Contents
Psoriasis is one of the most mysterious and difficult to treat diseases. It is impossible to get rid of it once and for all. The only thing that patients can count on is to achieve a stable remission. Moreover, there is no single and generally accepted method of treating psoriasis by the world medical community, just as there is no drug that one hundred percent guarantees the onset of remission.
The tactics of treating this most complex skin disease depends on a number of parameters:
Type of psoriasis;
The age of the patient;
The presence of concomitant pathologies;
Severity and chronology of exacerbations;
Location and size of lesions.
The treatment of psoriasis is almost always complex: some medications and procedures are aimed at eliminating the very cause of psoriatic exacerbations, some are designed to alleviate the unpleasant symptoms of the disease, and some are needed to maintain the body’s own defenses. The sad thing is that almost half of the patients do not help any of the three approaches to the treatment of psoriasis. And the drug that allowed a thousand people to drive psoriasis into stable remission for several years may very likely have no effect at all on another thousand.
In this article, we will discuss all currently known means and methods of treating psoriasis, even the most controversial ones, and we will try to answer the question of where to start for a person who has heard a disappointing diagnosis from a doctor. During the use of popular methods, procedures and medicines, it was possible to collect impressive statistics on their effectiveness. We invite you to read the reviews of patients and find out how many percent of the respondents really helped this or that method of treating psoriasis.
Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of psoriasis treatment methods
According to the results of numerous surveys of people suffering from psoriasis, the hit parade of the best treatments for this disease looks something like this:
Biologicals – more than 33% of patients completely clear the skin in 3 months of therapy (the cost of a course of treatment is from $ 20 and more);
37% – Ointments based on grease (Cytopsor, Kartalin, Akrustal, Magnipsor, Antipsor);
33% – Compliance with a special diet – that is, the rejection of products, the use of which provokes exacerbations of psoriasis;
26% – Climate change, balneotherapy and spa treatment. Almost a third of patients note that they feel better simply due to moving to an area where there is a mild maritime climate and clean air. The same number of patients avoid winter exacerbation helps annual rest in a sanatorium.
Here is a list of the best specialized resorts:
Sulfide mineral waters: Pyatigorsk, Yeysk, Kayakent, Kemeri, Khilovo, Hot Key, Sochi, Matsesta, Taminsk, Usolye, Krasnousolsk, Black Waters, Sergievsky mineral waters, Transcarpathian Sinyak;
Radon mineral waters: Belokurikha, Molokovka, Mironovka, Khmilnik, Zhitomir, Tskhaltubo, Pyatigorsk, Krasnousolsk, Nilova Pustyn.
Sodium chloride mineral waters: Druskininkai, Kuldur, Ust-Kut, Angara, Sosonovsky mineral waters, Lake Uchum, Lake Shira.
rape mineral water: Odessa, Evpatoria, Saki, Berdyansk, Lake Elton.
Healing mud: – Anapa, Evpatoria, Kuri, Luben-Veliky, Kayakent, Yeysk, Kemeri, Saki, Klyuchi, Lake Elton, Lake Uchum.
Children’s sanatoriums:“Lenin rocks” in Pyatigorsk, “Falcon” in Anapa, “Red assault and sanatorium named after N. A. Semashko in Sochi;
19% – Salt baths – are very effective both in the framework of spa treatment, and as home procedures. Sea salt contains potassium, magnesium, iodine and other beneficial minerals that have a beneficial effect on the skin affected by psoriasis, relieve itching and flaking, and even improve the patient’s sleep due to a relaxing effect on the nerve endings. It is recommended to purchase high-quality, natural sea salt in a pharmacy and take baths 2-4 times a week at night;
14% – Ointments based on tar (Colloidin, Anthramin and Anthrasulfonic ointment) – relieve itching well, contribute to scarring of psoriatic plaques and falling off of crusts;
12% – Selective phototherapy (SPT) – a physiotherapeutic method for the treatment of psoriasis, based on the therapeutic effect on the skin of ultraviolet radiation with a certain wavelength. Not suitable for all patients, but for some it allows for 1,5-2 months of regular procedures to achieve a two-year remission;
12% – Strong hormonal ointments – at first they give a very good therapeutic effect, but then the condition of the patients deteriorates sharply, you have to apply the ointment more and more often, and it helps worse and worse. A vicious circle is formed, comparable to drug addiction. Prolonged use of such drugs leads to dysfunctions of the adrenal cortex and gradual atrophy (necrosis) of the skin;
12% – Baths, steam rooms, saunas and pools – absolutely harmless, but ineffective method of treating psoriasis. According to most patients, staying in a steam room, followed by swimming in cool water, allows you to temporarily soothe the itching and ensure a restful sleep, which in itself is not bad. But there are also people whose psoriasis, on the contrary, is exacerbated by excessive humidity and sudden changes in temperature;
12% – Sports and active recreation – any pleasant physical activity, whether it’s cycling, dancing, hiking or playing football, helps to improve well-being, strengthen immunity, improve mood and self-esteem of the patient, which cannot but have a beneficial effect on the course of psoriasis;
12% – Ointments based on calcitriol – these drugs saturate the epidermis with the active form of vitamin D, penetrate well into the blood and normalize calcium metabolism, and this almost always leads to a decrease and gradual disappearance of psoriatic plaques. Of the minuses: ointments are expensive, the best are German-made, they are sold mainly on order;
10% – Ointments based on salicylic acid – strictly speaking, they do not treat psoriasis at all, but they contribute to the healing of plaques and the falling off of crusts. After the skin is cleansed of the stratum corneum, it is advisable to start treatment with other means, for example, the same grease. Salicylic ointments in a sense prepare the epidermis, as they improve the absorption of active substances;
8% – Weak and combined hormonal ointments – often used during seasonal exacerbations of psoriasis, when no other methods can stop the growth of plaques and unbearable itching. The treatment of psoriasis with hormonal ointments should be approached very carefully, not resorted to unnecessarily and canceled gradually;
8% — Enterosorbents – a good addition to the diet, they help cleanse the intestines of debris and normalize, thereby, the composition of the blood, which will not be slow to have a positive effect on the course of psoriasis;
Ointments for psoriasis based on grease
On sale you can find many ointments for the treatment of psoriasis, including those based on grease (by the way, one of the most effective, not counting hormonal ones), which one to choose? Everything is very individual, because the composition of the preparations is different, and even the concentration of grease in them is not the same. Although it is called the main active ingredient, it follows from most instructions that there is only a tenth of pure grease there, and everything else is additional components of dubious effectiveness.
To choose the best option for yourself, it is recommended to take one course of treatment with ointments of each group and compare the effect.
For comparison, here is the composition of the most popular solid oil ointments for psoriasis:
Solipsor Solipsor – fatty grease, petroleum jelly, lanolin, talc, potato starch, birch tar, olive oil, pumpkin seed oil, extracts of garlic, burdock, walnut, succession, calendula, birch and licorice; |
Magnipsor Magnipsor – fat grease, mineral salts of the Dead Sea, extracts of medicinal plants, vegetable oils of sea buckthorn, pumpkin and tea tree; |
Antipsorus Antipsor – fatty grease, vaseline, lanolin, camphor, linseed oil, extracts of string, birch, cudweed and celandine, chitin fibers from crustacean shells; |
Kartalin Kartalin – fatty grease, salicylic acid, bee honey, lysozyme, eucalyptus and lavender oil, string and chamomile extracts; |
Picladol Picladol – fatty grease, lanolin, birch tar, lard, fir oil, celandine extract; |
Cytopsor Cytopsor – fatty grease, petroleum jelly, purified mineral oil, citric acid, castor oil, boric acid, calendula alcohol tincture; |
Psorium Psorium – fatty grease, extracts of calendula, chamomile, rose hips, St. John’s wort, yarrow, wheat germ, aloe, honey and beeswax, eucalyptus, cedar and sea buckthorn oils, vitamins A, B, E and D; |
Psorilam Psorilam – fatty grease, petroleum jelly, lanolin, stearin, zinc pyrithione, glyceryl monostearate, boric and salicylic acids; |
Psori cream Psori-cream – fatty grease, vaseline, lanolin, naftalan oil, birch tar, mint and sea buckthorn oils, extracts of string, licorice, sage, milk thistle and eucalyptus. |
Diprosalic Diprosalic is a Swiss topical preparation with anti-inflammatory and keratolytic effects. |
Antipsoriasis The composition of the preparation contains aqueous extracts of white birch leaves, tripartite succession, greater celandine, medicinal calendula, marsh cudweed, lanolin, camphor, linseed oil, vaseline oil, medical grease. Not registered as a medicinal product. |
Medication
When a patient has been diagnosed with moderate to severe psoriasis, or when other treatments fail, the doctor may suggest an oral or injectable medication option.
The most common oral and injectable medications used to treat psoriasis include:
Biological preparations
This class of drugs works on your immune system, stopping inflammation from affecting your immune system. These drugs are administered intravenously.
Doctors prescribe biologics to patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. In addition, they are prescribed to those patients who have not responded to other treatments or because of possible side effects. Biological preparations are not recommended for use in patients with a weak immune system or an organism weakened by any infection. Before you start taking biological drugs, your doctor should conduct a complete examination for tuberculosis and the presence of other infectious diseases.
Price? Biological drugs are quite effective in the treatment of psoriasis, but are expensive. According to 2014 studies, treatment with adalimumab can cost over $39, with etanercept over $000 per year, and with ustekinumab over $46 per year.
Retinoids
Retinoids reduce the production of skin cells, however, as soon as you stop taking them, the symptoms of psoriasis are likely to return. Side effects from treatment with retinoids are extremely unpleasant: hair loss and inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth.
Women who are pregnant or planning a pregnancy in the next three years are strictly forbidden to take retinoids due to the high risk of birth defects in the fetus.
Other techniques
Surgery

No, this is not at all about using a scalpel to remove plaques that have not healed for years, as you might think. Domestic specialist, Dr. V. Martynov, proposed a very interesting, and most importantly, effective method of surgical treatment of psoriasis. He performs an operation on his patients to restore the valve of the small intestine, which is responsible for cleansing this part of the intestine from toxins and pathogenic microflora. As a result, after a few months, immunity is restored, and a person forgets about psoriasis for at least a few years.
Phototherapy with narrowband 311 nm ultraviolet radiation
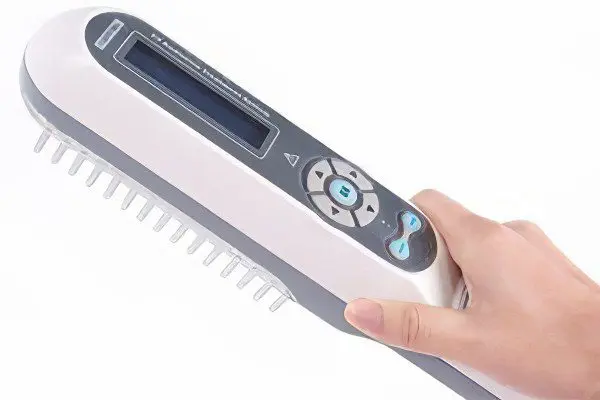

It is this method of ultraviolet irradiation that shows the best efficiency in the treatment of psoriasis. Narrowband phototherapy is suitable for patients with any skin type, including those with very fair and sensitive skin. The incidence of side effects is minimal, the procedure takes only a few minutes, and after 10 weeks of regular visits to a physiotherapist, a stable remission usually occurs.
Over the past few years, lamps for narrow-band phototherapy sessions have appeared in many public medical institutions, so the technique has become more accessible.
PUVA-therapy
PUVA therapy is a type of phototherapy. This method of treating psoriasis works using a photoactive substance and subsequent irradiation of the patient’s skin with ultraviolet radiation type A (wavelength from 315 to 400 nm).
A positive result with PUFA therapy is achieved in more than 80% of cases. The effect is already noticeable after the first 4-6 sessions, and remission can last up to several years.
PUVA therapy slows down the growth of epidermal cells, and this is achieved due to the impact on the patient’s body of ultraviolet irradiation type A after taking photoactive drugs of the psoralen group.