Contents
What is tubal ligation?
Tubal ligation is a surgical operation during which the fallopian tubes are blocked, ligated or cut off. According to many experts, this is a reliable method of contraception, but there is still no 100% guarantee, and already a year after such an operation, 5 women out of 1000 can become pregnant, and after another 10 years – 18 women out of 1000.
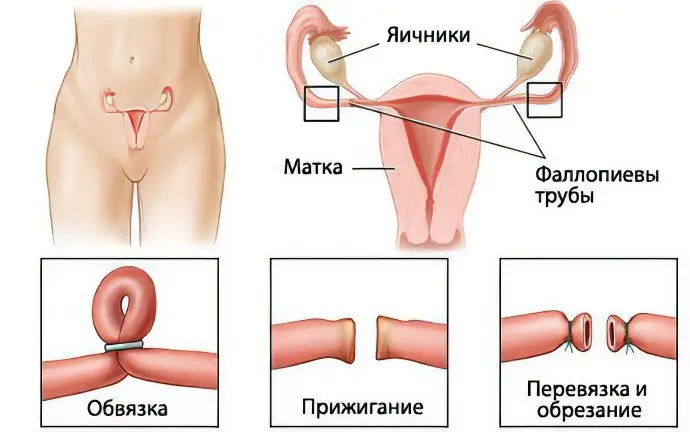
Ineffective ligation occurs in the case of tubal fusion, when there is a passage into which spermatozoa penetrate, as well as in case of improperly performed sterilization.
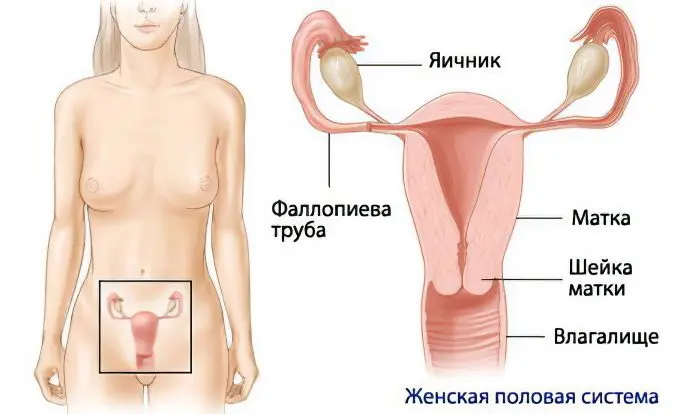
To understand the essence of the operation, it is necessary to recall that the reproductive system in women includes two ovaries, two fallopian tubes, a uterus and a vagina. Normally, both ovaries are able to expel an egg ready for fertilization (this process is called ovulation). This phenomenon occurs on the 12-17th day of the menstrual cycle every month. The egg is released from the ovary into the fallopian tube and travels through it to the uterus due to muscle contractions and movements of small, hair-like cilia.
Types of surgical intervention
Laparoscopy
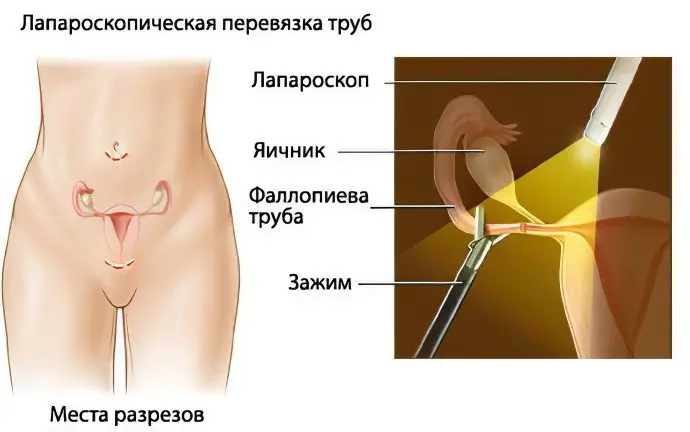
Closing of the fallopian tubes or tubal sterilization can be done by laparoscopy with the introduction of a microscopic camera and a surgical instrument through a small incision made in the abdomen. The operation is done under anesthesia in two ways.
Laparoscopic dressing begins with gas injection into the abdomen to make the procedure more comfortable. The fallopian tubes are then sealed with a ring, clip, or electric current.
The upper section, as seen in the figure, is intended for the indicated device, and the lower one is for the clamp. The dotted line marks the sites of incisions.
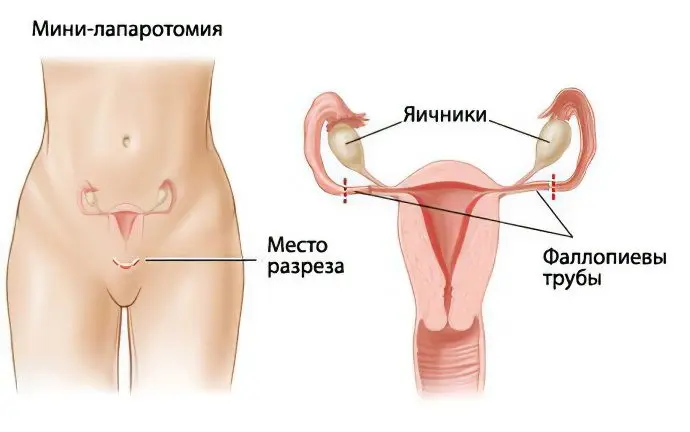
Mini-laparotomy
A mini-laparotomy (“mini-paw”) involves removing part of the tube and sealing the rest with sutures, tapes, clips, or electric current. Any woman over the age of 35 who does not want to give birth again can use this method of protection against unwanted pregnancy. This method of contraception is irreversible, does not allow you to conceive a child naturally, so this decision should be well thought out. Both fallopian tubes are crossed in a woman.
A mini-laparotomy is performed through an incision that is less than five cm long. As part of the operation, the surgeon makes two minor incisions. One of them falls on the pubic area. This type of intervention allows you to permanently prevent the onset of pregnancy.
An open laparotomy is performed through a significant incision in the abdomen.
It is recommended in the situation when:
An abdominal operation is required for the purpose of a caesarean section;
Have pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, or require pelvic surgery for another reason.
In some cases, resort to postpartum tubal ligation. Since in this case the fallopian tubes are located higher in the abdominal region, the incision is made below the level of the umbilicus. It is best to carry out the operation in the first one and a half days after the birth of the child. Because after 48 hours, the uterus shrinks, and postpartum tubal ligation will be much more painful and problematic.
It should be noted that laparoscopy is usually performed under general anesthesia. But all forms of this operation can be carried out not only under general, but also under local (epidural) anesthesia.
Tubal implant method
Implants are introduced into the area of the fallopian tubes without surgery and without anesthesia. It takes no more than half an hour, before the start of the operation, the woman should sit in a chair, as usual at a gynecologist’s appointment. First of all, the cervix should open – this will help avoid damage to it.
Next, the specialist introduces a catheter through the vagina into the cervix, then into the organ cavity, and then into the fallopian tube: first into the first, and then into the second. A catheter is used to place implants in the tubes. In some cases, cramps similar to menstrual cramps occur during the procedure.
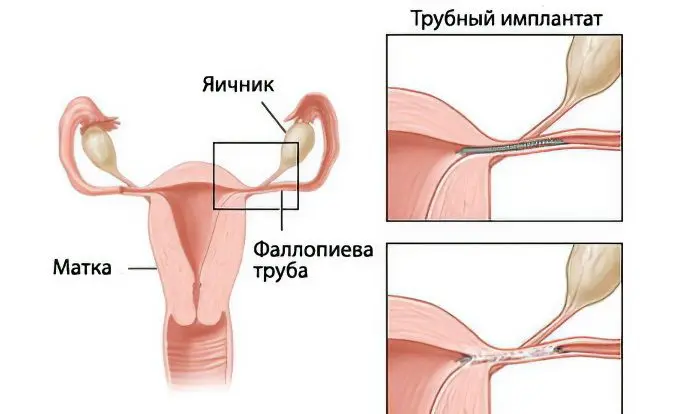
Over time, a scar tissue forms, which grows near the implants and overlaps the fallopian tubes. The presented type of operation makes it possible to prevent the removal of the egg from the ovaries into the fallopian tubes. As you know, it is in them that fertilization becomes possible.
In order to make sure that the pipes are securely closed, it is necessary to take an x-ray. In the first three months after implantation, it is recommended to change the method of contraception. At the end of this period, a dye is introduced into the area of u100buXNUMXbthe uterus and an x-ray examination, or hysterosalpingography, is again performed. This will make sure that the implants have not moved and the tubes are XNUMX% blocked by scar tissue.
Operation with an incision of the suprapubic zone
Conventional surgery with an incision in the suprapubic area of the abdomen requires a long stay in the clinic. After the operation, a scar is formed. With a culdoscopic operation, which is a puncture of the posterior wall of the vagina, no scars remain, there are no complications, and tissue heals quickly. It is known that such sterilization does not cause hormonal disturbances, libido and a normal menstrual cycle are preserved.
Mature eggs are absorbed in the abdominal cavity, and women have no fear of a possible unwanted pregnancy. As a rule, most patients prefer postpartum sterilization, which is performed immediately after childbirth. The operation usually takes less than 30 minutes and does not require a long hospital stay. Women after such a procedure may experience minor pain and cramps in the abdomen, bloating, decreased physical activity, dizziness, nausea.
Should I use this method of contraception?
Tubal ligation is a radical type of contraception that is almost impossible to reverse in the future.
Voluntary sterilization is allowed for women of reproductive age who already have at least one child and do not want to have children in the future. Tubal ligation is indicated for a number of diseases that can pose a threat to life and health during pregnancy.
Many women have contraindications to taking hormonal contraceptives and the use of intrauterine devices, then sterilization becomes the only reliable means of protection. Tubal ligation is highly effective and is the most popular method of contraception among mature couples with children. However, a serious complication of sterilization is an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Although doctors warn that tubal ligation is irreversible, and ask for good thought before doing it, if necessary, you can try to restore the functions of the tubes, after which pregnancy occurs in 60-80% of women. These are microsurgical operations that take place under general anesthesia, the difficulty arises with the reunification of the dissected ends of the fallopian tubes.
Before you make a decision, you should be aware of the statistics that show that many women who have had tubal ligation surgery regret it. Science does not stand still, and today a new, simpler and safer method has been developed that does not require intervention in the abdominal cavity. Its essence is the introduction of various drugs or devices into the uterus that cause local damage and an inflammatory reaction, as a result of which the connective tissue grows and the fallopian tubes become impassable.
The effectiveness of this method is more than 99%, but it is not yet used in clinics in the CIS countries.
The most reliable way is to simply cut the pipe with a scalpel or an electric knife, after which a puncture is made with a needle with a nylon ligature in two places of the pipe in its middle part. The ends of the threads are tied and cut off. Also no less reliable is sterilization by the type of resection of a part of the tube with immersion of its ends under the peritoneum.
What to expect after surgery?

After tubal ligation
After a successful tubal ligation, the patient returns to normal life within a day. However, minor bleeding from the vagina may occur. After laparoscopy is completed, abdominal distention is noted due to the gas used to lift the skin and muscles above the peritoneal organs, which is necessary for the operation. This effect usually wears off within a few days.
It is likely that there will be pain in the back or shoulders due to gas in the abdominal cavity, which will also pass after the gas is fully absorbed. It is permissible to take a shower a day after the operation, but without rubbing and other influences during the week.
Besides:
You can have sex if there is no pain;
Rest from cleaning, washing and household chores is recommended;
There is no need for an additional method of birth control.
After implant placement
After the implants are inserted, women return to their daily activities within a day. Precautions include using another method of contraception for three months and until an absolute blockage of the fallopian tubes is confirmed by X-ray.
How effective is such an operation?
Tubal ligation at the entrance to the uterus, as well as the introduction of implants, cannot be considered one hundred percent effective methods for preventing unwanted pregnancy.
There is a relatively small chance of getting pregnant after the tubes have been tied in this way. Five out of 1000 women experience this 12 months after surgery. 10 years after the intervention, at least 18 out of 1000 may already be in position.
This can happen if:
The tubes have grown together or a new passage has formed through which the egg will be fertilized by the sperm;
The dressing was done incorrectly;
The woman was already pregnant at the time of the operation.
What if tubal implants were used? This method does not have long-term statistics, since it is relatively new. Ongoing studies show that in two years, less than one in 100 women with implants become pregnant.
Reasons for visiting a specialist

You should immediately consult a doctor if symptoms of pregnancy are noted. This may be a failure in the menstrual cycle, increased sensitivity of the breast, as well as nausea. Causes for concern should be considered pain on either side of the lower abdomen, loss of consciousness and dizziness.
Risks and complications after bandaging
Tubal ligation is characterized by the fact that after it there are no severe complications. Less serious consequences include infection and dehiscence. It occurs in 11% of women after mini-laparotomy and in 6% after laparoscopy. More serious complications include tangible and dangerous blood loss, problems that are provoked by general anesthesia, as well as damage to organs during the operation and the need for even more significant incision.
Although there are fewer complications with laparoscopy than with other types of tubal ligation surgery, these complications can be more threatening. For example, when introducing a laparoscope, damage to the bladder or intestines is likely. The risk of surgery increases if the woman has diabetes, is overweight, is addicted to nicotine, or has a history of cardiovascular disease.
Risks and complications after tubal implants
After implantation, pain in the pelvic area may not go away. In such situations, the implants are removed six weeks after insertion into the fallopian tubes. This increases the risk of developing diseases of the pelvic organs. Before the implementation of the intervention, it is recommended to undergo an examination. This will make it possible to make sure that the patient does not have infectious diseases of the reproductive system.
The risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy
If the process of resection of the fallopian tubes or implantation was unsuccessful, and the woman nevertheless became pregnant, then her probability of forming an ectopic pregnancy increases many times over. This can happen several years after surgery, and most likely after three years or more.
What should I think about?

It is necessary to take into account the following points that are associated with tubal ligation and implant placement:
The menstrual cycle and menopause will remain unchanged because the egg will be produced every month;
Sexual desire will not change and even greater looseness is likely, because the woman stops worrying about unwanted pregnancy.
Advantages
The main advantage is the ability to have sex and not be afraid to get pregnant. Although this is a fairly expensive procedure, it is a one-time expense. In addition, sterilization does not require rehabilitation costs.
Disadvantages
Tubal ligation, like the introduction of tubal implants, does not create protection against those diseases that are sexually transmitted. Including the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). For full protection, it is necessary to use condoms from the very beginning of sexual intercourse.
Other considerations
Restoring the fallopian tubes to their original state involves the return of their former connection. The probability of a positive result with such a restoration is extremely low. It should be remembered that during tubal ligation, a woman must be 100% sure that in the future she will never want to have a child of her own.
Those women who are most likely not recommended for resection of the fallopian tubes include those who:
Has not reached the age of 30. This is especially true for those who have never given birth. According to statistics, women who have had a tubal resection in their 20s and 30s have a desire to restore fertility in the future;
Faced problems during pregnancy. Those women who decide on a resection of the fallopian tubes due to stress due to a complicated pregnancy almost always regret their decision in the future;
They do not have a stable and serious relationship that may yet appear;
Expect that they will be able to restore childbearing function in the future if they change their mind;
Does it because they are coerced by spouses, family members, etc.;
Have given up looking for an alternative method of contraception and do not trust any of them.
Thus, tubal ligation is a serious surgical intervention, for which strong arguments are needed. This operation is absolutely safe, but irreversible, so female representatives are advised to think carefully before resorting to it.










boolgson yma irgej tailj jiremsen bolj boloh boluu