weight of the body to it.
In most stages of treatment is accompanied by the following terms:
On the third day after applying a plaster cast, the patient must begin to massage the lumbar region. Then you should switch to an uninjured limb. A week later, you can begin to massage the thigh, which was injured. This should be done carefully, following the recommendations of the doctor.
After two weeks, if the plaster is removed, you can begin to perform knee movements. It is best to do this under the supervision of a doctor and only after his permission. Moreover, at the initial stages, the patient will need outside help. After about a month, you can begin to perform flexion and extension on your own. After 2 months, the patient may attempt to sit down. This must be done according to specialized instructions.
After 3 months, the patient will be allowed to get up using crutches and begin to move independently. In this case, the support should be on a healthy limb, you can only slightly start on a sore leg.
Gradually, the load on the thigh should be increased, and after six months, attempts can be made to return to a full life.
Sequelae of a hip fracture

Since most of the cases are affected by the elderly, the consequences are quite severe. But with proper treatment, they can be avoided.
However, the consequences of a hip fracture are:
As a result of circulatory disorders – necrosis of the head of the bone, up to its decomposition and complete disappearance. This condition is called aseptic necrosis. When there is a high risk of such a pathology, it is better to carry out prosthetics in advance, which does not make sense to refuse. This will be the best prevention of this type of complication.
Sometimes a false joint can form inside the fragments. It develops when they are not fused. Treated promptly. The degree of movement disorder is determined individually. A person either completely loses the ability to step on a limb, or moves on it, experiencing some discomfort.
The sooner a person restores motor activity, the less will be the risk that vein thrombosis will form. Pathology develops against the background of a long stay in one position. Venous blood stagnates and as a result, blood clots form. The consequences of such a complication are serious, up to the death of the victim. Proper care is essential for prevention.
Stagnant sputum can cause the patient to suffer from pneumonia. Due to a long stay in one position, the lungs are not able to function normally. Inflammation is severe and can be fatal. An additional risk factor is a decrease in immunity. Therefore, competent breathing exercises are extremely necessary.
Sometimes complications arise after the operation. This can happen because the screws are placed too deep into the bone or at the wrong angle. Nerves and blood vessels, the acetabulum are affected. All this refers to the early postoperative consequences.
Rarely, but still there are delayed complications after the operation. They are expressed in the rejection of the prosthesis or loosening of the metal structure implanted inside.
Infection during the operation.
Violation of the psychological nature, the development of depression, the appearance of unwillingness to live.
Sometimes bedsores can form, which occurs due to improper care of the injured immobilized person.
Joint contractures, osteoarthritis, osteomelitis can form.
Osteoarthritis can develop when a joint undergoes degenerative destruction and its functioning is impaired. Prevention consists in constant medical monitoring and adequate treatment of the disease in the early stages of its occurrence.
The main prevention of possible complications comes down to proper care of the victim, assistance in performing hygiene procedures. The psychological support of a person is also important; in the treatment of a fracture, a positive attitude and faith in the possibility of recovery are important. Strict observance of all doctor’s prescriptions, full implementation of rehabilitation procedures is a guarantee that the patient will restore the previous standard of living, regardless of the age and nature of the injury.
What is the risk of hip fracture in the elderly?

When you get a hip injury, especially in old age, there are some additional risks that are associated with:
The occurrence of severe complications. They are associated with both physical and psychological health of a person.
Due to a decrease in immunity, there is a risk of developing other diseases not related to the joints. Most often, the cardiovascular and respiratory systems suffer.
A long time spent in bed undermines the health of an elderly person, exacerbates those who already have chronic diseases.
The biggest danger is that a person can die. The most common causes of death after such a fracture are heart failure, thromboembolism, and pneumonia.
Sometimes an elderly person, deciding that he is becoming an unbearable burden for his family, decides to commit suicide.
Refusal of surgical intervention and complete immobilization of the patient.
First aid for a hip fracture
The most effective help in the event of such an injury is to call a team of medical workers.
If there is a need to independently deliver the victim to the hospital, then it is necessary to carry out a number of measures:
To begin with, a person needs to be laid on his back.
With severe, unbearable pain, anti-shock measures should be taken. They consist of anesthesia, both local and general. Any pain medication will work, in particular ibuprofen or ketoral.
It is important to immobilize the affected limb. To do this, it must be fixed with a tire. A rail, board or plywood is suitable as an improvised material. All joints of the leg, and not just the hip, need fixation. If no suitable thing was found, then you can tie the diseased limb to a healthy one.
It is important to apply the tire correctly. It should take its beginning in the groin, on the inside of the limb, and end near the heel. It should be fixed in the area of the heel, knee and groin.
Clothing and shoes should not be removed. If the injury was received in the cold season and the victim is on the street, then the limb must be additionally insulated. Since it will be more susceptible to frostbite than a healthy leg.
It is necessary to carry a person on a hard surface, best of all on a stretcher.
When bleeding, you need to tighten the leg with a tourniquet, but not too much. If the limb begins to turn blue, then it is important to loosen the bandage.
It is important to calm the patient, do not panic because of his screams and groans – this is a normal human reaction to such an injury. More attention should be paid to the victim, who remains indifferent to pain, most likely he is in a state of shock.
If you have to deliver a person on your own, then it is important to calm down and not exceed the speed limit.
Treatment of a hip fracture
Trauma therapy is a prerequisite for the recovery of the victim. In some cases, surgery is required, but sometimes it is possible to do without it. A surgeon will not be needed if the fracture is located in the lower part of the neck or it is of the impacted type. Moreover, the latter is not treated promptly only when its line is horizontal and there is no risk of splitting. Also, you can not perform an operation when the patient is not able to transfer it.
There is a certain sequence of therapeutic measures. The scheme consists of:
Finding the victim in a hospital. For this, there are specialized orthopedic and traumatology clinics and departments.
Skeletal traction is carried out during the first two months after injury.
Massage leads to a mandatory treatment regimen.
When the tension is removed, the patient will be able to move independently, for this he will need crutches. Reliance on a leg with a fracture is prohibited.
In the fourth month, you can begin to gradually use the limb, but under the strict supervision of a doctor.
After 6 months, the former patient most often begins to walk independently.
Immobilization for hip fracture
As a therapeutic technique, immobilization is used, that is, immobilization of the limb. It is shown in a number of cases and its purpose is to save human life.
Indications for its use are strictly limited:
If a sick person cannot endure the necessary surgical intervention for a number of reasons. Most often they are in the general serious condition of a person, for example, with increased bleeding, general exhaustion, the presence of certain diseases.
If the patient has persistent mental disorders, for example, senile insanity.
If even before the moment of injury, the person was not able to move independently.
Immobilization consists of a series of sequential actions:
Joint injection with local anesthetics, lidocaine and novocaine are mainly used.
The use of skeletal traction for a short period, up to 10 days.
Removing the structure.
Turning the patient from side to side, planting him on the bed.
Starting from the 20th day, the patient is allowed to get up using crutches.
If the patient feels satisfactory, he is discharged, but he will not be able to move fully, without the help of crutches.
Operation
Before carrying out an operative intervention, it is necessary to carry out a competent diagnosis. For this purpose, classical techniques, radiography, computed or magnetic resonance imaging are used. Naturally, visual inspection and palpation are necessary, as well as taking an anamnesis and listening to human complaints.
It should be understood that surgery is most often an unavoidable procedure. Depending on the nature of the injury, special structures will be inserted inside the fracture. It can be knitting needles, rods, or screws. If indicated, the doctor may recommend partial or total joint replacement. This intervention is called prosthetics.
It is desirable, and sometimes vital, to perform the operation in the early stages – on the first day after the injury. But sometimes the dates are postponed if a person has any contraindications. It is possible to spend some time on the hood.
Surgical intervention is based on several basic points:
Mandatory use of anesthesia, which can be local or general. This directly depends on the complexity of the operation and the condition in which the patient is located.
Before fixing the fragments, the doctor correctly compares them or, in another way, repositions them.
When the fracture is not complicated, the operation is performed under X-ray control, without opening the joint capsule. This method is called closed.
Sometimes an open reposition is required, for this the capsule is opened.
As for arthroplasty, it also has certain indications and is used when there is a high risk of complications. The older the patient, the more often they replace their native joint with a prosthesis. This is also done with a pronounced displacement of fragments, with the detection of fragments, with necrosis of the head.
Exercise After a Hip Fracture

The implementation of a specialized set of classes is a prerequisite for effective recovery. Exercises help to avoid serious consequences, give the proper load to the muscles, prevent their atrophy, and contribute to the speedy rise to the feet. Therefore, the complexes recommended by doctors must be performed.
They consist of three parts:
To begin with, it is recommended to simply imagine how the movements will be performed. Then you can move on to squeezing the muscles of the back, abs, buttocks, legs and arms. Keeping them in tension is not long, 30 seconds is enough. Bending of all movable joints is performed – the neck, limbs, shoulder girdle, etc. From the very first days, it is necessary to perform breathing exercises.
When the plaster is removed, you can proceed to perform more complex exercises, which consist in the active movement of healthy limbs. But the whole complex should be performed lying on your back.
After a person starts to get up, it is important for him to try walking with a stick, with one, with two, with the help of stilts, and then on his own.
Rehabilitation after a hip fracture
Recovery after an injury is not only about doing physical exercises, but also about normalizing the psychological state. Even after a person begins to move independently, he still feels vulnerable, may be depressed. If close people cannot help him get out of depression, then it is better to send the person to see a psychotherapist.
For the rehabilitation stage, normal sleep, proper nutrition, massage visits and treatment of exacerbated chronic diseases are important. An integrated approach will help the former hostage of the bed to recover faster and gain strength.









