Contents
Trichomoniasis in cattle is often the cause of miscarriages and infertility. This causes significant economic damage to farms and farms. The most common disease occurs in cattle in some regions of Our Country, Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan and the countries of Central Asia. Adult individuals who have recovered from trichomoniasis are resistant to these parasites in the future, but the disease often leads to a number of complications associated with reproductive function, after which many cattle are subject to culling.
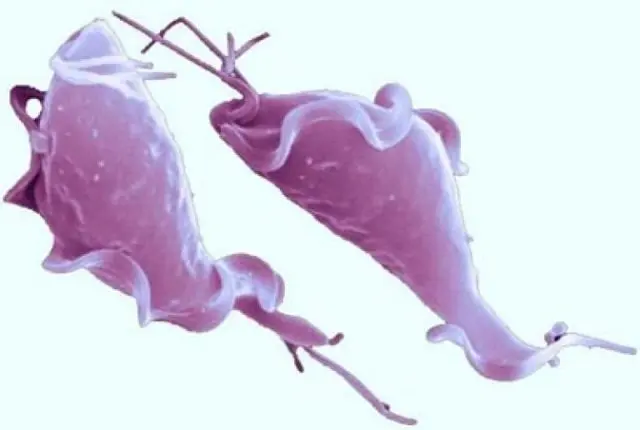
What is trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis (Trichomonosis) is an invasive disease that occurs in acute and chronic forms. Manifested by abortion in cows at an early stage of pregnancy, metritis, vaginitis, in bulls – impotence, balanoposthitis (inflammation of the inner layer of the prepuce and the membrane of the penis). Trichomonas are able to move towards the flow of tissue fluids, so they can easily move in the genitourinary system of the animal.
Parasites are quite active outside the body of cattle, they can exist separately from the host for up to a month. Moisture, manure, bedding, urine, various care items and hygiene products become a temporary habitat for Trichomonas. In the body of cattle, parasites can live up to 2 years in the vagina, urethra, prostate, seminal ducts.
Pathogen and routes of infection
Trichomoniasis is caused by single-celled parasites of the Trichomonade family. They have an oval, pear-shaped, spindle-shaped body with three flagella in front and one behind them. The cell body consists of cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuoles. The movement is carried out with the help of flagella, around the axis of the body forward. The main feature of this species of Trichomonas is the presence of a lateral undulating membrane of the axial rod – the axostyle. Other flagellar protozoa do not have such an organ.
They reproduce by simple, multiple division in the longitudinal direction or by budding, depending on the type of pathogen. Getting into adverse environmental conditions, outside the host organism they form capsules with a strong shell – cysts. They feed on blood cells, mucus, enzymes. Penetrating into the genital organs of cattle, they immediately begin to multiply. After a few days, Trichomonas cause an inflammatory process on the mucous membranes. Their vital activity is accompanied by the release of certain enzymes that can disrupt the connection between the uterus and the embryo and prevent the full nutrition of the fetus.
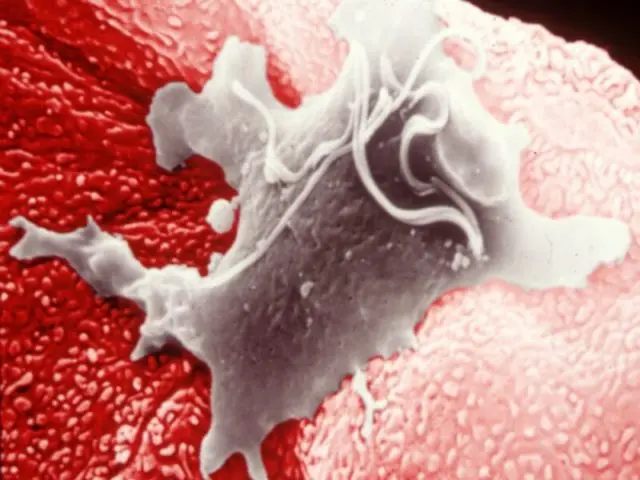
The source of infection are animals infected with trichomoniasis. Especially dangerous are individuals who have been carriers of the disease for many years and do not show clinical symptoms. Trichomoniasis is also transmitted through instruments during artificial insemination or if the male’s sperm is infected. Pathogens can also be found on an artificial vagina. When semen is collected, microorganisms can infect healthy animals. Trichomoniasis can be transmitted by household contact when using hygiene products, such as towels, when wiping the perineums of sick and healthy animals.
Trichomonas are able to cause pathological processes in the body not only by themselves, but also by the products of their vital activity. The microflora of the mucous membranes exacerbates inflammatory processes. During the pregnancy of cows, this leads to malnutrition of the fetus, improper synthesis of glycogen and some hormones, and a decrease in the production of progesterone and endorphins. The consequence of trichomoniasis is the death of the fetus and damage to tissues and mucous membranes.
Symptoms of trichomoniasis in cattle
In cows and bulls, the symptoms of trichomoniasis are slightly different. The first signs of the disease are visible a few hours after infection, since trichomoniasis does not have an incubation period.
Symptoms of trichomoniasis in cows:
- a slight increase in body temperature;
- constant movements of the hind limbs;
- manifestation of anxiety;
- constant fanning of the tail;
- looking back;
- loss of appetite;
- decrease in milk production;
- urge to defecate;
- discharge from the genital organs similar to pus;
- miscarriage in pregnant cows at an early stage;
- swelling of the vulva;
- redness of the vagina;
- rash on the mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- pain on palpation;
- rashes appear on the bottom of the vagina and around the cervix – dense nodules the size of a pea.
In bulls, the clinical manifestations of trichomoniasis are weaker, the symptoms are as follows:
- redness, inflammation of the prepuce;
- pain when urinating;
- purulent discharge from the penis;
- the mucous membrane is covered with nodules, then necrotic ulcers;
- discomfort during palpation of the penis.
After the pathogen moves into the seminal appendages, a number of symptoms disappear, the individual becomes a carrier of the disease.

The acute form of trichomoniasis in cattle ends with recovery within 1-2 months. If the uterus is infected, the discharge becomes more abundant, they indicate the development of purulent-catarrhal trichomoniasis. Animals during this period are not fertilized, and pregnant cows miscarry. In sick animals, barrenness, repeated hunting, overgrowths are observed, pyometritis develops – an accumulation of pus in the uterine cavity.
Chronic manifestations of trichomoniasis in cattle are poorly expressed. In males, the disease proceeds without symptoms, but their potency decreases and their reproductive function weakens. Cows have frequent abortions, and milk production is significantly reduced.
Trichomoniasis in cattle does not lead to death of animals. But in pathoanatomical studies, thickening of the uterine wall, purulent exudate up to 5-7 liters, vestibulitis of the vaginal mucosa, purulent-catarrhal vaginitis, cervicitis are detected in cows. The aborted fetus and the placenta are edematous, the oviducts are slightly thickened. Ovarian cysts are often found. In bulls, there are many small knots on the genitals. Traces of inflammation appear in the testes, seminal ducts, sex glands.
Testing cows for trichomoniasis
The diagnosis of trichomoniasis in cattle is made on the basis of the detection of Trichomonas by microscopic examination, when sown on a nutrient medium. For examination, mucous secretions from the genital organs of cattle, sperm or an aborted fetus, part of the placenta are sent to the laboratory. Produce samples on the environment of Petrovsky, Volkov. In cows, parasites can be detected 8-20 days after infection, and in males at any time. When making a diagnosis, it is necessary to take into account the clinical manifestations of the disease, the mass character of trichomoniasis in the herd or its absence.
Treatment of trichomoniasis in cows
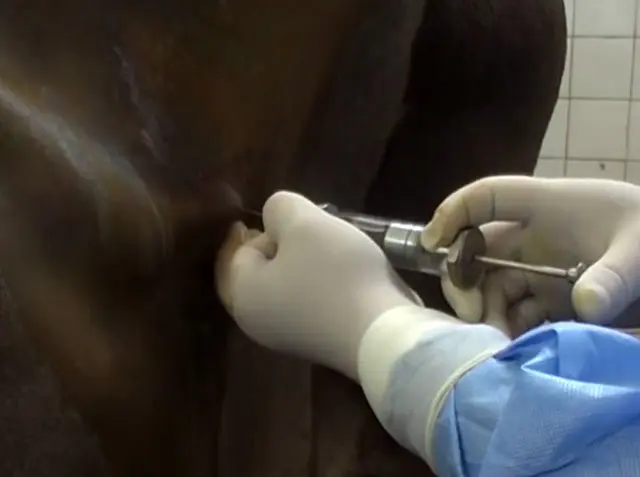
Treatment of trichomoniasis in cattle should be comprehensive, all drugs and procedures are prescribed by a veterinarian. Therapeutic measures are to free the genitals of infected animals from parasites and strengthen the general condition of the body. The following treatment regimen for trichomoniasis is usually prescribed:
- means for active contraction of the uterus to cleanse it of pus;
- regular washing of the vagina and uterine cavity with an antibacterial solution;
- metronidazole diluted with novocaine or saline is administered subcutaneously once a day for 1-3 days;
- from antibiotics appoint Trichopolum or Trichomonocide.
For the treatment of bulls, the same drugs are used, in addition to them, antiseptic ointments can be used. The genital organ, the foreskin can be treated with furacillin or prozerin for 7-10 days.
If trichomoniasis in cattle is detected on the farm, quarantine must be established. During this period, it is impossible to take animals out of the herd and bring in new ones.
Prognosis and prevention
As a rule, the prognosis of the disease in cattle is favorable, provided that trichomoniasis is recognized in a timely manner through laboratory tests, complex treatment prescribed by a qualified specialist, and repeated tests after complete recovery.

Despite the fact that trichomoniasis in cattle responds well to treatment, parasites can harm animals, after which cows and bulls lose their reproductive function. For the herd owner, this means huge economic losses. Therefore, the most effective method of control is the prevention of the disease. Main measures:
- The use of only artificial insemination of cows with the sperm of a healthy male. This will greatly reduce the risk of further spread of trichomoniasis in the herd.
- Cleaning and disinfection of the barn, stall, machines, tools. They must be processed regularly. For these purposes, soda ash, caustic soda, creolin solution are used.
- New individuals should be kept separately until tests for trichomoniasis are ready.
- Infected cattle are also kept in a separate room. It also needs to be processed daily with the use of special tools.
- Patients with trichomoniasis, males are subject to culling.
- Semen from cured bulls can be used after several negative tests.
- When artificially inseminating cattle, it is necessary to comply with basic sanitary standards; all instruments are sterilized before the procedure.
- If one infected individual is found, the entire herd of cattle should be examined for trichomoniasis.
- During the grazing period, livestock breeders should not allow contact with individuals from other farms.
- Be sure to periodically take bull semen for analysis.
Trichomoniasis spreads quite quickly, so it is important to quickly recognize the disease and start treating cattle. This will help to avoid an epidemic in the herd.
Conclusion
Trichomoniasis in cattle cannot be transmitted to humans, however, in any case, certain sanitary standards must be strictly observed when keeping animals. You should also know that the disease is not transmitted through dairy and meat products, but before slaughter, cattle undergo a mandatory examination. If there is the slightest suspicion of trichomoniasis, then after slaughter they take tests for the disease. If the results are positive, all affected organs and tissues of cattle are subject to urgent disposal.









