Contents
What is type 2 diabetes disease
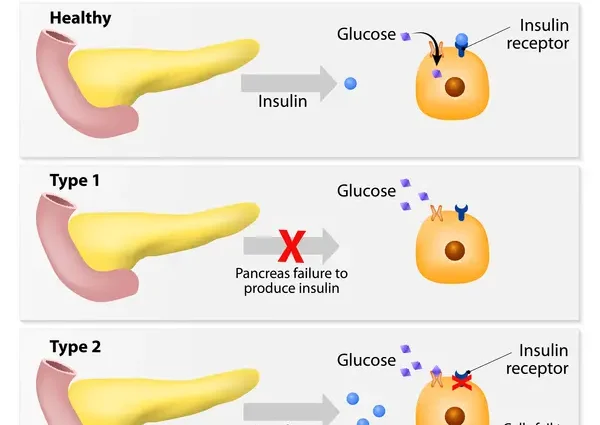
To understand what type 2 diabetes is and how it occurs, you need to delve a little into biology and anatomy. Let’s start with glucose. It is in the blood of each of us, as it is the main source of energy for humans. Glucose enters the body either with food, which contains carbohydrates, or from the liver, where glucose is stored in the form of glycogen. To become a source of energy, glucose must enter the cells of the body and this is where insulin is needed.
The hormone insulin is produced by special cells in the pancreas. To use an analogy, insulin is like a key that unlocks the tissue cells in our body so that glucose can enter. When this happens, blood sugar levels drop.
What happens in diabetes? In type 1 diabetes, the cells that produce insulin are destroyed, so patients have to take the hormone “from the outside” – hence the name insulin-dependent diabetes. In type 2 diabetes, the picture is different. First, the body develops resistance to insulin – insulin resistance. Simply put, the hormone is produced, only the tissues need a lot more of it so that glucose can get into them. One of the reasons for this condition is obesity – adipose tissue interferes with the work of insulin. Secondly, in type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance can be combined with insufficient production of insulin – this is called insulin secretion deficiency. The reasons for this may be different, for example, inflammatory processes in the pancreas.
Since insulin is still produced in people with type 2 diabetes, this disease is called non-insulin-dependent diabetes.
How Type 2 Diabetes Occurs
Most often, type 2 diabetes affects people over 40 years of age, although in recent years doctors have noted that this form of the disease is getting younger. There are several causes and factors for the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Overeating, obesity: body mass index ≥ 25 kg/m2.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Family predisposition (if mother / father, sisters / brothers have diabetes, then you are at risk).
- Problems with the pancreas – they can affect the production of insulin.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Gestational diabetes mellitus – it develops during pregnancy.
- Lipid metabolism disorders.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
The most insidious thing about type 2 diabetes is that it actually does not manifest itself in any way until complications begin. The classic symptoms of type 2 diabetes are the same as those of many diseases:
- Thirst and dry mouth.
- Rapid urination.
- Weight changes.
- Constant hunger.
- Itching itch.
Can type 2 diabetes be cured
Type 2 diabetes itself is a chronic disease that cannot be completely cured, but can be successfully controlled.
“Treatment for type 2 diabetes begins with lifestyle modification, dietary changes and physical activity,” explains endocrinologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor of the endocrinology department of Belarusian State Medical University Evgeniya Stepanova. – Then they add hypoglycemic drugs in tablets – there are several classes of them. Sometimes they are prescribed in combinations.
The order of treatment depends on the stage of type 2 diabetes. With a slight increase in blood sugar, the diet may be enough to control the condition. What is the Type 2 Diabetes Diet? Mainly the exclusion or minimization of fast carbohydrates in the diet: sweet (sugar, cookies, sweets), starchy foods (bread, pasta), fat restriction (butter, fatty meat, sausages).
It is recommended to supplement the diet with regular physical activity – at least three times a week for 30-60 minutes. If there are indications, then drugs are prescribed to lower blood sugar. They act in two ways: either increase the production of insulin, or increase the susceptibility of cells to glucose.
“Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus are often transferred to insulin therapy if the tablet treatment is ineffective,” explains Evgenia Stepanova. – It depends on the patient, the worse his performance, the more likely he is to switch to insulin.
Diagnostics
Type 2 diabetes is diagnosed by measuring glucose levels. If it is above certain values, then an appropriate diagnosis is made.
“You can donate blood glucose from a finger – capillary blood, from a vein – venous, or donate blood for glycated hemoglobin, it reflects the average level of glucose in the blood for three months,” explains the endocrinologist. – The upper limit of the norm for glucose in capillary blood is 5,5 mmol per liter, and from a vein – 6,1 mmol per liter.
These surveys can be supplemented by others:
- neurological – the study of tissue sensitivity.
- Ultrasound with dopplerography and measurement of blood pressure in the vessels of the lower leg.
- scanning of the arteries of the lower extremities.
- transcutaneous oscimetry, which also allows you to assess the blood flow in the tissues.
Modern methods
Scientists continue to search for new drugs and treatments for type 2 diabetes. Some of the new drugs have already attracted the attention of doctors.
– Among the modern drugs that are used to treat type 2 diabetes, one can note such drugs as glucagon peptide agonists. These are unique drugs that are used in the form of injections. One such drug can replace several at once: it alone lowers the level of glucose in the blood, normalizes the lipid spectrum, that is, cholesterol, normalizes blood pressure, reduces appetite, reduces weight – that is, it helps to achieve all the goals that we set in the treatment of diabetes 2 types. I note that this is not insulin, this is another hypoglycemic drug, – says endocrinologist Evgenia Stepanova.
Popular questions and answers
Is it necessary to follow a diet for diabetes?
But since a sharp change in eating habits is stressful, doctors are now trying to set patients up for a careful change in diet. The glycemic index of products is at the forefront. It reflects how quickly sugar from them is absorbed into the blood: the higher the index, the higher the absorption rate.
The main principle of nutrition for type 2 diabetics is to eat more low-glycemic foods throughout the day and dose your meals.
What happens if you don’t follow a diabetes diet?
The higher the blood sugar level, the sharper the jumps in glucose, the more small vessels suffer and the risk of complications increases: retinopathy – eye complications, nephropathy – kidney pathology, heart attacks and strokes, damage to the vessels of the lower extremities with the development of diabetic foot syndrome, which sometimes ends gangrene and amputation,” explains the endocrinologist.
Who should get test strips and how many?
— All patients should be provided with test strips. Preference is given to children and pregnant women, as well as patients with diabetic foot syndrome. By order of 2012, 750 test strips per patient with diabetic foot syndrome are required per year, explains Evgenia Stepanova.
What are the benefits for type 2 diabetes?
– Patients are provided with all hypoglycemic drugs, including insulin, free of charge. If patients are prescribed antihypertensive drugs, enzyme preparations, hormones, they receive them free of charge. Depending on the polyclinic, they are entitled to a day hospital twice a year free of charge. If a patient with diabetes mellitus has a disability due to this disease, then at the expense of the state he is provided with sanatorium-and-spa treatment on a first-come, first-served basis, ”explains the endocrinologist.