Contents
Toxoplasmosis is an infection caused by protozoa (toxoplasma). In adults, the disease is most often asymptomatic, but it harms the body. Toxoplasmosis is especially dangerous for pregnant women, since the infection can provoke congenital anomalies in the development of the fetus.
How is toxoplasmosis transmitted?
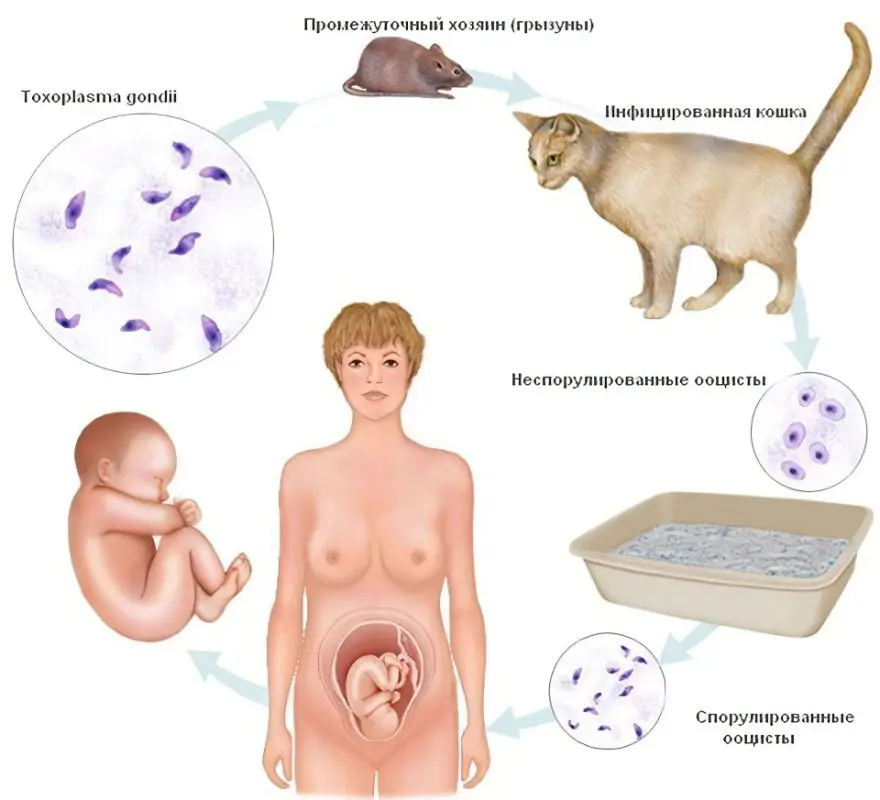
Toxoplasma carriers are domestic cats, which become infected while eating birds and raw meat. A person becomes infected from his pet through contact with his feces. Often this happens when hygiene rules are not followed while cleaning the cat litter box.
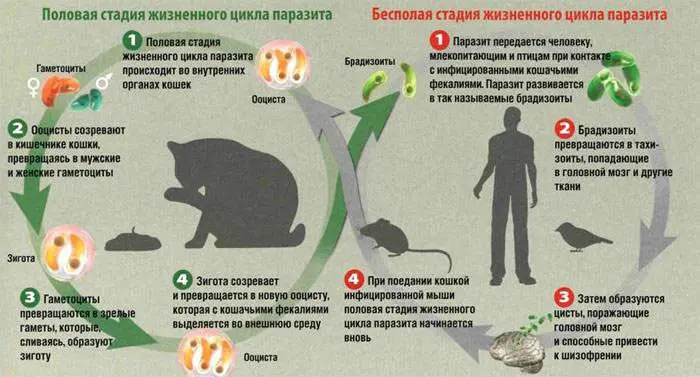
You can also become infected with toxoplasmosis by eating meat that has not undergone sufficient heat treatment. Another option for transmission of infection is the transfusion of sick blood to a healthy person.
The most dangerous form of toxoplasmosis is the one that is passed from mother to child.
Forms and symptoms of toxoplasmosis
Symptoms of toxoplasmosis depend on the form of the disease.
They can be distinguished as follows:
Acute form of toxoplasmosis. If the person’s defenses are not reduced, then the disease will not give any pathological symptoms. Rarely, people have enlarged lymph nodes, possibly an increase in body temperature. A person may experience pulling pains in the right side under the ribs. On palpation, the doctor notes an increase in the size of the liver and spleen. If the disease is not complicated by any other processes, then after 7-14 days it passes on its own, and a person develops immunity to infection.
A common form of toxoplasmosis. People with weakened immune systems suffer from this disease. First of all, this applies to HIV-infected patients, cancer patients, as well as those who are undergoing chemotherapy. Toxoplasmosis will cause inflammation in various organs and tissues. Muscles, lungs, heart suffer. Severe inflammation leads to the fact that they cease to perform their functions normally.
Cerebral toxoplasmosis. With this type of infectious process, the patient has inflammation of the brain. Most often it develops in people with a failure of the immune system. The patient complains of symptoms such as: headache, high body temperature, deterioration of sensitivity, etc. In a severe course of the disease, a person may fall into a coma or become paralyzed.
Ocular form of the disease. Most often, Toxoplasma affects the eyeballs when the disease is transmitted from mother to child. The first symptoms of infection appear in adolescence or adolescence. A person complains of pain in the eyes, bright points, flashes appear in the field of vision, blindness may develop.
congenital toxoplasmosis. The child becomes infected while still in the womb. The disease can cause miscarriage, missed pregnancy, death of the baby immediately after birth. Sometimes the symptoms of the congenital form of the disease do not manifest themselves for a long time, for example, as is the case with ocular toxoplasmosis. However, sooner or later the infection will make itself felt.
Symptoms of the disease in children

If a small amount of toxoplasma enters the child’s body, then he is able to cope with the infection on his own. Parasites are covered with a shell and blocked. In this form, they are unable to harm the health of the child. Since there are no symptoms, the fact of infection remains undetected.
If the infection has an acute course, then it will give such clinical signs as:
Hyperthermic reaction of the body. In this case, the body temperature rises to high levels.
Damage to the spleen and liver.
Yellowing of the skin.
Enlargement of lymph nodes.
Deterioration of vision.
Rashes on the skin.
How does toxoplasmosis manifest in pregnant women?
For pregnant women, toxoplasmosis is the most dangerous infection. It is passed on to the fetus during fetal development. This leads to the fact that he has various structural anomalies. Therefore, when it is possible to identify an infection in the early stages of pregnancy, it is urgently interrupted.
Symptoms of toxoplasmosis in pregnant women:
An increase in body temperature to subfebrile marks.
Headache.
Increased fatigue.
Enlarged lymph nodes in size.
Joint and muscle pain.
If a woman experiences these symptoms, then she needs to report them to the doctor. When the term for termination of pregnancy is too high, she will be prescribed treatment. The sooner this happens, the better.
Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis

To determine the presence of toxoplasma in the body, an enzyme immunoassay is required to detect specific antibodies. The study makes it possible to detect immunoglobulins in the blood, which appear in response to the penetration of infection. Depending on the type of immunoglobulins detected, it is possible to understand whether a person is a carrier of toxoplasmosis, or whether his disease is in an acute phase.
Immunoglobulins are divided into early and late. Type M antibodies appear in the body during the acute phase of the disease (in the first 7 days). For 30 days from the start of the infection, they gain peak values, and after 2-3 months they completely disappear. In newborn initiated children, such antibodies are found in 75% of cases, and in adult patients – in 97% of cases. A negative analysis indicates that the acute phase of the disease has passed, but this does not exclude the fact that the infection has existed in the body for a long time.
Immunoglobulins G appear in the body 2-3 days later than immunoglobulins M. Over time, they do not disappear, since these protein complexes provide the patient with immunity for life. If after some time Toxoplasma again enters the human body, then the disease will not develop.
The circulation of immunoglobulins G in the blood indicates that the acute phase of the disease has ended, and the body itself has specific protection against the disease. Additionally, the patient is prescribed an analysis to determine the activity of IgG. This will determine their ability to neutralize Toxoplasma.
Also confirming the fact of infection allows the determination of protozoan DNA in the blood. The method of their detection is called PCR. This is a high-precision study that has a minimum margin of error.
The most severe infection occurs in newborns who were infected during fetal development. Therefore, pregnant women should be especially attentive to their health and, if signs of infection appear, be examined.
Explanation of results
It is difficult to interpret the results of the analyzes on your own, since the reference values uXNUMXbuXNUMXbare different in different laboratories. Exceeding the allowable threshold of immunoglobulins indicates infection.
IgM | IgG | Evaluation of results |
— | — | There is no infection in the body, but if a woman is at risk, then she should be regularly tested during pregnancy. |
— | + | A person has a lifelong immunity to infection. If such a result was obtained in a pregnant woman, then you need to take a blood and urine test, and also determine the activity of immunoglobulins G. If they are highly active, then this indicates that immunity was formed even before pregnancy. |
+ | — | The infection has an acute course. During pregnancy, there is a high risk of infection of the fetus, to ensure the reliability of the results, the analysis is repeated. |
+ | + | There is a possibility of acute infection, but it must be taken into account that immunoglobulins M retain their activity for 3 months and up to 2 years. |
Assessment of immunoglobulin G activity
Percentage | transcript | Score |
Less than 40 | Low activity | The infection is in the acute phase. If we are talking about a pregnant woman, then a second analysis is required. |
41-59 | transition values | Uninformative result. The analysis is repeated after 14 days. |
More 60 | high activity | A person has developed immunity to toxoplasmosis. He is either a carrier of the infection, or he has a chronic form of the disease, which does not pose a threat. |
Treatment of toxoplasmosis

If a person becomes infected in adulthood and his state of health is satisfactory, then he does not need treatment. With toxoplasma, the immune system can cope on its own.
Therapy is prescribed for pregnant women, since in such cases there is a high probability of infection of the fetus and the birth of a child with a congenital form of the disease. Also, treatment is indicated for all patients with a reduced immune system.
Drugs that can be used to rid a person of Toxoplasma:
Pyrimethamine (Daraprim) and Chloridine.
Delagil, Trichopol, Aminoquinol.
Sulfadiazine.
Prednisolone.
Clindamycin.
Spiramycin.
If the patient needs toxoplasmosis therapy, then the treatment is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting. In addition to antibiotics of the tetracycline group and sulfonamides, the patient is prescribed vitamins, minerals, antihistamines. Sulfonamides can be combined with drugs such as: Lincomycin, Metacycline, Erythromycin. Sometimes patients are shown taking combined drugs: Biseptol and Poteseptil. They are taken for 10 days, 1 tablet 2 times a day. The course will need to be repeated 2-3 times.
Fansidar’s reception has proven itself well. The patient is prescribed a tablet 1 time in three days. To achieve a positive result, you will need to take 5-6 tablets.
Coping with chronic Toxoplasma is difficult, as the infection does not respond well to drugs. Therefore, it is necessary to direct efforts to increase immunity and to eliminate the main symptoms of the disease. Patients with a chronic form of the disease are prescribed Pyrimethamine in combination with sulfonamides (Sulfapiridazine, Sulfadimezin, Bactrim). The drugs are taken in courses of 5 days with an interval of 5-7 days. The number of courses can be two or three. The daily dose of pyrimethamine is 50 mg. For one course, the patient will have to take 250 mg, and for the entire duration of treatment, 500-750 mg. The dose for pregnant women should not exceed 500 mg.
Sulfonamides are prescribed 2-4 g per day, in parallel, patients are shown taking Tindurin. The course should be repeated 2-3 times.
Treatment with corticosteroids continues for 10-14 days. Patients are administered 1,5-2 mg/kg of body weight. These drugs are indicated for admission when a person has damage to the brain or organs of vision. To increase immunity, Wobenzym is prescribed.
The chronic form of toxoplasmosis requires careful selection of drugs. Only a multicomponent scheme will cope with the problem. If the disease is diagnosed in pregnant women in the early stages of development, then an abortion is indicated for her.
Prevention

Preventive measures to prevent the development of the disease:
During pregnancy, contact with domestic cats is not recommended. Do not engage in earthworks.
If there is a cat in the house, then you can not give her raw meat. You need to make sure that she does not catch rodents.
The meat must be thoroughly fried or boiled.
Foods that a person eats raw must be thoroughly washed.
After cutting the meat, the knives and the board should be washed and disinfected.
Toxoplasmosis is an infection that can pose a serious threat to health. Therefore, when its symptoms appear, you need to consult a doctor and receive treatment. This measure is especially relevant for pregnant women and children.









