Contents
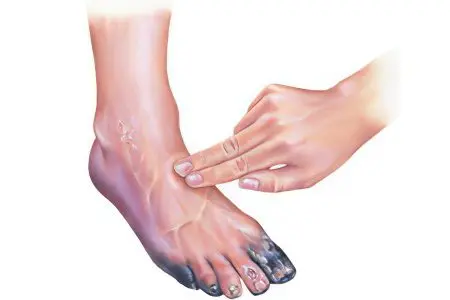
Gangrene – This is a rather complex disease characterized by necrosis. The causes of gangrene are different. Tissue death can be the result of insufficient blood circulation through the vessels or a complete cessation of blood circulation in a certain part of the body, as well as the result of exposure to adverse external factors, such as chemicals, electric current, high or low temperatures.
A characteristic sign of gangrene is a change in the color of tissues affected by the necrotic process. They become black or earthy grey. If an infectious infection occupies a large area, and the therapy of the disease did not start on time, a third of the patients die, and the rest become disabled. To increase the chances of returning to a full life, you should consult a doctor at the first symptoms of gangrene.
Common places of localization of the disease are the legs, arms, torso, face, as well as the lungs, intestines, appendix. Depending on the diagnosis, a treatment strategy is formed, the prognosis of the patient’s recovery is determined.
Classification of gangrene
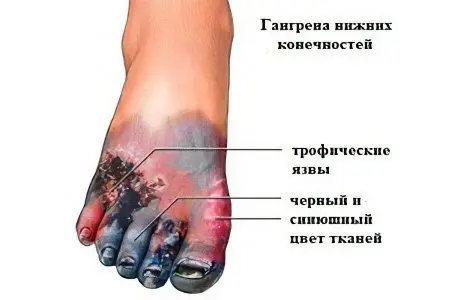
Types of gangrene depending on the nature of the damage:
Dry gangrene – the area of the lesion is clearly limited, the pathological process does not spread further. The diseased part of the body takes on a “mummified” appearance – the tissue shrinks, thickens, and loses moisture. This type of disease has the most favorable prognosis.
Wet gangrene – processes of decay occur in the tissue, the fiber swells, softens, acquires an unpleasant odor.
Gas (anaerobic, or airless) gangrene – is a kind of wet form, it is provoked by pathogenic bacteria – clostridia. This type of disease is very dangerous, as the process quickly captures healthy tissues, and the body suffers from severe intoxication.
Bed-sore – develops in soft tissues, on the skin and in subcutaneous tissue due to prolonged pressure on the same place. Occurs in bedridden patients who do not change their position for a long time.
Another type of gangrene – noma – is formed in children with congenital immunodeficiency who have had a severe infection or somatic disease. With this type of gangrene, necrosis of facial tissues (lips, cheeks, gums, fatty tissue) occurs. The outcome of this form of the disease is the death of the patient.
Causes of gangrene depending on the type
Gangrene can be caused by internal or external factors. Severe bruises with vascular ruptures and damage to nerve endings, exposure to high or low temperatures, radiation damage, exposure to chemicals – all these factors are external causes of gangrene.
Processes occurring inside the body – such as arterial sclerosis, which can cause a heart attack, or the formation of blood clots – lead to circulatory disorders and are related to the internal causes of gangrene. If microbes take part in the development of gangrene, then this is a septic or putrefactive disease. If microbes do not participate in this process, then the disease is aseptic.
There is a strong opinion that gangrene can be the result of injuries or gunshot wounds. In addition to these reasons, it is caused by blockage of blood vessels by blood clots or cholesterol plaques, nerve damage, and complications of infectious diseases. An accurate diagnosis is impossible without establishing the cause of gangrene.
Type of gangrene | Causes | Localization area |
Dry |
| Skin, parts of hands and feet |
Wet |
| More often feet of extremities, less often lungs, intestines, gallbladder |
Gas | Infection of a deep wound with anaerobic bacteria when combined with the following conditions:
| The onset of the disease is the skin, muscles, subcutaneous tissue of the extremities, then the pathology spreads throughout the body |
Bed-sore | It occurs after 4-5 days of pressure on the tissues, the appearance is complicated by diseases:
| Shoulder blades, sacrum, spine, hip joints |
Letter | Complication of infectious diseases (rubella, measles, meningitis) in combination with impaired immunity | Facial tissues, gums, deep subcutaneous tissue |
The definition of symptoms helps to accurately classify the type of gangrene, determine the tactics of treatment.
Symptoms of the main types of gangrene
Even a few hours late with treatment can lead to a patient’s death. It is important to timely distinguish and assess the severity of the symptoms of the disease, the rate of its spread throughout the body. There are local symptoms and general signs of intoxication (hyperthermia, weakness, loss of consciousness or its disturbance).
Gangrene can affect both a part of the body and an entire organ. A symptom of gangrene is that the affected area changes its color, becoming blue or even black. Gangrene can also appear when there is a violation or cessation of oxygen supply. Gangrene develops most easily in tissues located far from the heart. And such parts of the body, first of all, include the lower limbs.
Symptoms of dry gangrene
Dry gangrene usually affects a specific area of the body and does not spread further. At the first stage of the development of this disease, a person feels severe pain in the place of a dead vessel, after which the diseased limb turns pale, in the affected area the skin becomes “marble”, noticeably colder, the pulsation in this place disappears. Further, the limb completely loses sensitivity. Pain torments a person for a long time, since the nerve endings do not die in the affected tissues immediately. There is a violation of blood circulation in the main vessel and in its branches.
The cause of dry gangrene is the difficulty in the process of blood circulation in the limbs, that is, in the arms or legs, or severe dehydration of the tissues. In this case, parts of the body dry out, then mummify and change color.
There are effective methods for determining circulatory disorders:
Raise your arms, alternately bend your hands. If there is a violation of the patency of the arteries, pain, goosebumps, weakness will appear in the hands.
In the supine position, raise the legs at an angle of 45 °, symptoms similar to those in the hands will appear. In addition, with impaired blood circulation or at the initial stage of the disease, it will be very difficult to keep the legs in a given position for more than 25 seconds.
When the artery is blocked, signs of necrosis, or tissue necrosis, begin to appear. The leg or arm takes on a characteristic appearance.
Symptoms of necrosis:
The tissues of the limb become black. Such a symptom is characteristic exclusively for this form of gangrene, because in other forms of the disease, with the exception of noma, parts of the body take on an earthy green or bluish color.
The affected limb is reduced in volume, the symptom is detected when measured in comparison with the same part of the symmetrical limb.
The limb becomes dry, sweat in the affected part of the body does not separate.
Due to the loss of fluid, the tissues of the limbs are compacted.
Nails and hair in the affected area stop growing.
Since the nerve endings die off, no pain is felt in the affected limb. The body’s defense system creates a barrier against the spread of the gangrenous process, so intoxication does not occur, there is a clear boundary between the diseased and healthy part of the limb.
Dry gangrene extends from the tips of the capillary vessels to the main vein. A protective barrier is formed at the junction of the dead tissue with a healthy part of the body. It takes quite a long time for the complete necrosis of tissues and the recovery process. During this period, microbes that have entered the focus of the disease can cause the development of another type of gangrene – wet.
With dry gangrene, dead tissues do not decompose as they do with wet gangrene, and toxic substances enter the blood in very small quantities, so their accumulation does not cause severe intoxication. The state of health of the patient during this period is quite satisfactory. This allows not to immediately perform an operation to remove the limb, but to allow the protective barrier to fully form.
In exceptional cases, tissues affected by dry gangrene spontaneously separate from the body, recovery occurs. Unfortunately, this does not always happen, more often the pathological focus persists. Therefore, when the first signs of the disease appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of wet gangrene
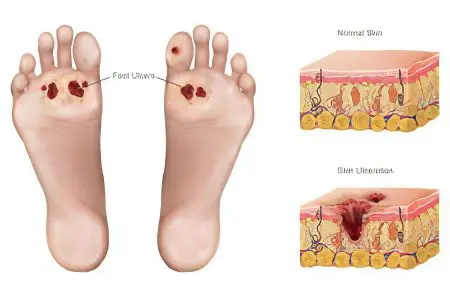
Wet gangrene develops for the same reason as dry gangrene. However, in the first case, there is a faster process of circulatory disorders in the vessels. Wet gangrene most often affects obese people. The tissues in this disease are not completely dehydrated, and therefore the process of decay begins. With wet gangrene, extensive intoxication of the body occurs due to the fact that a lot of decomposition products penetrate into the blood. Bacteria actively develop in dead tissues, due to which the disease progresses very intensively. This form of the disease affects not only the limbs, but also the internal organs.
The reason for the development of wet gangrene can be disorders in the intestines, gallbladder or lungs. Blood clots in large veins can also provoke wet gangrene.
The initial stage of the disease is very similar to dry gangrene. Only with a wet variety on the affected area, the skin becomes covered with spots, blisters with purulent contents. The patient feels very bad, the affected area hurts a lot, the pressure drops, dryness of the tongue is observed, body temperature rises.
Local symptoms:
The affected area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe limb becomes dark purple or cyanotic purple.
There is no clear boundary between healthy and diseased tissue because the body is unable to stop the spread of pathogenic microbes.
In the transition zone between healthy and affected areas, hyperemia, an increase in local temperature, and pain are noted.
There is a pronounced putrid odor.
The extremity is edematous, pastosity is observed.
Due to irritation of the receptors, constant acute pain is felt.
On dead tissues, the local temperature decreases.
Intoxication of the body due to wet gangrene poses a serious threat to human life, sepsis can develop, which will cause death. Patients with diabetes are very difficult to tolerate the disease, because due to the large amount of sugar in the blood, the body cannot fully fight the disease.
With severe diabetes similar symptoms of vascular lesions are noted. Any wound becomes an entrance gate for infection, and reduced immunity leads to the development of gangrene. To prevent such a development of events, the most minor wounds should be treated with antiseptics (Fukortsin, Zelenka, Levomekol), protected with sterile dressings and a bactericidal plaster. In case of difficulties with wound healing, you should consult a doctor no later than 1-2 days.
If a patient is diagnosed with a noma or a transition of the gangrenous process to the internal organs, general symptoms occur. They are non-specific in nature, because they are found in many serious infectious diseases.
Common symptoms of wet gangrene:
Hyperthermia, reaching 38-39 °, with the addition of peritonitis – up to 40 °;
increased sweating;
Weakness, fatigue;
Nausea, dizziness;
Convulsions with gangrene in children whose immunity cannot cope with the disease.
In older people, all symptoms can be smoothed out due to an inadequate response of the body.
Symptoms of anaerobic (gas) gangrene
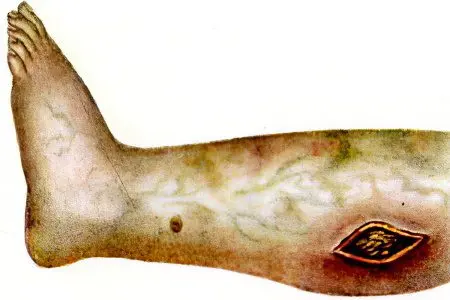
Airless, or anaerobic gangrene, has the most unfavorable prognosis. It is caused by clostridia – anaerobic bacteria, putrefactive microorganisms that actively grow on dead tissues without oxygen. Clostridia secrete a large amount of toxins into a closed wound, destroying the skin, fatty tissue, and muscles in their habitat. Pathogens intensively spread along the limb, releasing decay products into the patient’s body.
Symptoms of anaerobic gangrene:
The skin is pale, its temperature is reduced;
There are blue or reddish spots around the wound;
The tissues are edematous and pasty, the swelling increases all the time;
Discharge from the wound is cloudy, fetid, green or brown in color;
The exposed muscles resemble boiled meat, they are pale, their fibers are stratified;
On palpation of the affected limb, crepitus (crunching) is noted, the symptom is characteristic only for anaerobic gangrene.
Gas gangrene destroys the body’s muscle tissues. After getting to where there is a favorable environment for the development of microbes, they begin to release toxic substances that, penetrating into the connective tissues, destroy their cells. This process is quite fast. Microbes produce compounds that contribute to the breakdown of proteins and carbohydrates of affected tissues with the release of a special gas.
The initial symptoms of anaerobic gangrene are tenderness and swelling at the site of infection. Further, a dark liquid with a bad smell begins to stand out from the wound, the skin around the wound darkens. With a light touch of the skin in the wound area, a sound resembling crackling is heard.
Unfortunately, this type of gangrene cannot be cured without surgery. The entire affected area is removed, in the most advanced cases, they resort to amputation of the limb with the focus of the disease.
Melnikov’s symptom is used to diagnose edema. A thread or a strip of tissue is freely wound around the affected limb, leaving a gap between the bandage and the limb of 1-2 cm. If after a few hours the knot tightly cuts into the tissues, swelling increases, which is typical for the anaerobic form of the disease.
General symptoms in anaerobic gangrene in many cases are fatal to the patient. Intoxication with the waste products of clostridia leads to death.
Common symptoms of gas gangrene:
Loss of ability to move, weakness;
Severe hyperthermia, reaching 39-41 °;
Loss of consciousness, hallucinations, delirium;
Nausea and vomiting that does not relieve the condition;
Falling blood pressure below 100/70 mm Hg. Art., an even more pronounced decrease (by 30 mm Hg) is an extremely unfavorable sign;
Tachycardia up to 100-120 beats per minute, felt by the patient.
Clostridia toxins affect the brain, kidneys, liver. Delayed medical care can lead to death from intoxication.
Symptoms of gangrene-decubitus
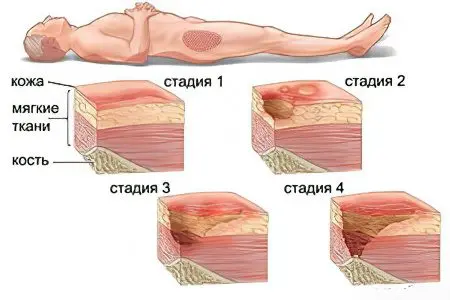
The process develops gradually, starting with blanching of the skin in the area that is subjected to pressure. There is a decrease in the sensitivity of the skin to pain and temperature changes. On the second or third day, swelling of the subcutaneous tissue begins, skin areas become brown.
How to prevent bedsores:
To reduce pressure on the tissues, the bedridden patient should be encouraged to move: turn him from side to side, if possible, move him to a sitting position;
Regularly massage problem areas (between the shoulder blades, on the sacrum, along the spine);
Use anti-decubitus mattresses.
Without treatment, an infectious process joins the symptoms of a bedsore, which is expressed by hyperthermia, weakness, nausea, and increased sweating.
Diagnosis of gangrene
Visual examination and analysis of the patient’s complaints in most cases is sufficient to establish a diagnosis.
To clarify the nature of gangrene and determine the sensitivity of pathogenic bacteria to antibiotics, the doctor prescribes laboratory tests:
Complete blood count – a decrease in the level of leukocytes below 4 * 109 /l is a sign of reduced immunity;
Biochemical blood test – can detect the onset of kidney failure;
Urinalysis – with anaerobic gangrene, protein or glucose appears in the urine;
Bacterial culture from the affected area – performed within a week;
The Bethe test is used to determine the type of gangrene, for this a piece of tissue is taken from the gangrenous area and placed in 4-6% sodium chloride solution, the floating of the sample is a sign of anaerobic gangrene.
Similarly, the results of an X-ray examination of the affected limb are interpreted. Gas bubbles in the picture are a sign of anaerobic gangrene.
Treatment of gangrene
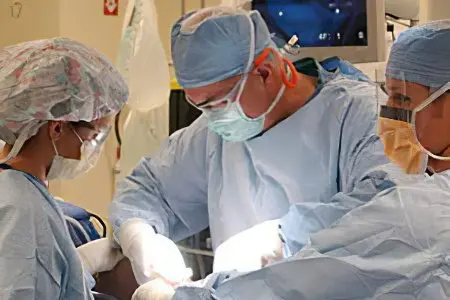
The most effective treatment for gangrene of the extremities is surgery. The hand or shin of the leg affected by dry or wet gangrene is amputated. In case of intoxication with the waste products of pathogenic bacteria, antibacterial drugs or an infusion of crystalloids are prescribed:
Ringer’s solution;
0,9% sodium chloride solution.
These universal tools cover most varieties of pathogens, since there is often no time for differential diagnosis.
Naturally, the doctor seeks to preserve the limb as much as possible.
Treatment of gas gangrene of the legs takes place in several stages:
Remove all dead tissue.
Perform “lamp” incisions along the skin and adipose tissue for a constant supply of air and reduce the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
Appoint reception of several antibiotics, antigangrenous serum.
Perform intravenous infusions of crystalloids up to 4-5 l / day.
Ineffective treatment of gas gangrene of the extremities is completed by amputation, provided that the disease has not passed to the patient’s torso.
Prognosis of the disease

Even with a favorable prognosis for the course of dry and wet gangrene, the disease ends with amputation of the limb and disability of the patient. The outcome of noma in 90-95% of cases due to significant intoxication is the death of the patient. With gas gangrene in 30-40%, death occurs due to damage to internal organs.
Complications of the disease affecting the gallbladder or appendix have a favorable prognosis. After surgery on the affected intestine, you have to follow a diet and take medication throughout your life. Complications on the lung force the patient to constantly suffer from shortness of breath, respiratory failure.
Cured gangrene does not affect life expectancy, but its complications worsen the quality of life. For adequate prevention of the onset of gangrene, it is necessary to immediately treat any wound with an antiseptic and seek medical help. Even with adequate treatment of gangrene, death or injury to the patient is possible. This probability increases with gangrene in children, patients with weak immunity, as well as with too late access to a doctor.









