Contents
The human body is made up of various organs that perform a particular function. Eyes, for example, allow us to see the world around us – the shape of objects, colors, people, and so on. Those who are not interested in anatomy do not know that the eye has a perfect structure, and provides vision in three dimensions and with the highest sharpness …
Some people do not like it when they look into their eyes, and there is an explanation for this – they, as they say, “the mirror of one’s heart”, to look into it, you first need to create a trusting relationship …
Well, what are we talking about eyes?! There are no less interesting organs: the liver, spleen, kidneys, for example. Let’s find out more about them. We bring to your attention a list of the 10 largest human organs: large and heavy internal parts of the human body – information for grade 4.
10 Colon
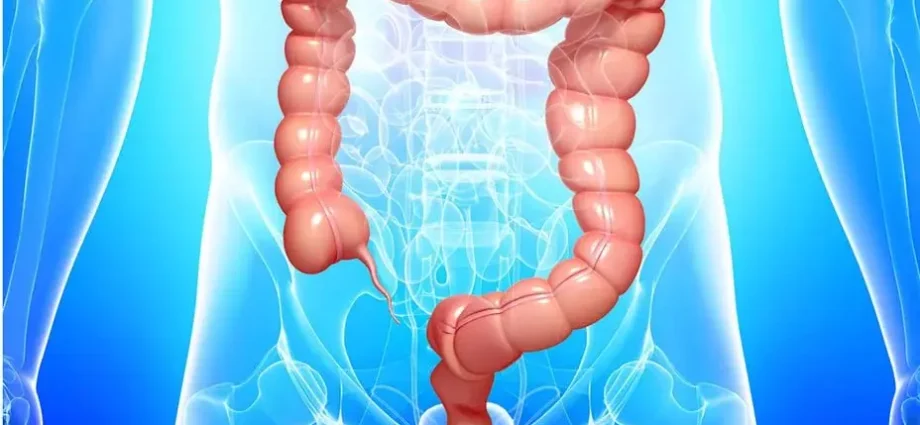
The intestine not only supplies us with nutrients, but also removes harmful substances from the body. It also helps support immunity. The intestine includes several sections: small intestine, rectum, large intestine, duodenum.
Our attention is now directed to large intestine is the largest organ in our body. It is located along the perimeter of a relatively thin, and shaped like a frame. Its main function is to absorb water from the remaining mass and accumulate feces for their further removal from the body.
9. Spleen
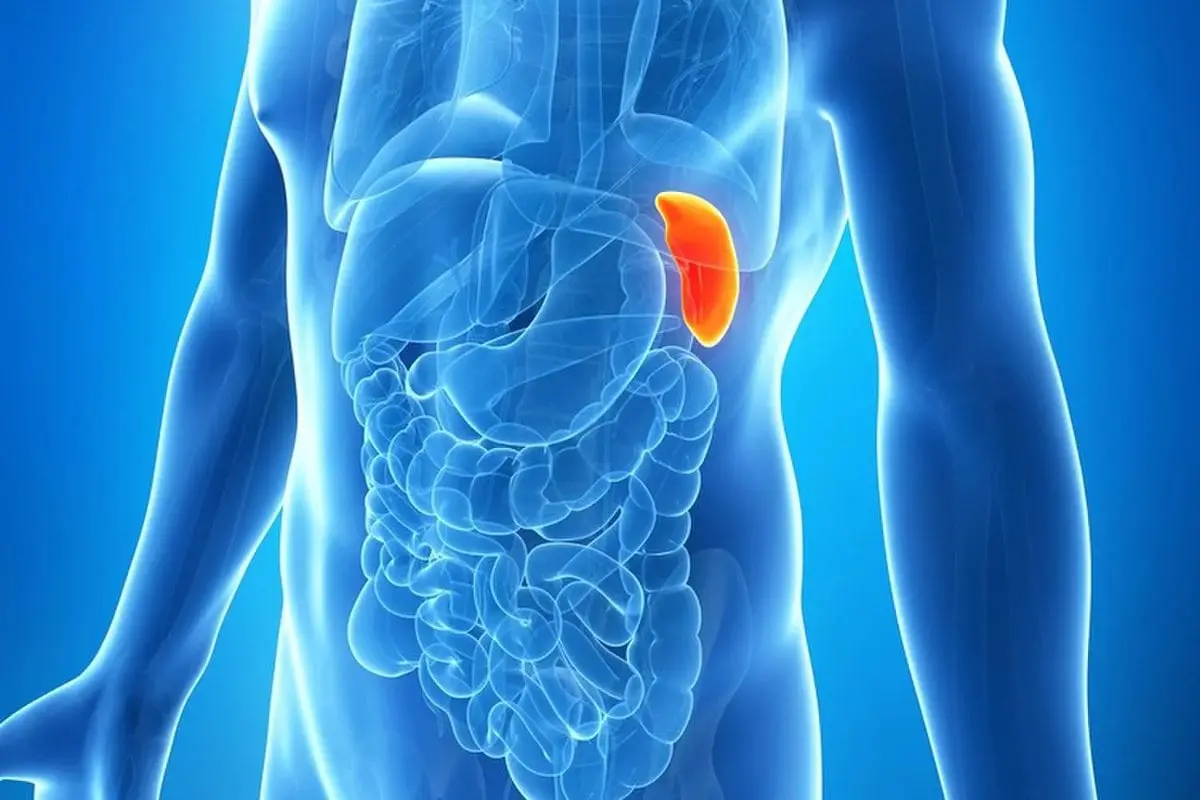
Spleen it is a kind of “filter” of our body. It absorbs and processes bacteria that enter our bloodstream, as well as other harmful substances. Produces antibacterial bodies.
The spleen is one of the largest organs, it is very important for maintaining immunity, in addition, it contains a supply of blood – if necessary, the blood enters the systemic circulation of the body.
The mysterious organ, about which not much is known, also stores iron, which is converted into hemoglobin, promotes good digestion and has effects on the nervous system.
8. Stomach
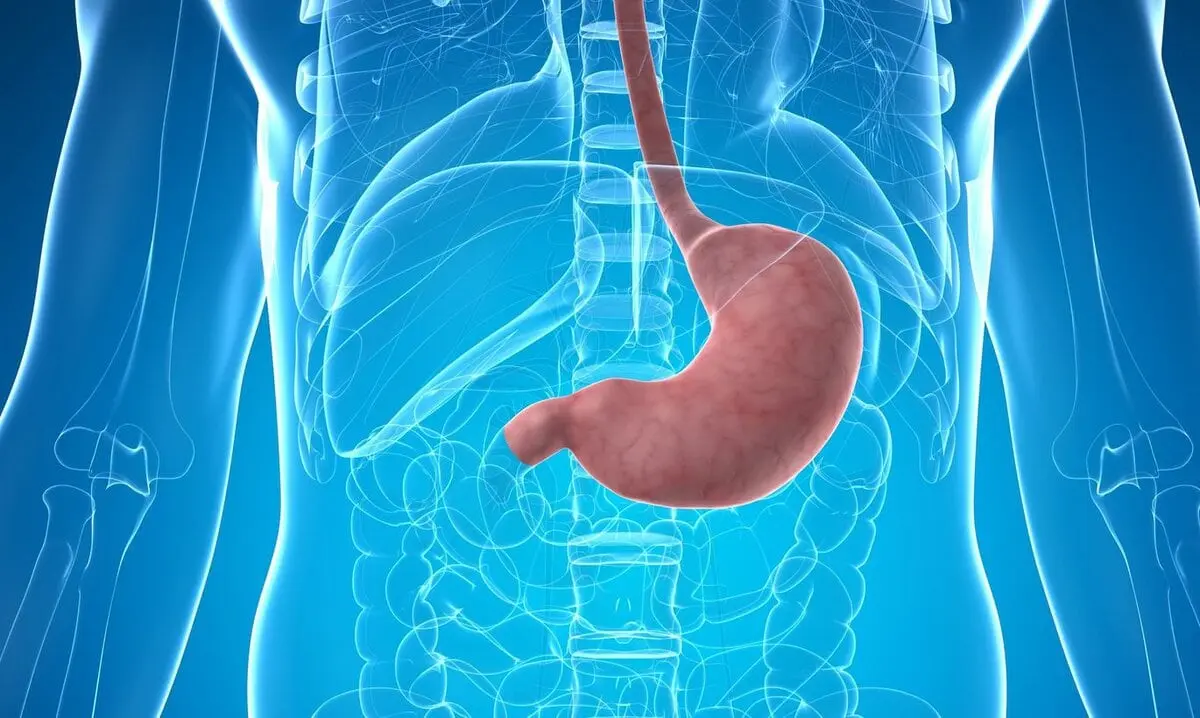
In the upper part of the abdominal cavity there is such an important organ as stomach. It is a muscular sac that provides a favorable environment for the breakdown and digestion of food.
The shape of the stomach changes with the age of a person, there are only 3 of its forms: stocking, hook and horns. On average, the length of the stomach along its long axis is 22-25 cm. The stomach holds 3 liters. This organ can be called part of the digestive tract chain, and, of course, its important link.
The stomach is located in front of the duodenum and is a continuation of the esophagus. It is in this organ that the thickest region of the muscle layer is located.
7. Kidneys
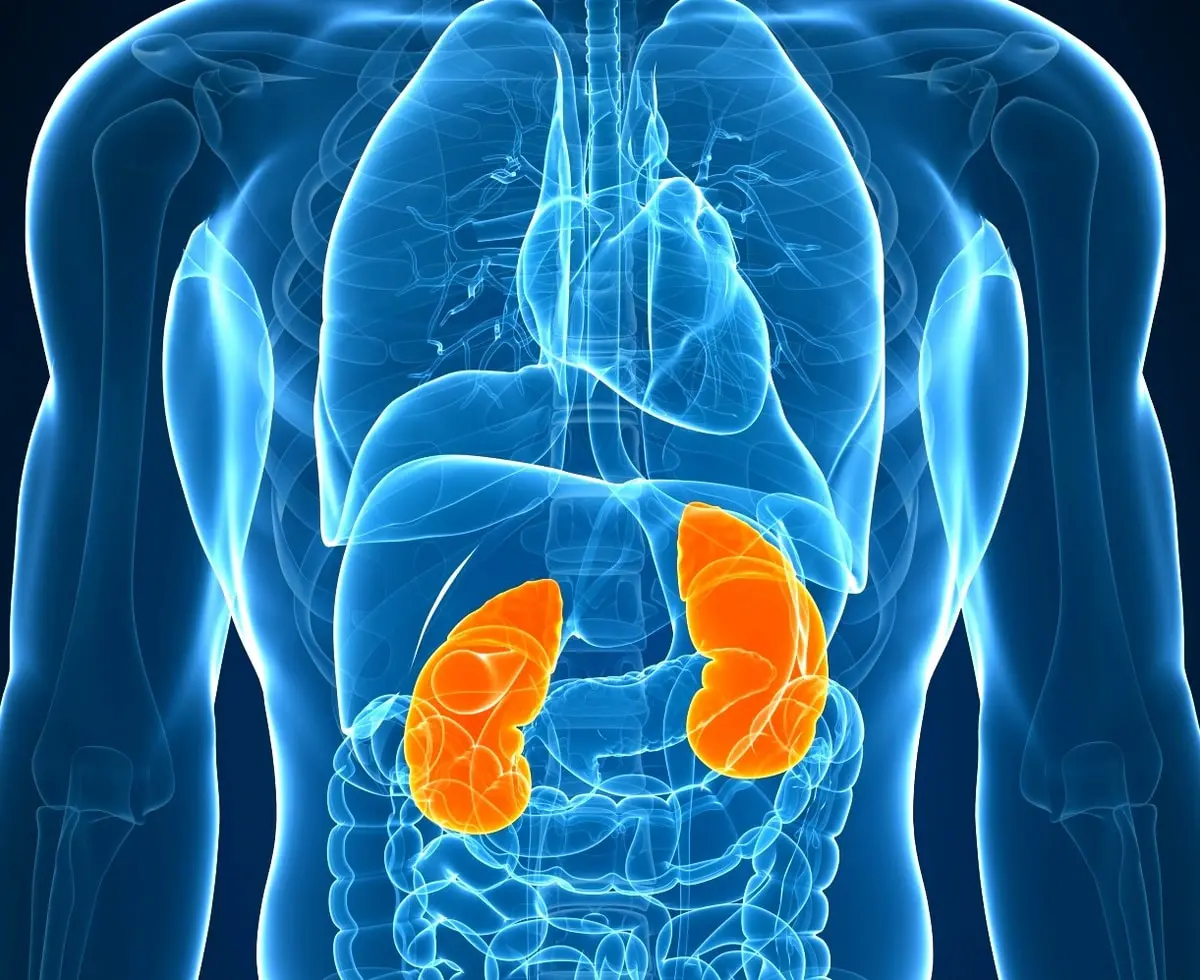
The vital human organ is kidneys. This is a paired organ, which is located in the retroperitoneal space on the sides of the spinal column.
The kidneys form urine. The boundaries of the location of these important organs vary even within the normal range – most often the left kidney is located slightly higher than the right one. One organ weighs approximately 100-200 g, width – 5-6 cm, length – 11-12 cm, thickness – 3-4 cm. If the organs noticeably deviate from these sizes, then this is a sign of pathological changes.
Anatomically, the organ looks like beans. The main function of the kidneys is excretory. They form urine, with which toxic products are washed out of the body.
6. Lungs
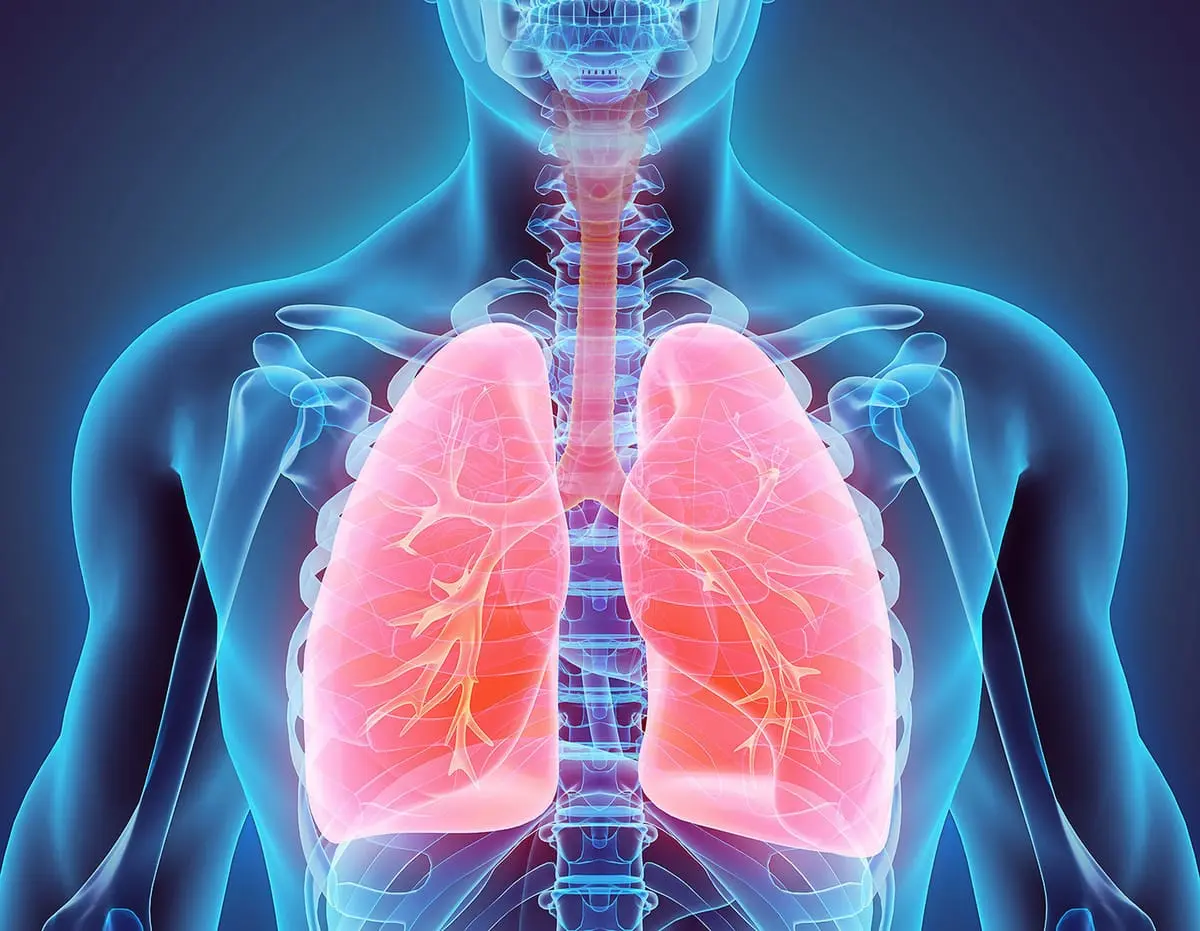
Lungs, like the kidneys, is also a paired organ. We owe every breath we take to this most important organ. Gas exchange takes place in the lungs, thanks to which our body is saturated with oxygen and removes waste carbon dioxide from the body – everyone knows this from school textbooks.
The right lung is slightly wider than the left and shorter. Such a structure is quite natural, because the heart is located in the left and partially central chest cavity. On the left lung there is a kind of recess, thanks to which the heart feels quite comfortable. The left lung is a kind of shock-absorbing pad that protects the heart from mechanical damage.
In shape, the organ resembles a cone – it has a base and an apex. The process of breathing is quite an interesting phenomenon, because we do not even notice how we breathe. The brain decides how much air it needs.
However, a person himself can learn to control his breathing, there are even special techniques for this, thanks to which you can relieve stress, remove pain and even get rid of unnecessary emotions.
5. Brain
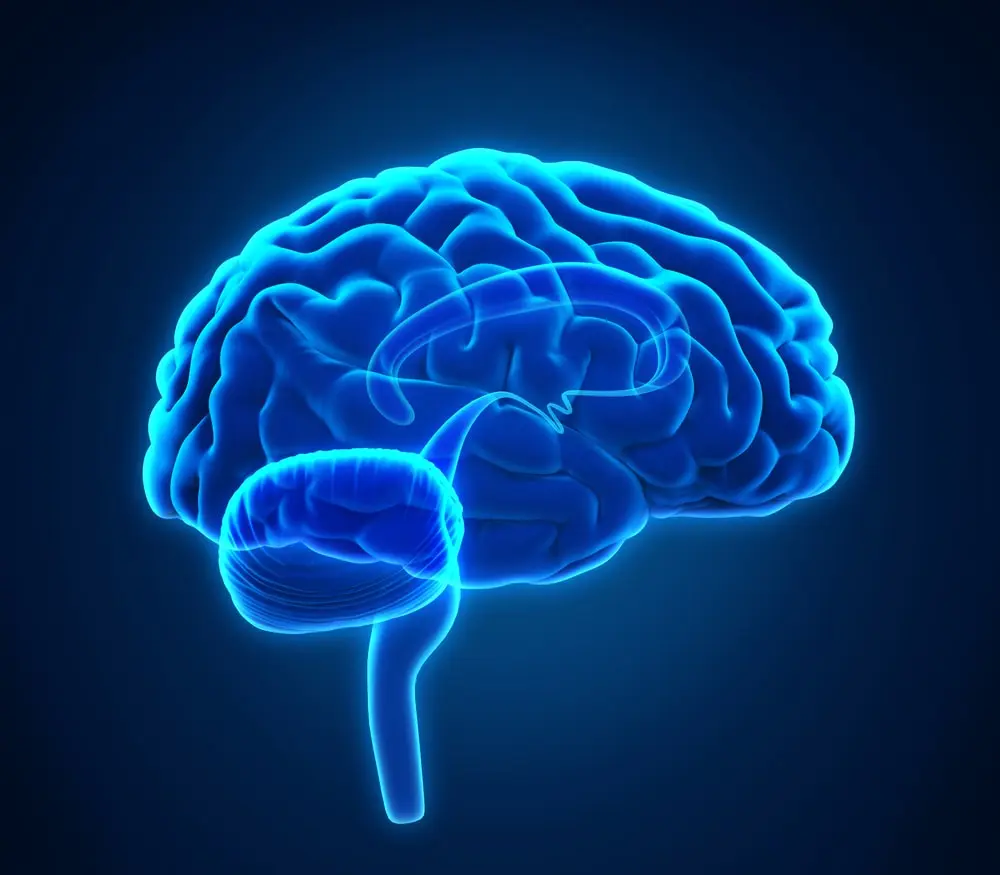
An amazing three-pound organ located inside the skull – brain, has always attracted and attracts scientists. This organ is the main one. It is he who is responsible for the work of other organs. Despite the fact that the brain is constantly being studied, much of its work still remains a mystery … People have only a superficial idea of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbhow it works and transmits information.
The brain is made up of cells called neurons that create electrical impulses and transmit data. Neurons consist of a body and processes of two types: dendrites and axons. The first receive the impulse, and the second transmit.
The brain is responsible for emotions, creativity, memory… And these are just some of the things that are controlled by the brain. It is very important to take care of him, to solve various problems – what is not paid attention to, will atrophy over time.
4. Heart
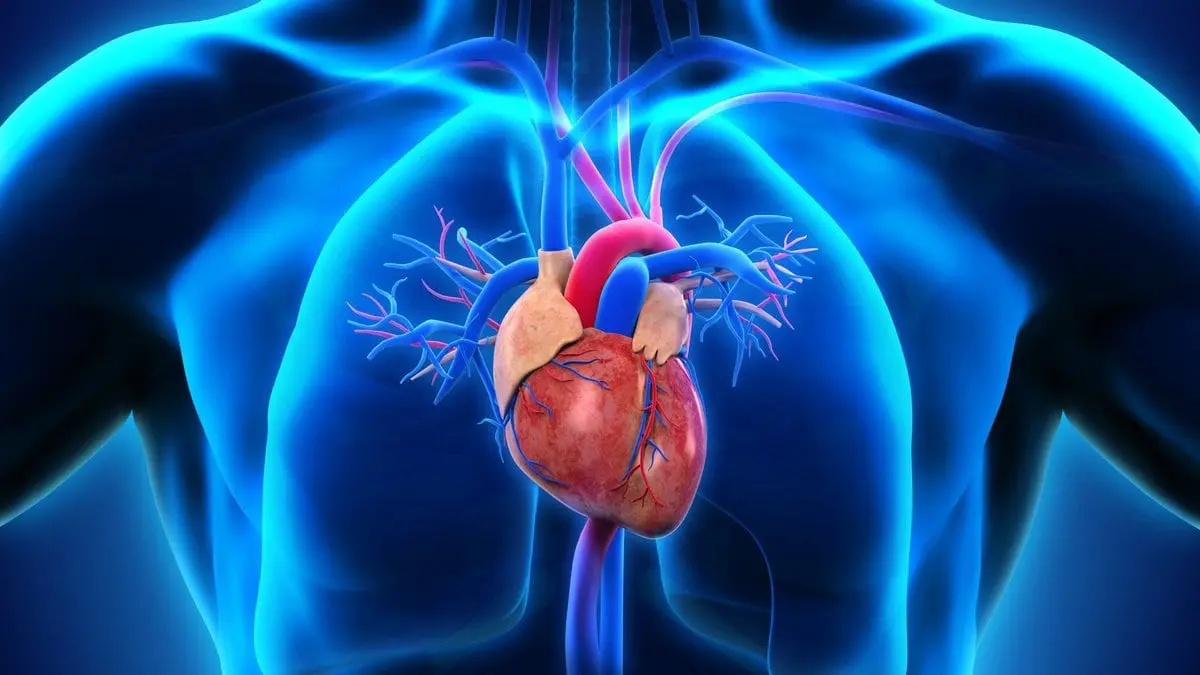
What do you imagine when you hear the word a heart? Surely something romantic, connected with feelings, pops up in your imagination …
The heart that is drawn is a symbol of love, but the organ looks different. There is a version that the symbol of the heart appeared in Ancient Greece as a symbol of femininity, beauty, and it represented nothing more than a reproduction of the female breast and buttocks.
In many cultures, this organ is considered the seat of the soul, the place where love and affection are born, but in reality it is more and more prosaic… men.
When a person is born, his work does not stop even for a second. By pumping blood, the heart supplies all tissues and organs with oxygen.
3. Liver
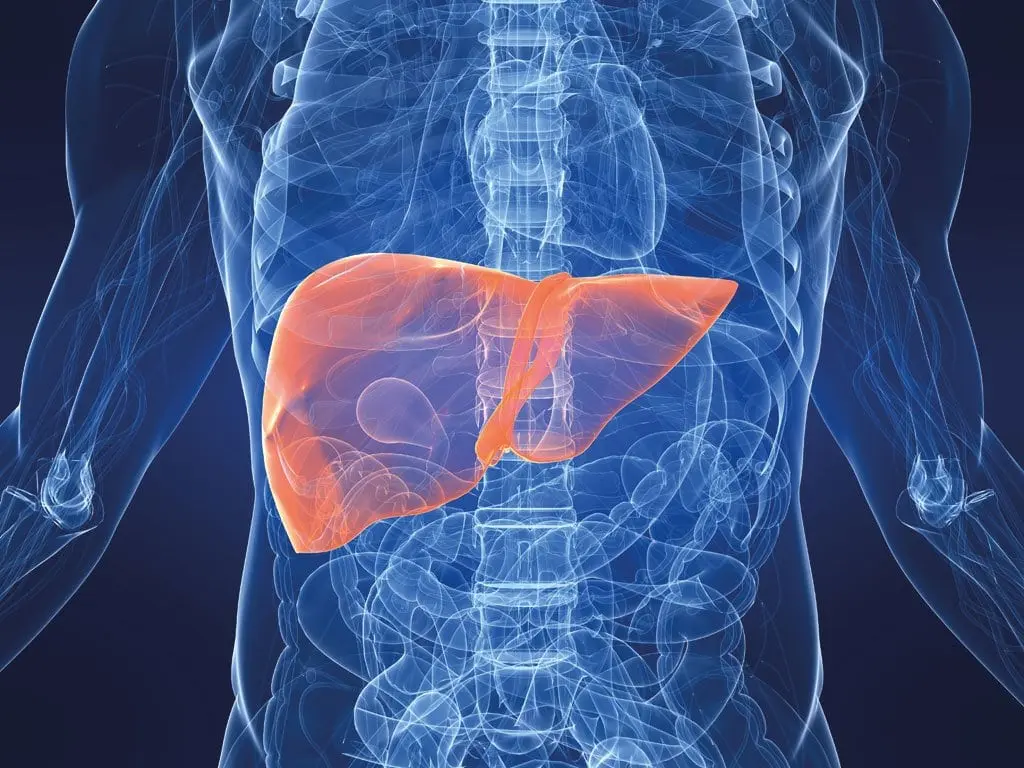
Liver can rightly be called a unique organ of our body, because it performs many functions. The liver is the largest organ in the digestive system. If conditions are favorable, then the organ can renew itself.
The liver is located in the right hypochondrium under the diaphragm, its weight depends on the age of the person, in an adult it is approximately 1500-1700 g.
The liver is a multifunctional organ, its main functions are: normalization of carbohydrate metabolism, secretion of good cholesterol, detoxification, production of part of immune cells, etc.
2. Small intestine
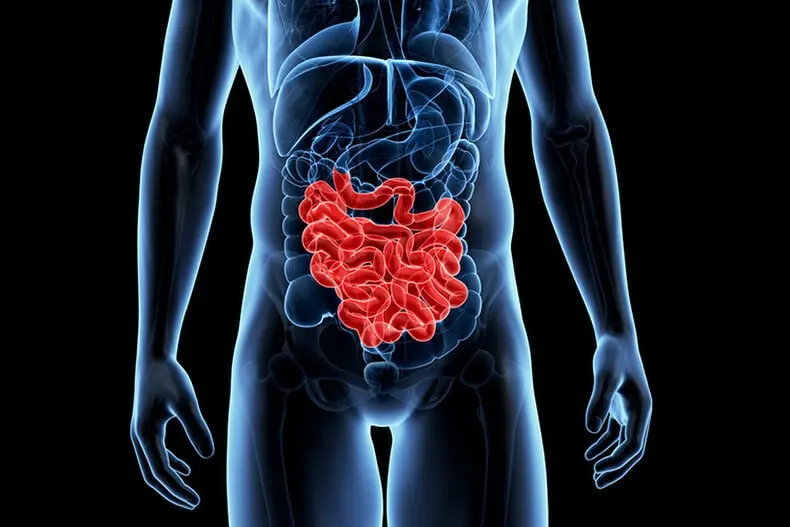
The small intestine in the structure of the intestine is the longest section of the digestive tract, consisting of two sections. Small intestine forms a large number of loops and passes into the large intestine. Its length is approximately 2,6 meters. Anatomically, the small intestine is divided into three sections: jejunum, duodenum, and ileum.
The food mass passes through the small intestine in about 4 hours. During this time, the nutrients that are contained in the food are broken down by the enzymes of the intestinal juice into smaller components. In the small intestine, digestion also consists in the active absorption of nutrients.
1. Leather
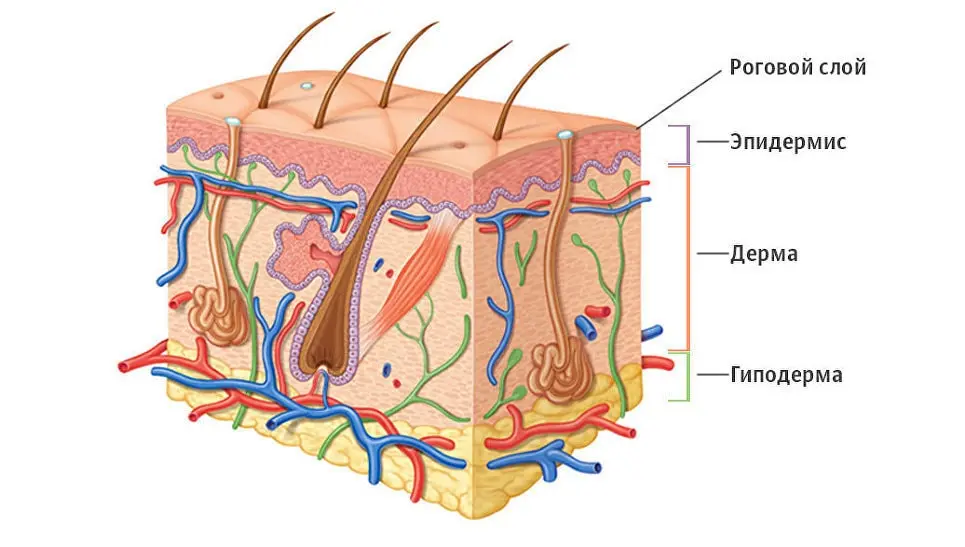
Our list ends with such an organ as skin. It performs a protective role, as well as a number of other biological functions. Our entire body is covered with skin. In a healthy adult, the total area of the skin is up to 2 square meters. meters, and weight up to 6% of the total body weight.
The condition of our skin depends on such factors as: nutrition, age, lifestyle, etc. The skin includes three layers: epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous fatty tissue. Each of them includes several layers.
Interesting fact: all cosmetics that we use affect only the upper skin layer – the epidermis.