Contents
- 10 All living organisms are made up of genes.
- 9. Which population does not have Neanderthal genes in its own DNA?
- 8. There are butterflies that combine the characteristics of both sexes.
- 7. Closely related ties lead to the appearance of weak heirs
- 6. The DNA of all people matches 99,9%
- 5. The occurrence of certain types of tumors is associated with a genetic predisposition
- 4. 8% of human DNA is made up of viruses
- 3. Genetic predisposition
- 2. The most common chromosomal abnormality is Down syndrome.
- 1. 3D printing of DNA molecules
Genetics is truly a miracle science, the development of which makes it possible for mankind not only to effectively escape diseases, but also to some extent determine the future, influencing the appearance and intelligence of its offspring.
Currently, genetic scientists are on the verge of incredible discoveries, thanks to which you can find a recipe for eternal youth and generally significantly increase people’s life expectancy.
In addition, such integral branches of human existence as practical medicine, agriculture, food industry, etc. are associated with genetics.
Now scientists are actively trying to find methods for directly influencing the structure of the genes of future generations so that people with a certain set of qualities can be born. From all of the above, we can conclude that genetics is the science of the present and the future, so each of us needs to have at least knowledge of what it is.
We recommend you 10 interesting facts about genetics for a message or a project in the 6th grade – the amazing discoveries of scientists.
10 All living organisms are made up of genes.
 Moreover, all people living on Earth are descendants of one group. This conclusion was reached by researchers who studied the genetic variations of monkeys and humans. There are far more hereditary variations in the DNA of 50 African monkeys than in the DNA of all people on Earth.. In addition, scientists have come to the conclusion that we are all distant descendants of Africans.
Moreover, all people living on Earth are descendants of one group. This conclusion was reached by researchers who studied the genetic variations of monkeys and humans. There are far more hereditary variations in the DNA of 50 African monkeys than in the DNA of all people on Earth.. In addition, scientists have come to the conclusion that we are all distant descendants of Africans.
9. Which population does not have Neanderthal genes in its own DNA?
 Crossing between Neanderthals and modern humans has occurred several times. Neanderthal DNA has been found in the genome of modern populations in Europe and Asia, accounting for 1-4% of the total genome. Neanderthal genes are missing from most modern populations in sub-Saharan Africa.
Crossing between Neanderthals and modern humans has occurred several times. Neanderthal DNA has been found in the genome of modern populations in Europe and Asia, accounting for 1-4% of the total genome. Neanderthal genes are missing from most modern populations in sub-Saharan Africa.
8. There are butterflies that combine the characteristics of both sexes.
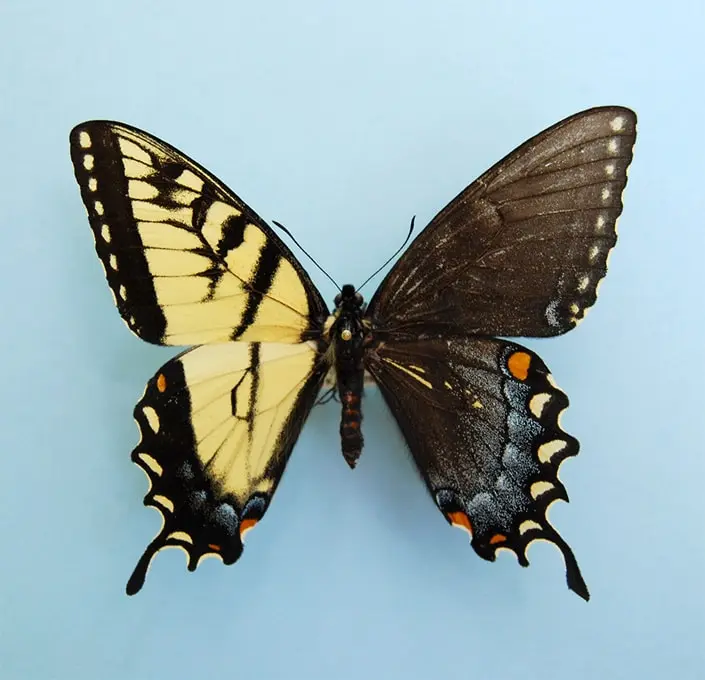 Most of us have seen at least once in our lives butterflies with different patterns on their wings (not symmetrical patterns). This sign indicates the presence of an incredible natural phenomenon. The point is that this a butterfly is a carrier of genes of both sexes, that is, it is a hermaphrodite.
Most of us have seen at least once in our lives butterflies with different patterns on their wings (not symmetrical patterns). This sign indicates the presence of an incredible natural phenomenon. The point is that this a butterfly is a carrier of genes of both sexes, that is, it is a hermaphrodite.
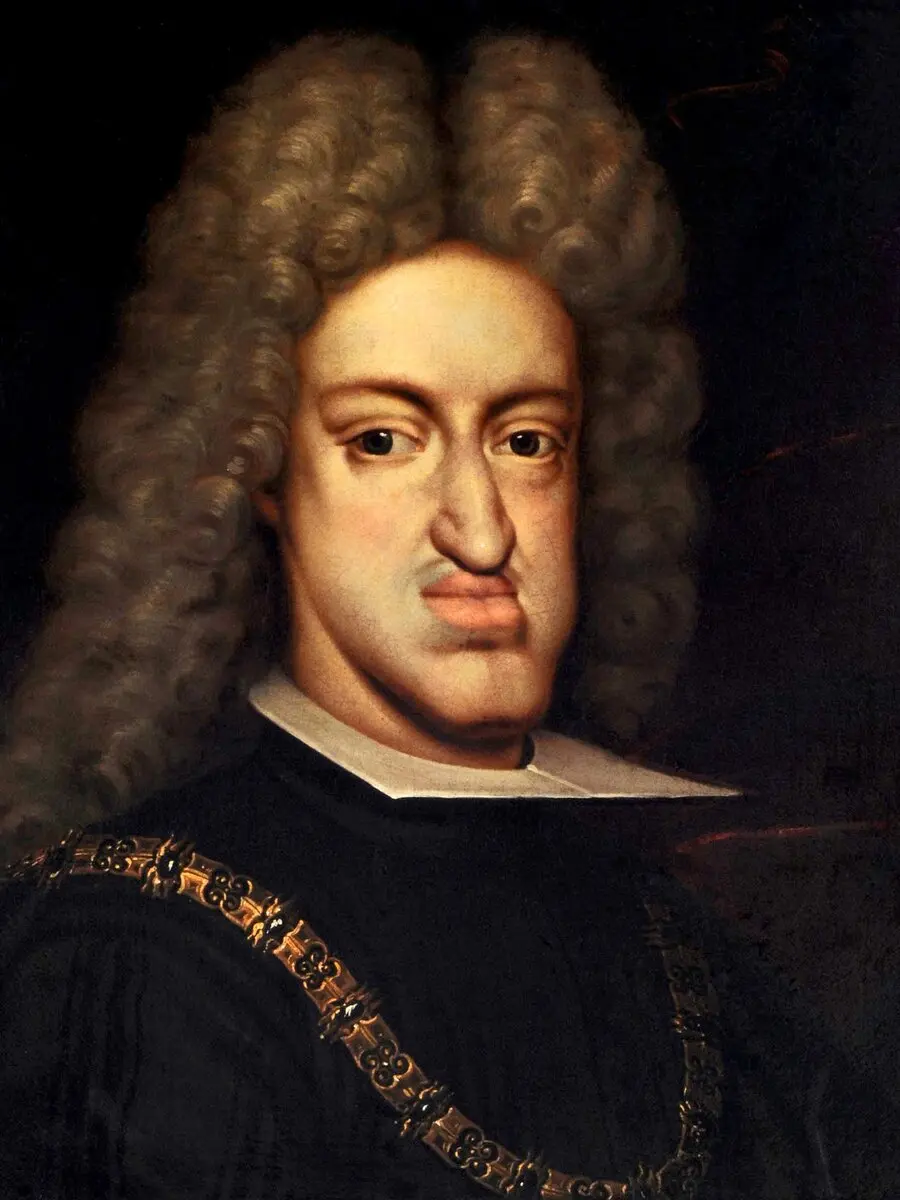 We all know about the dangers of close relatives getting intimate. Although, before the emergence of genetics as a science, this practice was widespread on the European continent, especially in noble circles.
We all know about the dangers of close relatives getting intimate. Although, before the emergence of genetics as a science, this practice was widespread on the European continent, especially in noble circles.
For example, Charles II, King of Spain, had only four instead of eight great-grandfathers (as it should be in the norm). This of course led to the emergence of various genetic mutations, which subsequently had an extremely negative impact on children born in incestuous tanks.
It has been proven that the children of people who are not related by family ties often show a level of physical fitness significantly higher than any of the parents. This effect is called heterosis or hybrid energy. This also explains the modern trend of crossbreeding purebred dogs.
6. The DNA of all people matches 99,9%
 All life forms on Earth share the same basic genetic structure. The same four foundations, the building blocks of DNA, are found everywhere there is life. There are two theories to explain this amazing phenomenon. Either only these four bases can be used to form stable DNA, or there are only two common ancestors for all people living on Earth (which confirms the biblical theory of the origin of life).
All life forms on Earth share the same basic genetic structure. The same four foundations, the building blocks of DNA, are found everywhere there is life. There are two theories to explain this amazing phenomenon. Either only these four bases can be used to form stable DNA, or there are only two common ancestors for all people living on Earth (which confirms the biblical theory of the origin of life).
5. The occurrence of certain types of tumors is associated with a genetic predisposition
 Oncogenes, suppressor genes and mutator genes are genes that turn on or off certain signaling pathways in our body and cause cancer when certain negative mutations occur.. Therefore, malignant tumors arise due to the malfunction of genes that play an important role in cell metabolism.
Oncogenes, suppressor genes and mutator genes are genes that turn on or off certain signaling pathways in our body and cause cancer when certain negative mutations occur.. Therefore, malignant tumors arise due to the malfunction of genes that play an important role in cell metabolism.
Due to the increased metabolic rate and the ability of cells to divide, they can degenerate and multiply. For example, in the case of Li-Fraumeni syndrome, the dose of the p53 protein changes, which leads to the development of breast cancer, brain tumors, osteosarcoma and leukemia, even at a young age. This is due to the fact that the p53 protein binds to DNA as a transcription factor and can stimulate its reading.
4. 8% of human DNA is made up of viruses
 Some viruses replicate by inserting their DNA into the cells of their hosts. Then copies of it are created and thus the virus spreads throughout the body.
Some viruses replicate by inserting their DNA into the cells of their hosts. Then copies of it are created and thus the virus spreads throughout the body.
However, sometimes when a virus integrates, a mutation occurs that deactivates it. This “dead” virus remains in the genome and is copied each time the cell divides. If the virus integrates into the germ cell (egg or sperm), then it can end up in the cell of the offspring. Thus, built-in viruses accumulate in genomes over time.
3. Genetic predisposition
 Complex chronic diseases, such as asthma, diabetes or alcoholism, are caused by multifactorial features, since the interaction between genes and the environment in these cases is critical.
Complex chronic diseases, such as asthma, diabetes or alcoholism, are caused by multifactorial features, since the interaction between genes and the environment in these cases is critical.
Genetic predisposition creates the basis for the overall clinical picture of the disease, which is formed under the influence of environmental factors..
2. The most common chromosomal abnormality is Down syndrome.
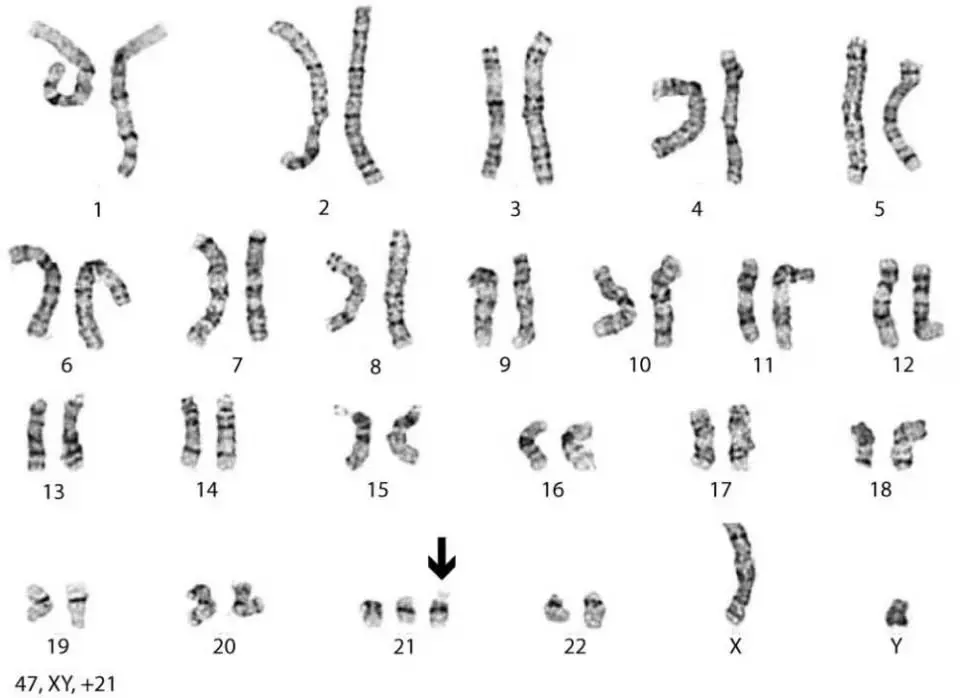 Aneuploidies are numerical chromosomal aberrations, as a result of which the number of individual human chromosomes changes. The most famous chromosomal aberration, called Down’s Syndrome, is caused by the fact that chromosomes are not properly distributed during cell division. Such chromosomal abnormalities cause up to 35% of miscarriages..
Aneuploidies are numerical chromosomal aberrations, as a result of which the number of individual human chromosomes changes. The most famous chromosomal aberration, called Down’s Syndrome, is caused by the fact that chromosomes are not properly distributed during cell division. Such chromosomal abnormalities cause up to 35% of miscarriages..
Scientists have proven the fact that the age of the expectant mother has a huge impact on the likelihood of the birth of such a child: the older the woman, the greater the percentage of the likelihood of developing Down syndrome in the fetus.
Of course, this does not mean that a young woman in labor cannot have a baby with a similar feature, but it has been proven that girls under the age of 25 give birth to such a child with a probability of 1/1400, up to 30 – 1/1000, while expectant mothers 35 years old have much greater risks equal to about 1/350. For women over the age of 42, the threat of having a child with Down syndrome rises to 1/60.
Despite this trend, according to statistics, it is women under 30 who often give birth to children with this genetic anomaly, but this is due to the fact that they generally account for the bulk of babies born.
1. 3D printing of DNA molecules
 It all started with the fact that doctors learned how to print human organs using a 3D printer, which made it possible to significantly increase the possibilities of transplantation.
It all started with the fact that doctors learned how to print human organs using a 3D printer, which made it possible to significantly increase the possibilities of transplantation.
RўRμRїRμSЂSЊ, Geneticists succeeded in printing the real DNA of a living organism for the first time. So far, such a three-dimensional printer can recreate the structure of extremely primitive life forms, such as viruses or bacteria, but science does not stand still.
Interestingly, scientists have learned not only to reproduce the structure of DNA, but also to use it as an information carrier. It has been proven that if you use a DNA molecule as, for example, a well-known flash drive, then it will be possible to save and later read a huge amount of information on it.










