Contents
Both humans and plants need food to survive. Tomatoes are no exception. Proper feeding of tomatoes in a greenhouse is the key to a plentiful harvest of tasty and healthy fruits.
Tomato belongs to plants with medium nutritional requirements. On different soils, these needs can vary greatly. On fertile, especially chernozem soils, they will be small. On poor soils with a low humus content, tomatoes need fertilizers to a greater extent.
The main nutritional elements of tomatoes
Research by physiologists suggests that tomato plants consume about 50 different chemical elements for their life. All nutrients consumed by plants can be divided into macro and micronutrients.

Macronutrients
Macronutrients include the following substances.
- Carbon – comes to tomatoes from the air through the leaves and through the roots from the compounds in the soil, an important component of the photosynthesis process. Organic fertilizers applied to the soil increase the carbon dioxide content in the near-earth air layer, which speeds up photosynthesis, and, consequently, increases the yield.
- Oxygen – is involved in the respiration of tomatoes, in metabolism. The lack of oxygen in the soil not only causes the death of beneficial soil microorganisms, but can cause the death of the plant. Loosen the soil in the top layer near the tomatoes to enrich it with oxygen.
- Nitrogen – the most important element for the nutrition of tomatoes, is a component of all plant tissues. It cannot be absorbed from the air, so nitrogen must be added from the outside. Nitrogen is well absorbed by tomatoes only with a neutral or slightly acidic soil reaction. If the soil has a high acidity, it is necessary to carry out its liming.
- Phosphorus – affects the growth and development of tomatoes, especially the root system, it is also important during the period of budding and fruit formation. Phosphorus is an inactive element. Its salts are poorly soluble and slowly pass into a state accessible to plants. Most of the phosphorus is absorbed by tomatoes from stocks introduced last season.

Phosphate fertilizers must be applied annually to maintain soil fertility.
- Potassium. It is most needed by tomatoes during the period of fruit formation. It helps to grow both the root system and the leaves and stem. The introduction of potassium will help tomatoes become resistant to various diseases, endure any stress without loss.
The main phosphorus-potassium fertilizers and their benefits for plants are presented in the video:
Trace Elements
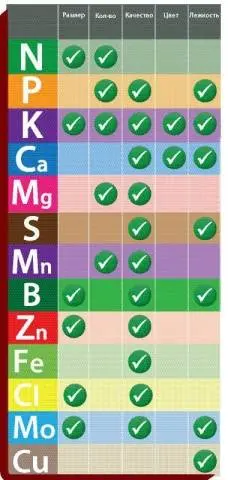
These elements are called so because they are consumed by plants, including tomatoes in small quantities. But for the proper nutrition of tomatoes, they are needed no less, and the lack of each of them can affect not only their development, but also the harvest. The most important elements for tomatoes are the following elements: calcium, magnesium, boron, molybdenum, sulfur, zinc. Therefore, fertilizers for tomatoes in a greenhouse should include not only macro, but also microelements.
Types of top dressing of tomatoes in the greenhouse
All top dressing of tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse and in a film greenhouse are divided into root and foliar.
Root top dressings are most effective on the waning moon, since it is at this time that all the juices of the plant are directed to the roots, which are growing vigorously. Since the greenhouse creates its own special microclimate due to low air circulation, root dressing for tomatoes is preferable, since they do not increase the humidity of the air in it, and this is important for the prevention of late blight.
Foliar top dressing of tomatoes is carried out on the growing moon, it is at this time that the leaves are best able to absorb the substances introduced with nutrient solutions. What fertilizers does foliar top dressing of tomatoes imply in a greenhouse? Usually such a procedure is an ambulance for tomatoes, it is designed to quickly compensate for the lack of any nutrient. It helps quickly, but unlike root dressing, it does not last long.

In the video you can see how the lack of different nutrients affects tomatoes:
Caring for tomatoes in case of a lack of any micro or macro element will consist in foliar top dressing with a solution containing this element. Any water-soluble fertilizer is suitable for top dressing, which includes the substance most needed by tomatoes at the moment.
Such it can be in the period of fruiting. During the growth of leaf mass and flowering, it should be even less and be 0,4% and 0,6%, respectively.
Foliar top dressing is best done in the late afternoon, when the absorbency of tomato leaves is maximum.
The amount of root dressing in the greenhouse depends on several factors:
- soil fertility;
- soil type;
- the amount of starting fertilizer;
- the state of seedlings during planting;
- on what varieties are grown there – determinate or indeterminate, as well as on the intensity of the variety, that is, its ability to produce a large crop.
Soil fertility and its preparation in the fall
Soil fertility is an important factor for successful plant growth. If the soil is poor, a sufficient amount of organic matter will be required during its autumn preparation. Depending on fertility, from 5 to 15 kilograms of humus or well-rotted compost per square meter of greenhouse are added to the soil.

Plants overfed with nitrogen will not only not give a high yield, but will also become easy prey for pathogenic bacteria, which are abundant in fresh manure.
If you scattered compost or humus before digging, do not forget to shed the soil with a 0% solution of copper sulfate. This will not only disinfect the soil, but also enrich it with the necessary copper. Since autumn, the soil is also filled with superphosphate – from 5 to 50 grams per square meter.
Potash and nitrogen fertilizers are best applied in the spring, when preparing the soil for planting seedlings.
They can only be applied in autumn to polycarbonate greenhouses; there is no snow in them in winter. It will take 40 grams of potassium salt per square meter. It is better if the potassium is sulphate, because tomatoes do not like the chlorine contained in potassium chloride.
Soil type and adjustment
Caring for tomatoes includes preparing the soil that is optimal for their development. The soil most suitable for growing tomatoes should meet the following conditions:
- contain enough, but not excessively organic components;
- keep moisture well;
- easy to saturate with air;
- the soil should have optimal acidity.
If tomatoes are planted after crops under which a lot of organic matter has been applied, it should be refrained from applying it in the fall. Sandy or loamy soils are best suited for growing tomatoes. Sandy soils dry out very quickly, so clay is added to them to increase its moisture capacity. Clay soils are poorly saturated with air, so sand will have to be added to them.
Tomatoes are tolerant of soil acidity and grow well with its value from 5,5 to 7,5, but they are most comfortable with a pH of 5,6 to 6,0. If the soil does not meet these requirements, it should be limed. Liming should be done in the fall.

Lime removes nitrogen from organics, because when humus or manure is mixed with lime, ammonia is formed, which simply evaporates into the air.
Top dressing of tomatoes when planting seedlings
Caring for tomatoes in a greenhouse begins with preparing planting holes for tomatoes.
Fertilizers for tomatoes in a greenhouse when planting seedlings are an indispensable element for the proper development of plants. A handful of humus and two tablespoons of ash are added to the planting holes. Growing the root system of seedlings will provide phosphorus fertilizer added in the fall.

Tips from experienced gardeners:
- it is good to add ground eggshells to the hole when planting – a source of calcium;
- sometimes one small raw fish is added to the wells – a source of phosphorus and trace elements available to plants – this is what the ancient Indians did; on the video you can see more about this exotic method of fertilization:Tomatoes fish top dressing.
- Bread crusts are infused for a week in water and watered with a dilute solution of the hole, thereby enriching the soil with nitrogen and the air with carbon dioxide.
The state of seedlings when planting plants and top dressing
Weak seedlings will require care in the form of additional dressings in the initial period after planting. This is nitrogen – for building up the leaf mass and phosphorus – for the rapid growth of roots. Humic fertilizers will also help tomatoes in this, when they are used, the roots grow much faster. Foliar top dressing with these fertilizers will be most effective.
The intensity of top dressing for different varieties of tomatoes
Determinate varieties of tomatoes require less nutrition for their development than indeterminate varieties, since they are smaller. Intensive varieties for the formation of a large yield require intensive feeding. For varieties with low yields, their number should be less.

What are the best mineral fertilizers for tomatoes? There is no exact answer to this question. The best fertilizer will be the one that the tomatoes need the most at the moment.
Proper care of tomatoes in a greenhouse is impossible without mineral supplements. In order not to get confused and not miss anything, it is best to draw up a schedule or feeding scheme. The most suitable fertilizer for tomatoes should have a percentage ratio: nitrogen-10, phosphorus-5, potassium-20. It should be water-soluble and contain a set of trace elements necessary for tomatoes. There are many types of such fertilizers. For example, “Mortar”, “Harvest”, “For tomatoes”, “Sudarushka”.

Each gardener himself makes the choice of the fertilizer that is available to him.
Advice from experienced gardeners: the first dressing of greenhouse tomatoes is done when the tomatoes on the lower brush become the size of an average plum.
Schedule of root dressings of tomatoes in the greenhouse
As a rule, tomatoes are planted in a greenhouse with the first flowering brush. Usually planting seedlings is carried out in early May. Therefore, the first root dressing coincides with the first decade of June. If the seedlings are weak, the first top dressing should be done with a foliar solution of nitrogen fertilizer to increase the leaf mass with the addition of humate for better root growth. Further feeding should be carried out once a decade, finishing them in the first decade of August. It is easy to calculate that 7 root dressings will be needed.

The most obvious way is to bring all top dressing into a table.
Type of fertilizer | June 1 – 10 | June 10 – 20 | June 20 – 30 | July 1 – 10 | July 10 – 20 | July 20 – 30 | August 1 – 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Mortar or other complex soluble fertilizer with the same composition | 30 g per 10 liters | 40 g per 10 liters | 40 g per 10 liters | 40 g per 10 liters | 50 g per 10 liters | 40 g per 10 liters | 30 g per 10 liters |
Potassium sulphate (potassium sulphate) | — | — | — | 10 g per 10 liters | 10 g per 10 liters | 20 g per 10 liters | 30 g per 10 liters |
Saltpeter calcium | — | — | 10 g per 10 liters | 10 g per 10 liters | — | — | — |
Humate | 1 teaspoon per 10 liters | 1 teaspoon per 10 liters | 1 teaspoon per 10 liters | 1 teaspoon per 10 liters | 1 teaspoon per 10 liters | 1 teaspoon per 10 liters | 1 teaspoon per 10 liters |
Irrigation rate per bush in liters | 0,5 | 0,7 | 0,7 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0, 07 |
Two top dressings with calcium nitrate are necessary to prevent blossom end rot of tomatoes. When adding calcium nitrate to the solution, we reduce the rate of solute by 10 grams. Humate is compatible with complex fertilizer, so it can not be diluted with water separately, but added to a bucket of mortar.

It is carried out after feeding, well spilling the entire bed.
In July and August, pour water and fertilizer all over the soil in the garden, and not just under the bushes, since the root system is growing by that time.
You can also take care of tomatoes by fertilizing tomatoes in a greenhouse with folk remedies. A very good tool that increases the yield and immunity of tomatoes is green manure. How to prepare and apply it, you can watch the video:
Proper care of tomatoes and timely feeding are guaranteed to provide the gardener with a large harvest of tasty and healthy fruits.










