Contents
- 10 In ancient Babylon, the doctor paid dearly for his mistakes
- 9. Bloodletting was considered a universal remedy in the ancient world.
- 8. The great importance of ginseng in Chinese medicine
- 7. The placebo effect and its role in medicine
- 6. In the ancient world, diseases were considered a punishment of the Gods.
- 5. First anesthesia – a mixture of wine and hemp
- 4. Plastic surgery originated in India
- 3. Ayurveda occupied a high place in the medicine of ancient India.
- 2. Pirogov first applied plaster
- 1. Medicine has several traditional symbols
Medicine is the science that studies diseases. This is a system of scientific knowledge and practical actions that we need to maintain health, prolong the life of people, prevent or cure diseases, and alleviate the suffering of the patient.
Latin “I burned the medicine” can be translated as “healing art“. Allocate preventive medicine, the purpose of which is to prevent the occurrence of various diseases both in one person and in a group of people. In addition, there is clinical medicine, it detects and treats various diseases, tries to prevent their reappearance.
Doctors and other medical workers are very important for humanity, because. they help keep us healthy, enable all people to live a full life.
It is the health of a person and loved ones that is the most valuable. Without it, neither luxury resorts, nor exotic dishes, or other pleasures of life give pleasure.
10 interesting facts about medicine will help you learn more about this ancient, vital science.
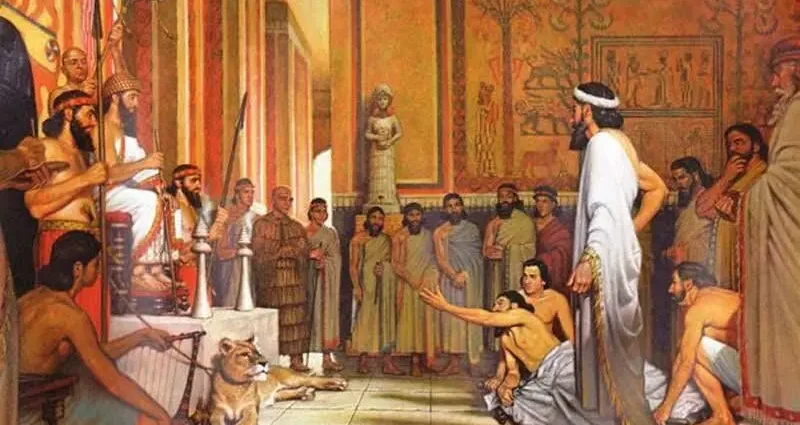
10 In ancient Babylon, the doctor paid dearly for his mistakes

Once upon a time, doctors of Babylon could pay a huge price for their medical error – they cut off their hands. However, the doctors of that time did everything to protect themselves. A limited number could enter their circle. Many texts were written in the language of the ancient Sumerians, so only an initiated person could understand them. All drug names were encrypted, their composition was carefully hidden.
Doctors left seriously ill people unattended, moreover, they were forbidden to approach them, because. it was believed that he had to die and could not recover.
Doctors of that time described the symptoms of many diseases. But most of them were priests who acted as doctors, so many of them relied on prayers and spells. They attributed all their failures to the fact that the person they were treating paid little attention to astrology and the gods.
Gradually, medical science was completely supplanted by superstition, magic and the occult and remained at the lowest stage of development.
9. Bloodletting was considered a universal remedy in the ancient world.
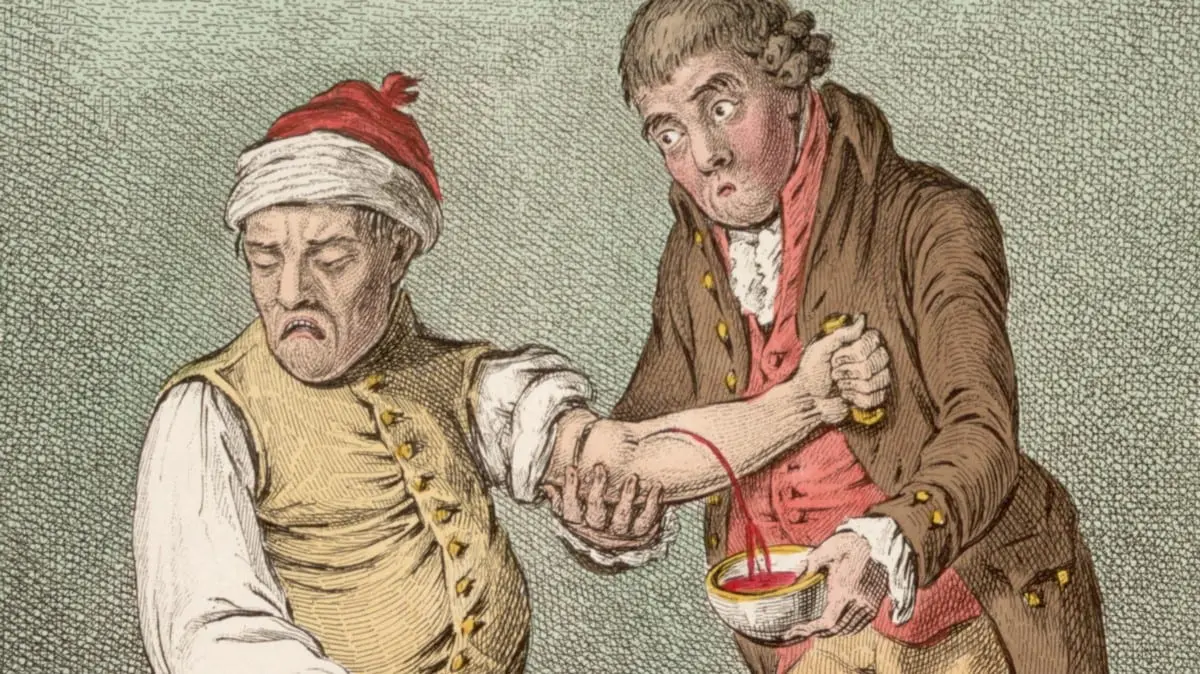
One of the most popular methods of treatment, which was used until the end of the XNUMXth century, was bloodletting.. It was believed that by ridding a person of excess fluid in the body, many diseases can be cured.
“Excess” blood was removed with leeches, or by cutting a vein. For the last procedure, a lancet and a bowl into which blood flowed were used. Since the XNUMXth century, this has been practically the only medical procedure, because. it was believed that in this way “bad” blood was removed.
Now this method of treatment is practically not used, because. it just seems to give relief. In fact, it weakens the human body, deprives it of the ability to fight the disease. So, King Louis XIII had 47 bloodlettings in 10 months, and, of course, there was no talk of any recovery.
8. The great importance of ginseng in Chinese medicine

Literally translated from the Chinese word “ginseng”, it will work”root man”, because in shape it resembles a human figure. It began to be used in Chinese medicine more than 4 thousand years ago, and the first written mention appeared in the 1st century BC. in the essay on medicines “Shen Nong pen cao”.
The Chinese believed that this plant could get rid of almost all diseases, they called it the most useful, capable of even resurrecting a dead person.. It was believed that if you constantly take drugs from ginseng, you can lead an active life up to 100 years. It was also a powerful aphrodisiac. Previously, if a Chinese man wanted to become a father at the age of 8, he chewed the root of this plant daily.
7. The placebo effect and its role in medicine
A placebo is when a drug or other treatment works, even if it’s all fake. The patient inspires himself that it is easier for him, and this helps.
The placebo effect really works, it has been proven by many studies, and it is based on the deep mechanisms of the human subconscious.
It was first discovered in the XNUMXth century. Then the doctor Elisha Perkins treated people “tractors”. So he called small (8 cm) metal sticks, which were supposedly made of special materials, but in fact they were brass and steel. He claimed that they remove inflammation, relieve pain, you just need to attach them for 20 minutes to the sore spot. And people really got better.
Many doctors doubted that this “medicine” helps. British doctor John Haygarth decided to test and made “tractors” from different materials, they all helped. Then it became clear that a lot depends on thoughts and expectations, the patient got better only because he believed in it.
6. In the ancient world, diseases were considered a punishment of the Gods.
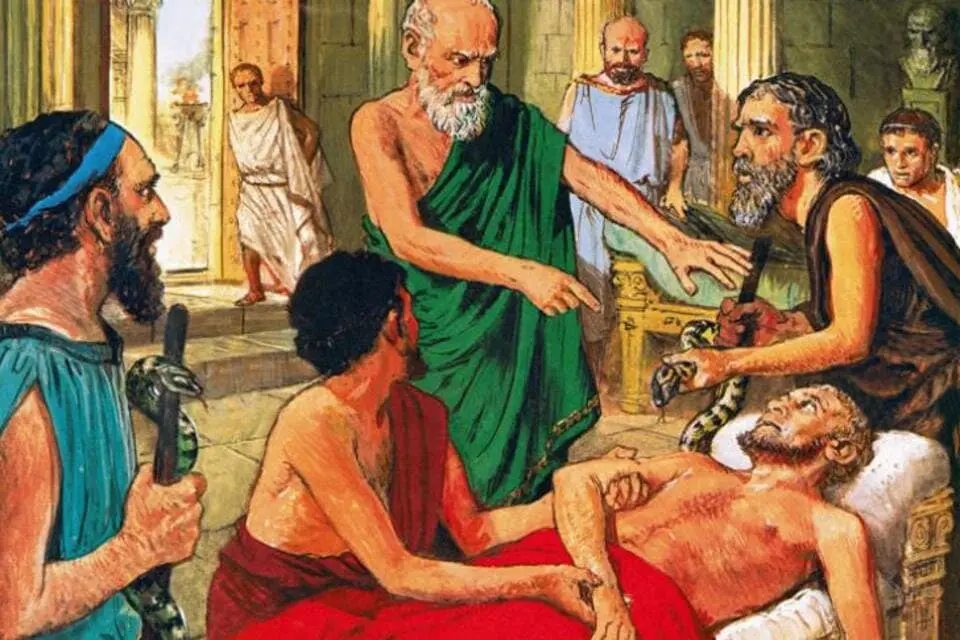
Medicine and religion were once closely intertwined. People believed that illness was a punishment from God or the result of demons. If a person recovered, it meant that he was forgiven. The monasteries not only helped the needy, but also healed the sick.
At the end of the XNUMXth century, many poor people ate bread, which was baked every few months. Ergot caused a strong fever. But they fought this disease in a peculiar way: prayers, processions.
There was a cult of saints, each allegedly helped from another illness. Therefore, people died early, 50-year-olds were considered people of advanced age.
5. First anesthesia – a mixture of wine and hemp
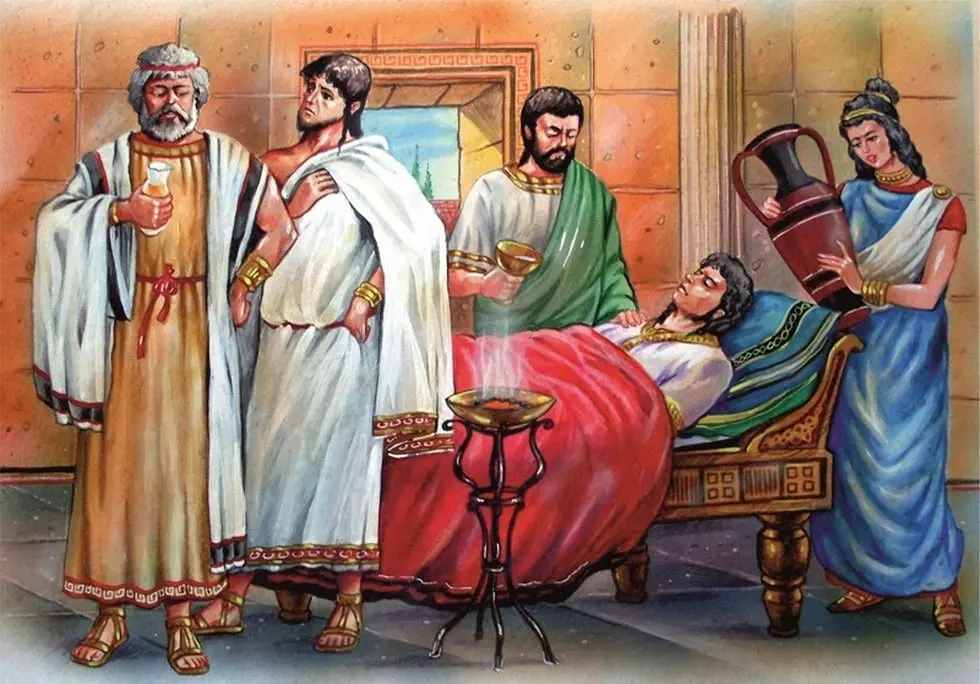
In ancient Greece, mandrake root was used for pain relief. This is a poisonous plant that could cause death.
In ancient India, shamans used coca leaves containing cocaine. They were chewed and spat on wounded warriors. In China, hemp was used for this purpose..
In medieval Europe, if an operation was to be performed, the patient was beaten on the head with a mallet to make him lose consciousness.
4. Plastic surgery originated in India
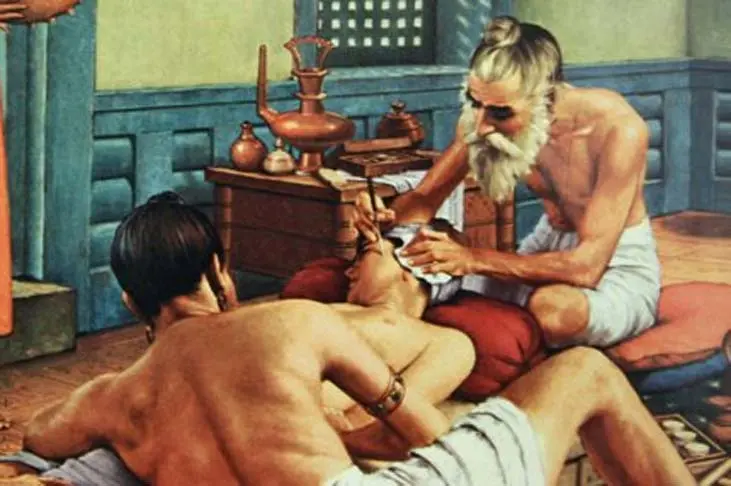

In 800 BC India has already done the first operations to correct the nose, for this they took the skin from the forehead and cheeks. Until the XNUMXth century, Indian surgery was at its best when compared with European. In Europe, only a few operations were performed, while in India they were performed constantly.
3. Ayurveda occupied a high place in the medicine of ancient India.
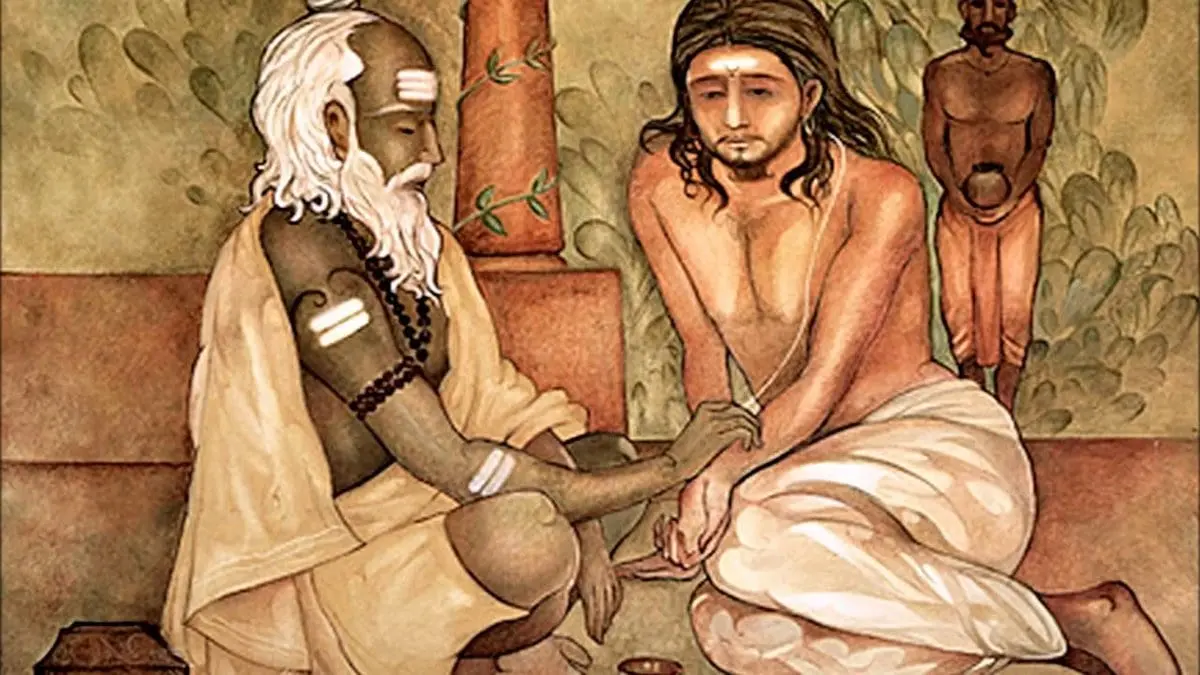

This title can be translated asknowledge of life” or “life science“. This is Indian folk medicine, which is now considered a pseudoscience. But the first medical text of this country appeared in the Vedas. It also contains the first text on the use of antibiotics (Aushadhi lichen with such properties), as well as a detailed description of human bones.
2. Pirogov first applied plaster
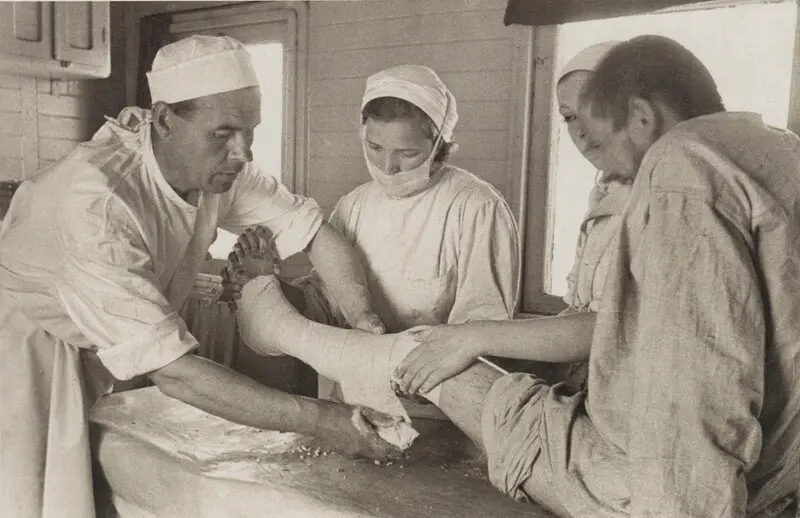
Fractures have been treated since ancient times. Arab doctors used clay for these purposes, in Europe they mixed camphor alcohol, whipped proteins and lead water.
The Russian surgeon Karl Gibenthal pioneered the use of plaster. But the fixing bandage was invented by the Russian surgeon Nikolai Ivanovich Pirogov. In 1847, he participated in the hostilities in the Caucasus, where he began to use a “stuck” bandage. First he used starch, then colloidin, and finally gypsum. This invention of Pirogov is still used.
1. Medicine has several traditional symbols

Medicine has several symbols. The most common is the Red Cross and Red Crescent are symbols of the humanitarian movement founded in 1863. The staff of Asclepius is also known.
There is a legend that the god of healing Asclepius walked with a staff. The snake wrapped around his staff, and he decided to kill her. Then another snake crawled and gave her an herb that helped resurrect her dead predecessor. Asclepius found this herb and learned to resurrect the dead.
The daughter of Asclepius was Hygeia (the discipline of hygiene was named after her). She was depicted as a young woman feeding a snake from a bowl. Later, the snake and the cup became one of the symbols of medicine.










