Contents
A peninsula is an interesting formation that juts out of a large piece of land into the nearby waters. Almost an island, but not quite: water, whether it be the sea, ocean or river, surrounds the protruding land on three sides.
Peninsulas include headlands (large, raised areas of land) and may belong to one or more countries.
We present you a list of the 10 largest peninsulas of the Earth: large territories of Russia and North America, as well as other countries of the world.
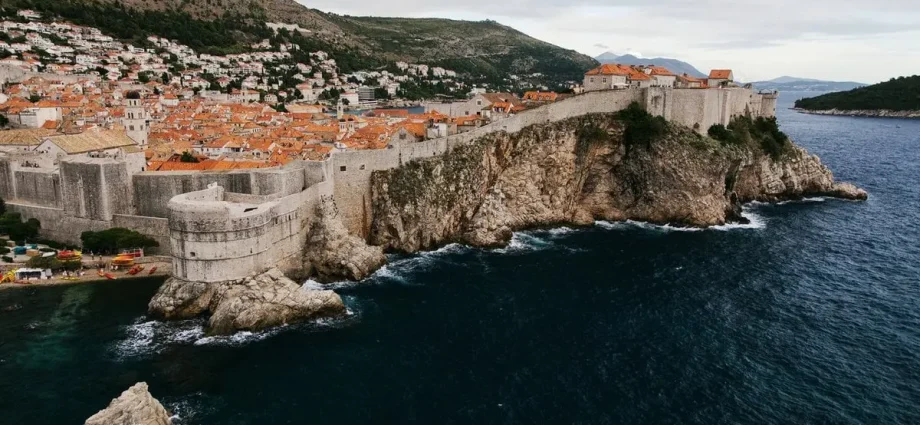
10 Balkany, 505 km²
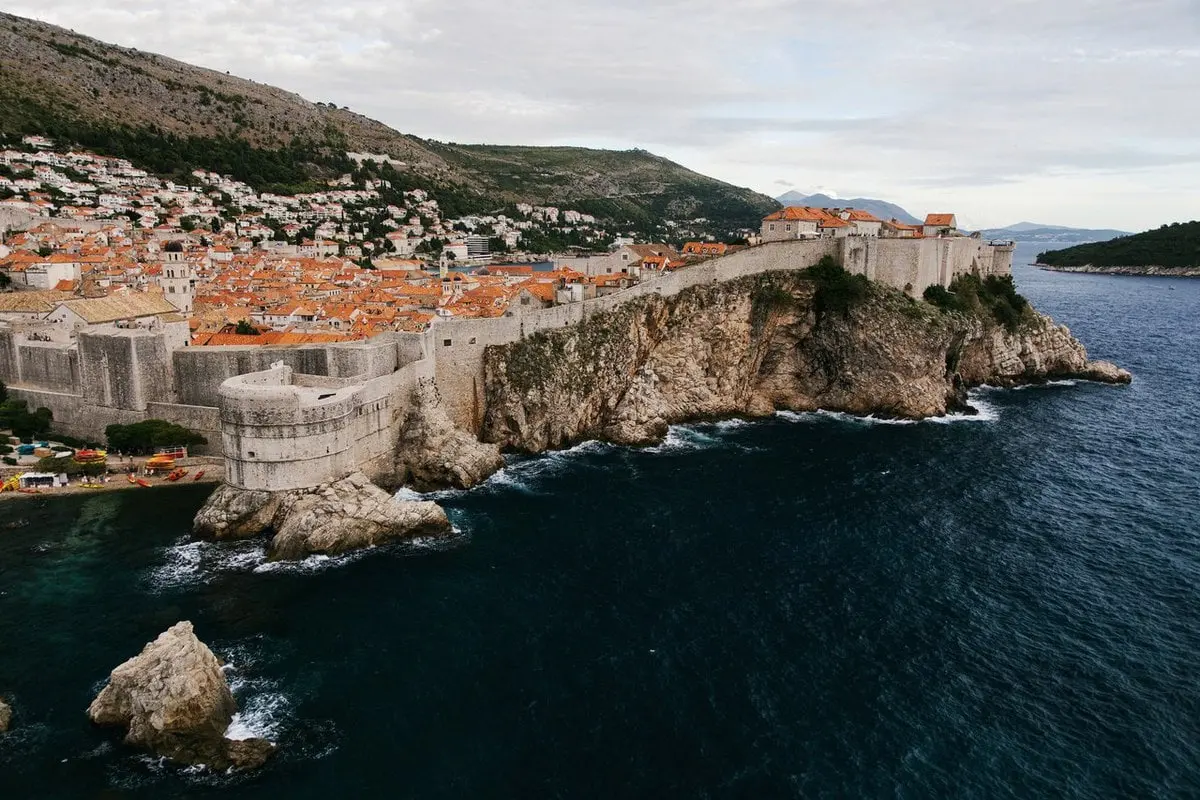 Balkans, also called the Balkan peninsula, the easternmost of the three great southern peninsulas of Europe. There is no universal agreement on the components of the region. The Balkans are usually characterized as Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia and Slovenia – with all or part of each of these countries located on the peninsula.
Balkans, also called the Balkan peninsula, the easternmost of the three great southern peninsulas of Europe. There is no universal agreement on the components of the region. The Balkans are usually characterized as Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Kosovo, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Serbia and Slovenia – with all or part of each of these countries located on the peninsula.
Parts of Greece and Turkey are also located in the geographic region commonly referred to as the Balkan Peninsula, and many descriptions of the Balkans include these countries as well. Some define the region culturally and historically, and others geographically, although interpretations vary among historians and geographers.
Generally, the Balkans are bordered to the northwest by Italy, to the north by Hungary, to the north and northeast by Moldova and Ukraine, and to the south by Greece and Turkey or the Aegean Sea (depending on how the region is defined).
The Balkans are washed by the Adriatic Sea in the west, the Ionian Sea in the southwest and the Black Sea in the east. In the north, a clear geographical demarcation of the Balkans becomes difficult, as the Pannonian Basin of the Great Alfold (Great Hungarian Plain) extends from Central Europe to parts of Croatia, Serbia, and Romania.
9. Asia Minor, 506 km²
 Asia Minor, also known as Anatolia, is a peninsula located in the Middle East, currently occupied by the Asian part of Turkey. It is bordered to the north by the Black Sea, to the east by the Taurus and Antitaurus mountain ranges, to the south by the Mediterranean Sea and to the west by the Aegean Sea and the Sea of Marmara. The Bosphorus and the Dardanelles separate it from Europe.
Asia Minor, also known as Anatolia, is a peninsula located in the Middle East, currently occupied by the Asian part of Turkey. It is bordered to the north by the Black Sea, to the east by the Taurus and Antitaurus mountain ranges, to the south by the Mediterranean Sea and to the west by the Aegean Sea and the Sea of Marmara. The Bosphorus and the Dardanelles separate it from Europe.
In ancient Greece, the western part of the peninsula was known as Asia, later expanding the name to the entire continent, the peninsula became known as Asia Minor.
Since Anatolia is a mountainous region, historically it has been a successive military stronghold of several cities.
8. Iberian Peninsula, 596 km²
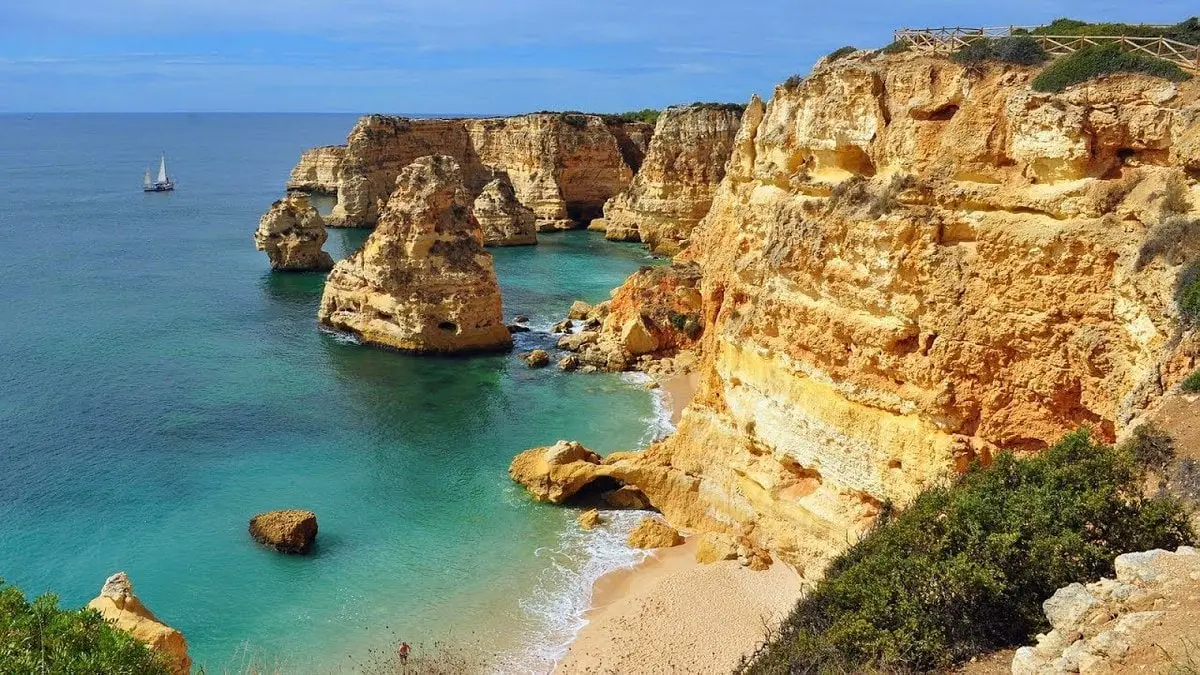 The Iberian Peninsula, a peninsula in southwestern Europe occupied by Spain and Portugal. Its name comes from its ancient inhabitants, whom the Greeks called the Iberians.
The Iberian Peninsula, a peninsula in southwestern Europe occupied by Spain and Portugal. Its name comes from its ancient inhabitants, whom the Greeks called the Iberians.
The Pyrenees mountain range forms an effective land barrier in the northeast, separating the Iberian Peninsula from the rest of Europe, and in the south near Gibraltar, the peninsula is separated from North Africa by the narrow Strait of Gibraltar.
The Atlantic Ocean washes the northern, western and southwestern coasts, while the Mediterranean Sea washes the southern and eastern shores.
7. Somalia, 750 km²
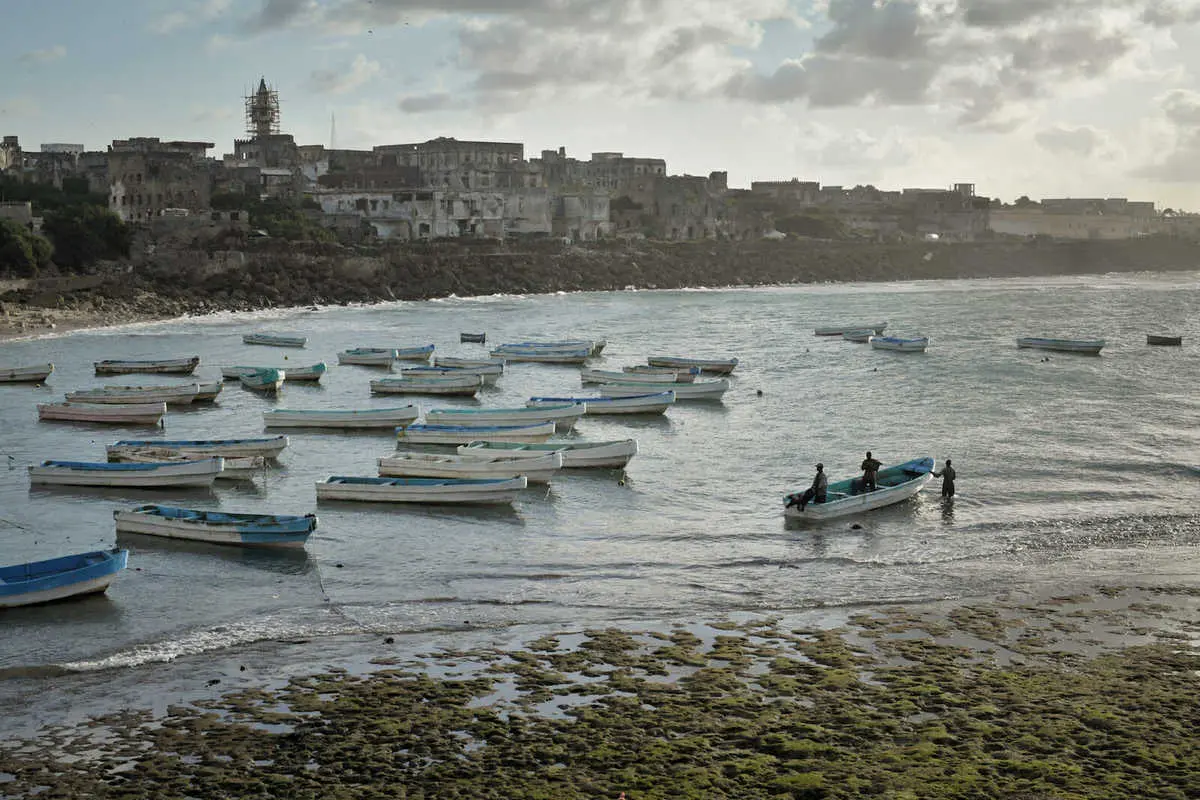 Somalia, the easternmost country in Africa, the Horn of Africa. It extends from the Equator north to the Gulf of Aden and occupies an important geopolitical position between Sub-Saharan Africa and the countries of Arabia and Southwest Asia. The capital, Mogadishu, is located north of the equator in the Indian Ocean.
Somalia, the easternmost country in Africa, the Horn of Africa. It extends from the Equator north to the Gulf of Aden and occupies an important geopolitical position between Sub-Saharan Africa and the countries of Arabia and Southwest Asia. The capital, Mogadishu, is located north of the equator in the Indian Ocean.
Somalia is a country of geographical extremes. The climate is mostly dry and hot, with thorny savanna and semi-desert landscapes, and Somalis have developed equally demanding strategies for economic survival.
Apart from a mountainous coastal zone in the north and a few distinct river valleys, most of the country is extremely flat, with few natural barriers to restrict the mobility of nomads and their livestock.
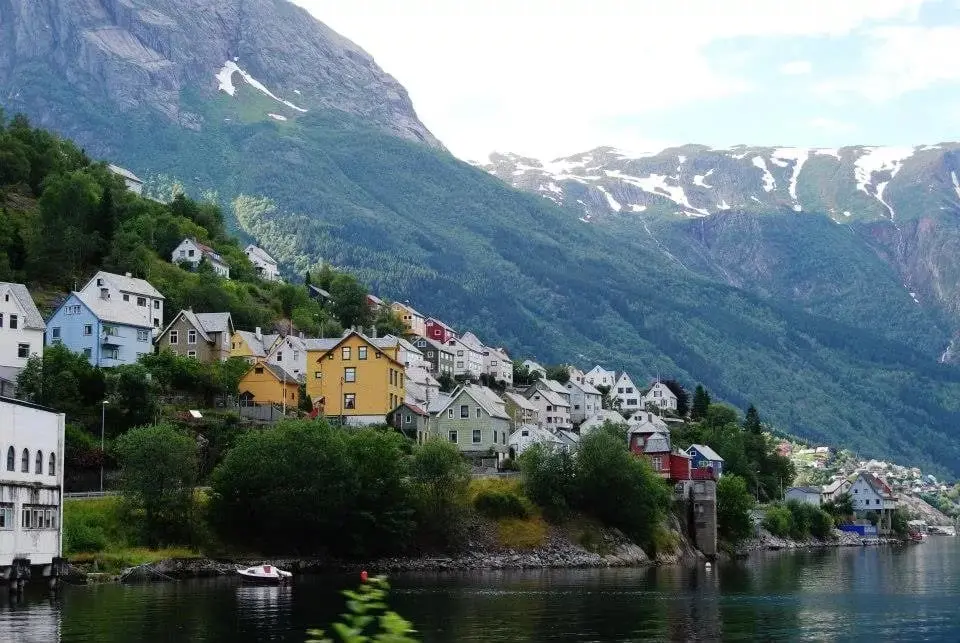 Scandinavian Peninsula is a large peninsula in Northern Europe, consisting mainly of the mainland territories of Norway and Sweden. A small part of northwestern Finland is sometimes also considered part of the peninsula. It is part of the larger region of Fennoscandia, which includes the Kola Peninsula, Karelia and Finland.
Scandinavian Peninsula is a large peninsula in Northern Europe, consisting mainly of the mainland territories of Norway and Sweden. A small part of northwestern Finland is sometimes also considered part of the peninsula. It is part of the larger region of Fennoscandia, which includes the Kola Peninsula, Karelia and Finland.
The peninsula is bounded by the Barents Sea of the Arctic Ocean in the north, the Kattegat and Skagerrak seas in the south, the Norwegian Sea and the North Sea in the west, and the Baltic Sea, the Gulf of Bothnia in the east, The Scandinavian mountain range, part of the ancient Baltic Shield, forms the border between Norway and Sweden.
In Norway, the mountains reach the coastline and are deeply dissected by fjords. The eastern side of the range is in Sweden and has extensive slopes with a slight downward slope towards the Baltic Sea and consists mainly of flat, heavily forested lands dotted with lakes.
5. Labrador, 1 km²
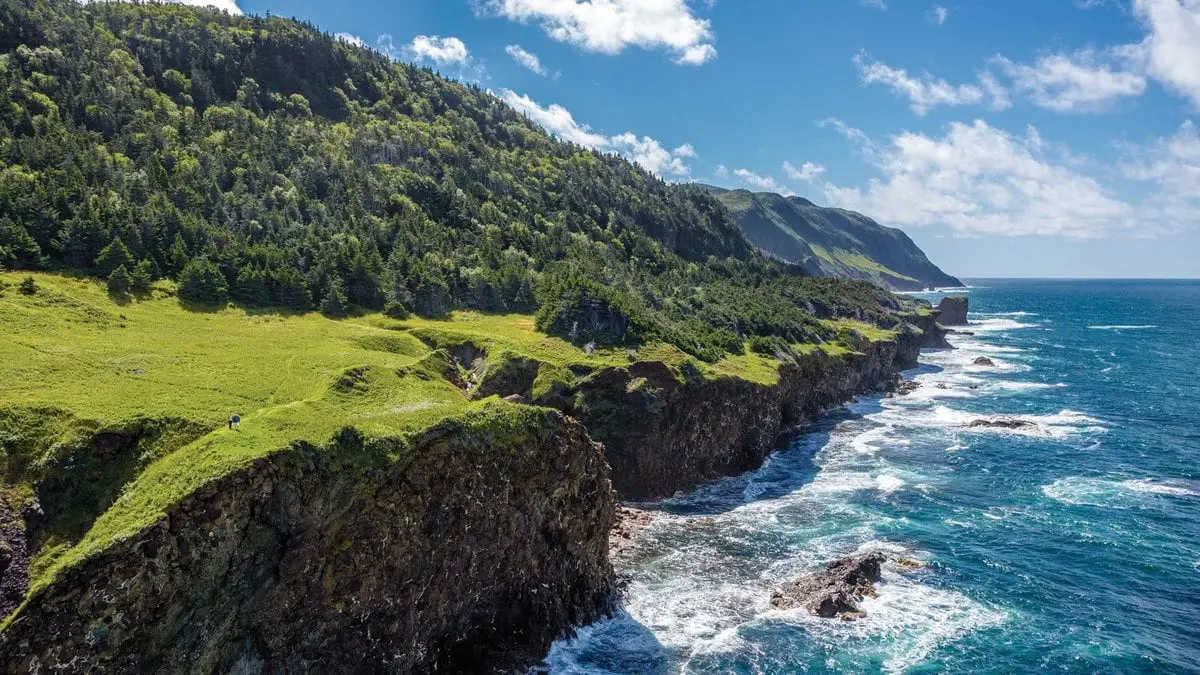 A wide peninsula in eastern Canada, between Hudson Bay, the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Consists of the Ungava Peninsula and Labrador, it contains most of Quebec and the mainland of Newfoundland and Labrador. Also called Labrador Ungava.
A wide peninsula in eastern Canada, between Hudson Bay, the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Consists of the Ungava Peninsula and Labrador, it contains most of Quebec and the mainland of Newfoundland and Labrador. Also called Labrador Ungava.
4. Indostan, 2 km²
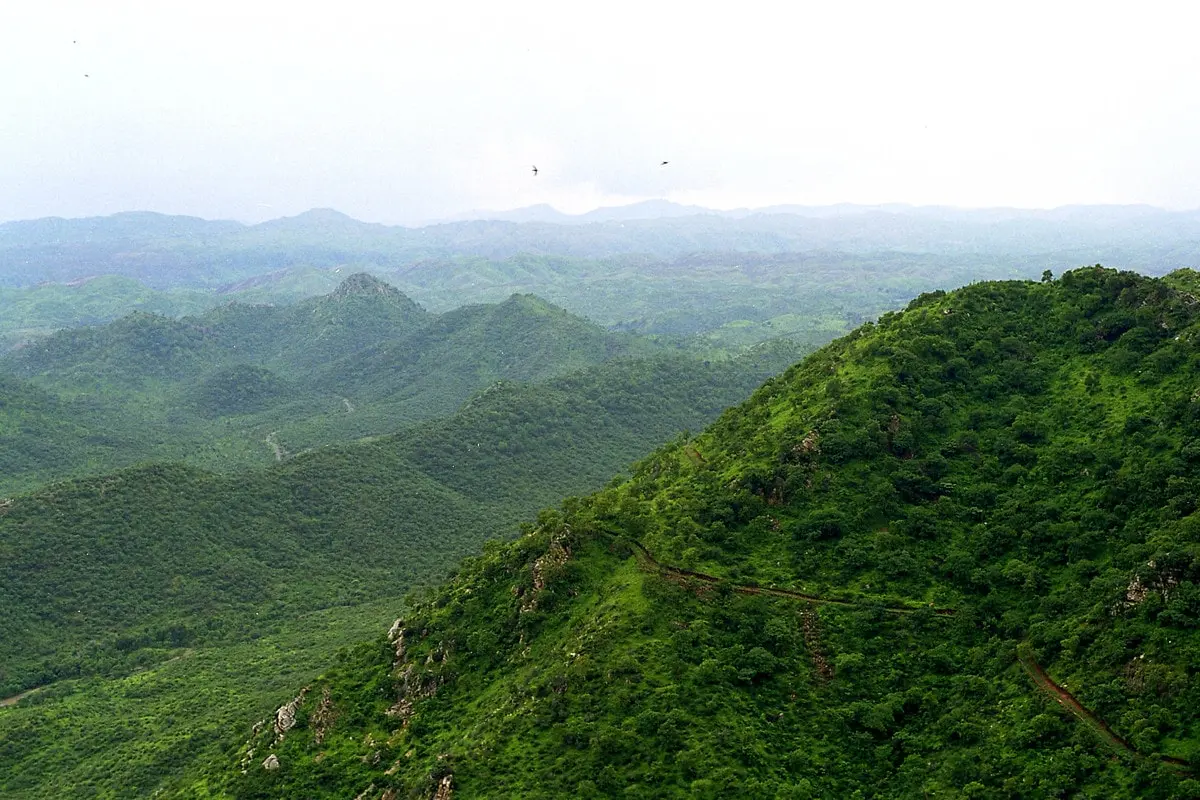

Area Indostan can be defined more specifically as the basin of the five rivers of the Punjab and the upper Indo-Gangetic plain. As the most fertile and populous corridor nestled between walls of mountain, desert and sea, Hindustan is considered the main center of power in the Indian subcontinent, containing most of the wealth and physical energy.
The name Hindustan is sometimes used to refer to the lands “north of the Vindhya range”. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for the entire Indian subcontinent.
3. Indochina, 2 km²
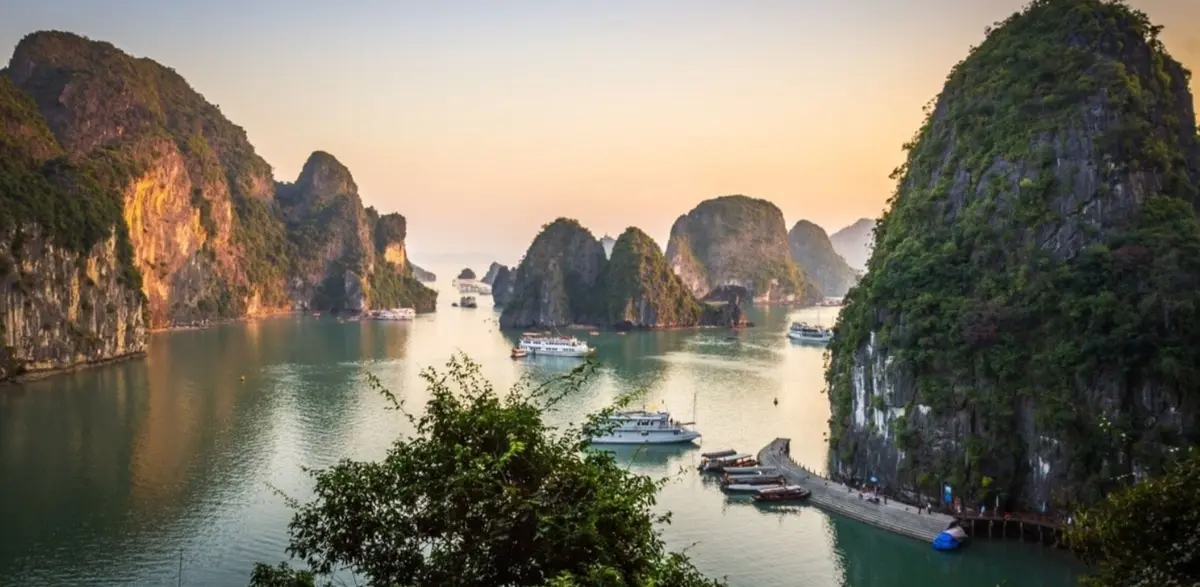

Peninsula Indochina, is a subregion of Southeast Asia. Historically, the continental countries of Southeast Asia have been variously and nuanced under the influence of the two great cultures that border it, India and China.
For example, the culture of Cambodia and Laos was influenced mainly by Indian cultures, respectively, to a lesser extent, the culture of China. Other cultures such as Vietnam were much more influenced by China, having only minor cultural influences from Indian civilizations, especially due to the Champa civilization.
2. West Antarctica, 2 km²
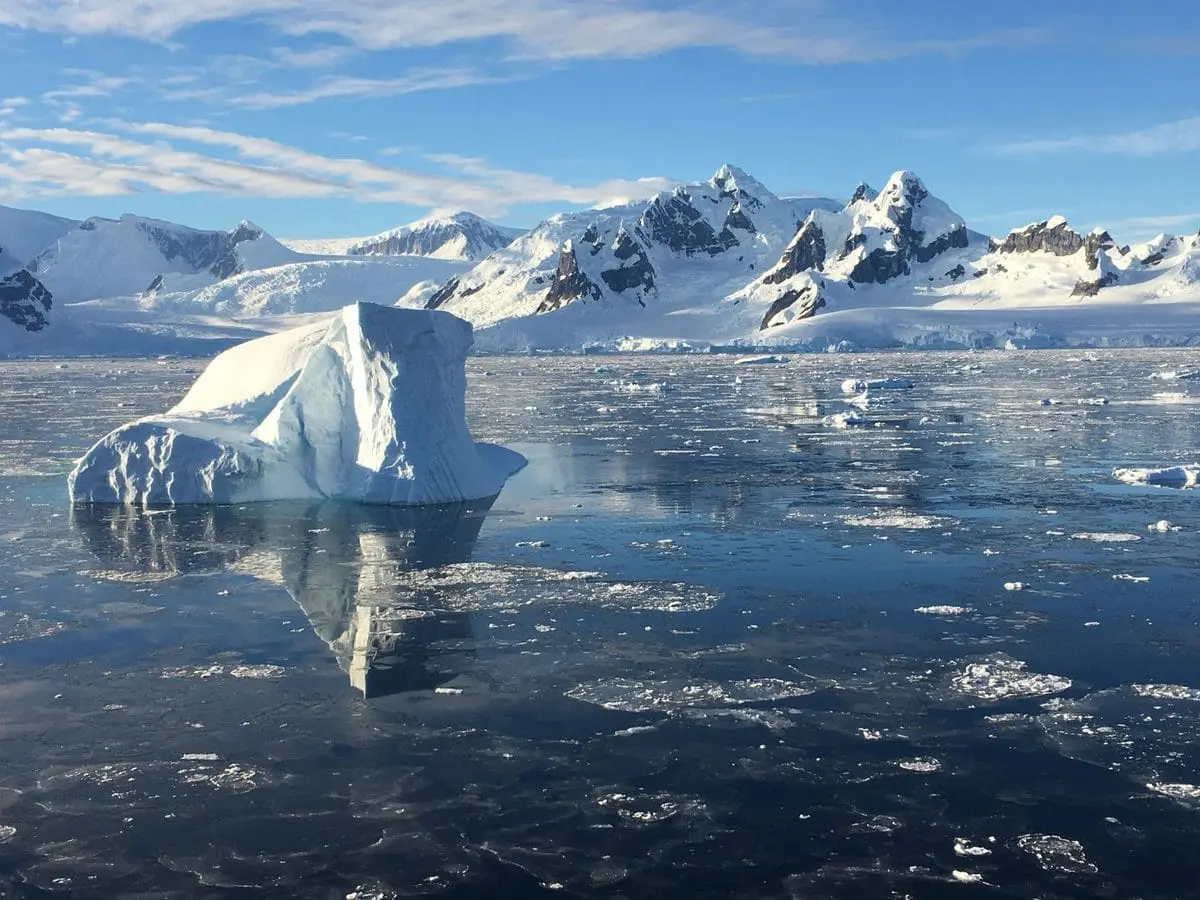

Antarctic Peninsula is a relatively long, thin ridge alpine mountain range. The Antarctic Peninsula Ice Sheet (sometimes referred to as APIS) is widely considered to be sensitive to climate change due to its small size and northern location, and because the region is one of the fastest warming places in the world.
This sensitivity is manifested in the collapse of numerous ice shelves, increased ice velocities and the retreat and thinning of glaciers and ice caps.
1. Arabian Peninsula, 2 km²
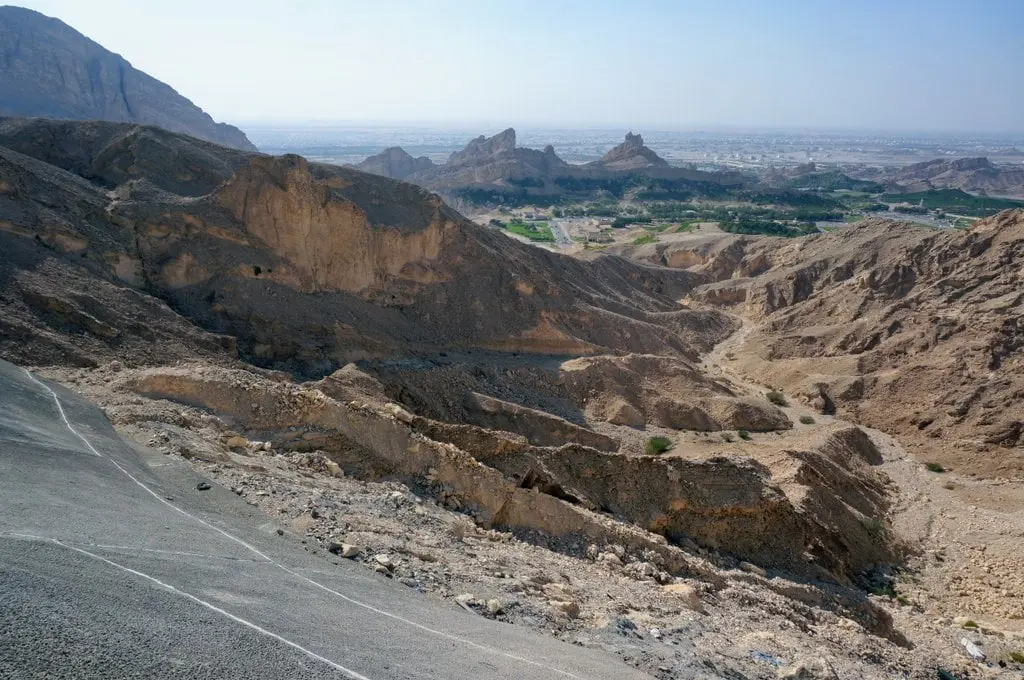

Arabia – a peninsula, together with coastal islands, located in the extreme southwestern corner of Asia. The Arabian Peninsula bounded by the Red Sea to the west and southwest, the Gulf of Aden to the south, the Arabian Sea to the south and southeast, and the Gulf of Oman, and the Persian Gulf (also called the Arabian Gulf) to the east.
Geographically, the peninsula and the Syrian Desert merge in the north with no clear demarcation line, but the northern borders of Saudi Arabia and Kuwait are generally considered to be the boundary of Arabia.
The geographical cohesion of the Arabian Peninsula is reflected in the common interior desert and common outer coast, ports, and relatively greater opportunities for agriculture.
The fact that most of the peninsula is unfavorable for settled agriculture is of great importance. Competition for habitable land is fierce, and the efficient use of land and water is critical to the well-being of every nation.










