Contents
- 10 Viruses and viroids do not have cells
- 9. Cytology is a branch of biology that studies cells
- 8. Robert Hooke first saw the cells
- 7. Leeuwenhoek first saw animal cells
- 6. Schwann and Schleiden formulated the Cell Theory
- 5. Mitosis in plants was discovered by Chistyakov, in animals by Flemming
- 4. Microscopy is one of the most important methods for studying cells.
- 3. The division of life forms into two kingdoms
- 2. Groups of similar cells form tissues
- 1. The cell nucleus contains DNA molecules
Cells are the basic building blocks of living beings. The human body is made up of trillions of cells, each with its own specialized function. Each cell type is different and performs different functions.
There are nerve cells in the human body that can be as long as our legs to our spinal cord. Nerve cells help transport messages throughout the body. We also have billions of little brain cells that help us think and muscle cells that help us move. There are many more cells in our body that help us function and stay alive.
We have collected 10 most interesting facts about cells that everyone should know!
10 Viruses and viroids do not have cells
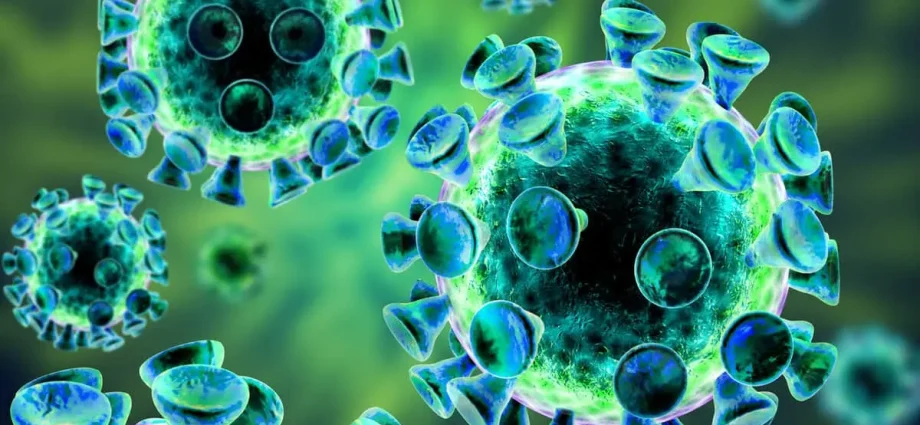
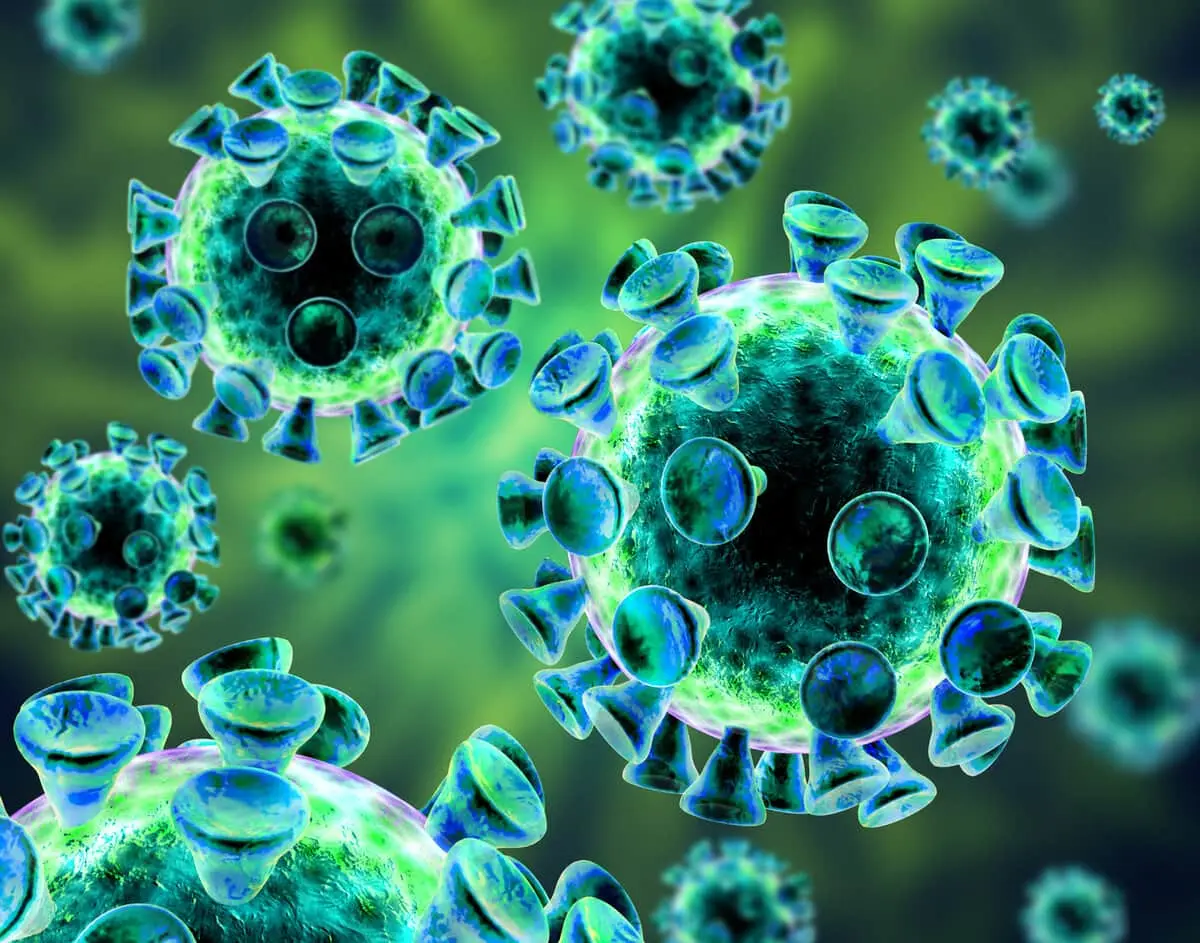 We are all familiar with the action of viruses: these particles infect living cells and basically wreak havoc throughout the body. But viruses are not the only villains around, causing mayhem in living beings.
We are all familiar with the action of viruses: these particles infect living cells and basically wreak havoc throughout the body. But viruses are not the only villains around, causing mayhem in living beings.
Other infectious agents, called viroids, are also tiny but powerful, and can wipe out both plant life and entire animals.
How are viruses and viroids similar? Both of them are cell-free particles.
9. Cytology is a branch of biology that studies cells
 Cytology is the branch of biology that studies cells, the building blocks of life.. The roots of cytology go back to 1665, when the British botanist Robert Hooke, studying the cross section of cork, gave the space the name “cells”, which means “small rooms” or “cavities”.
Cytology is the branch of biology that studies cells, the building blocks of life.. The roots of cytology go back to 1665, when the British botanist Robert Hooke, studying the cross section of cork, gave the space the name “cells”, which means “small rooms” or “cavities”.
The beginning of cytology as a science occurred in 1839 with the first well thought out cell theory. This theory states that all organisms, plants and animals, are made up of one or more similar units called cells. Each of these units individually contains all the properties of life and is the cornerstone of almost all living organisms.
In addition, cell theory states that hereditary traits are passed from generation to generation through cell division.
8. Robert Hooke first saw the cells
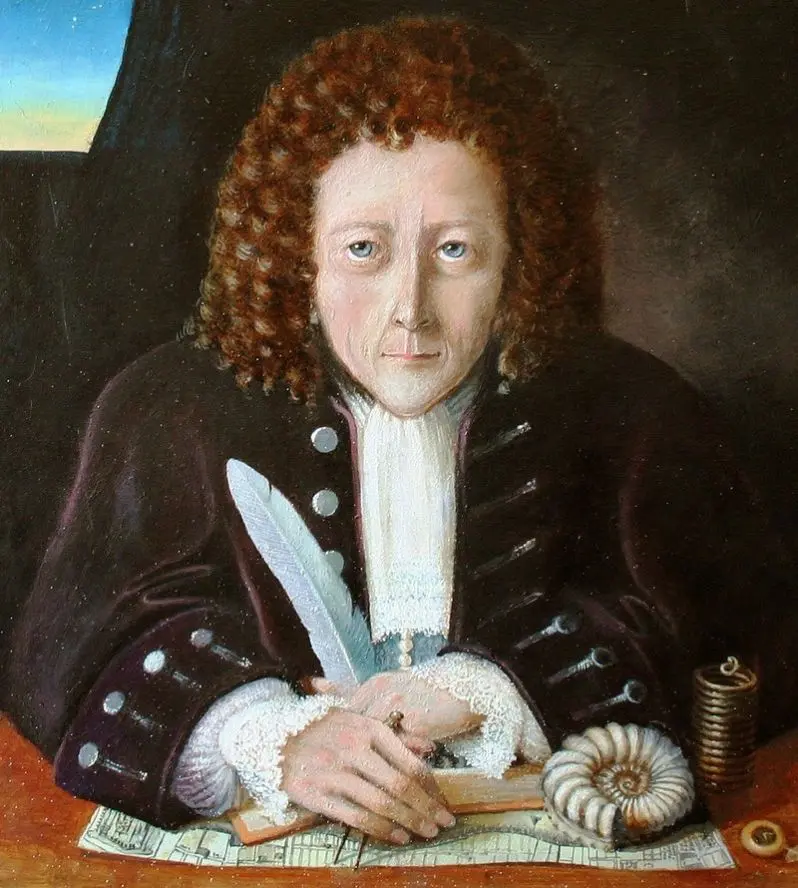 While the invention of the telescope made the cosmos accessible to human observation, the microsop opened up smaller worlds, showing what living forms are made of. The cell was first discovered and named by Robert Hooke in 1665.. He noted that it looked strangely like a cell or small rooms where the monks lived.
While the invention of the telescope made the cosmos accessible to human observation, the microsop opened up smaller worlds, showing what living forms are made of. The cell was first discovered and named by Robert Hooke in 1665.. He noted that it looked strangely like a cell or small rooms where the monks lived.
However, what Hooke actually saw was the dead cell walls of plant cells (plugs) that appeared under a microscope. Hooke’s description of these cells was published in Micrographia. The cell walls observed by Hooke showed no evidence of the nucleus and other organelles found in most living cells.
7. Leeuwenhoek first saw animal cells
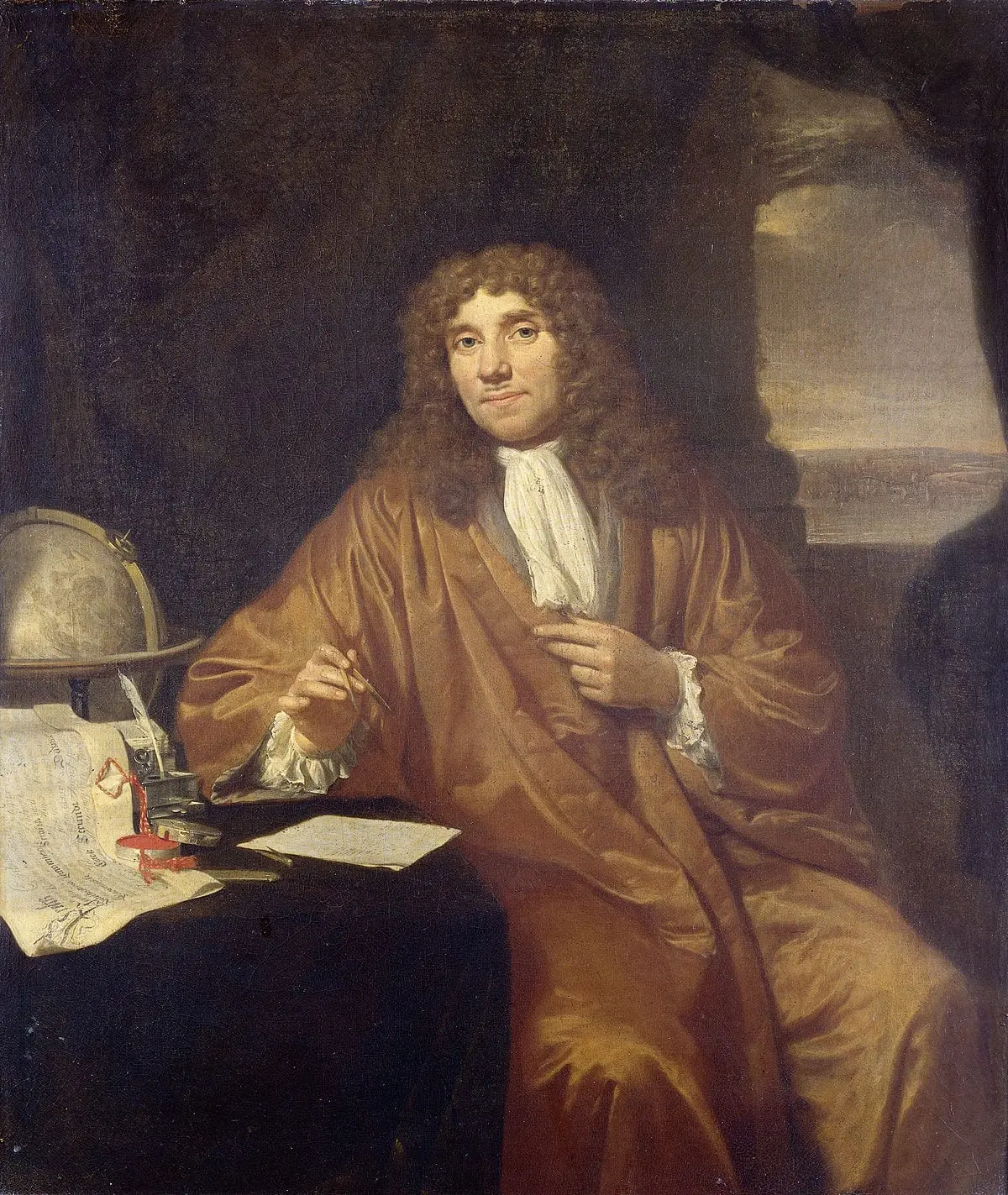 The first person to see a living camera under a microscope was Anton van Leeuwenhoek, who described the algae Spirogyra in 1674. Van Leeuwenhoek probably also saw bacteria.
The first person to see a living camera under a microscope was Anton van Leeuwenhoek, who described the algae Spirogyra in 1674. Van Leeuwenhoek probably also saw bacteria.
His studies of the lower animals refuted the doctrine of spontaneous birth, and his observations helped lay the foundations for the sciences of bacteriology and protozoology.
6. Schwann and Schleiden formulated the Cell Theory
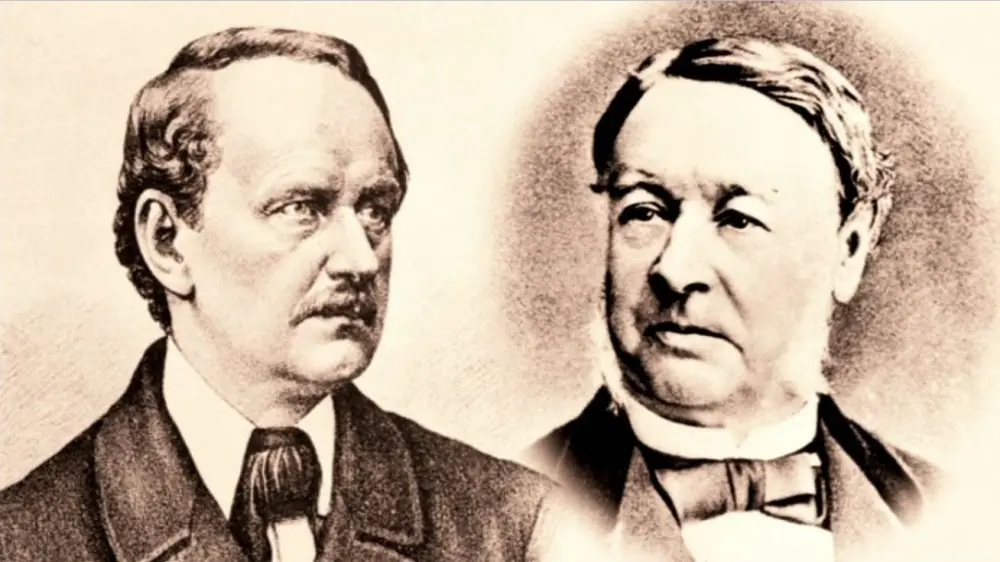 Towards the end of the 30s botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann studied tissues and proposed a unified cell theory.
Towards the end of the 30s botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann studied tissues and proposed a unified cell theory.
The single cell theory states that: All living things are made up of one or more cells; the cell is the basic unit of life; and new cells arise from existing cells. Rudolf Virchow later made important contributions to this theory.
Schleiden and Schwann proposed spontaneous generation as a method for producing cells, but spontaneous generation (also called abiogenesis) was later refuted.
5. Mitosis in plants was discovered by Chistyakov, in animals by Flemming
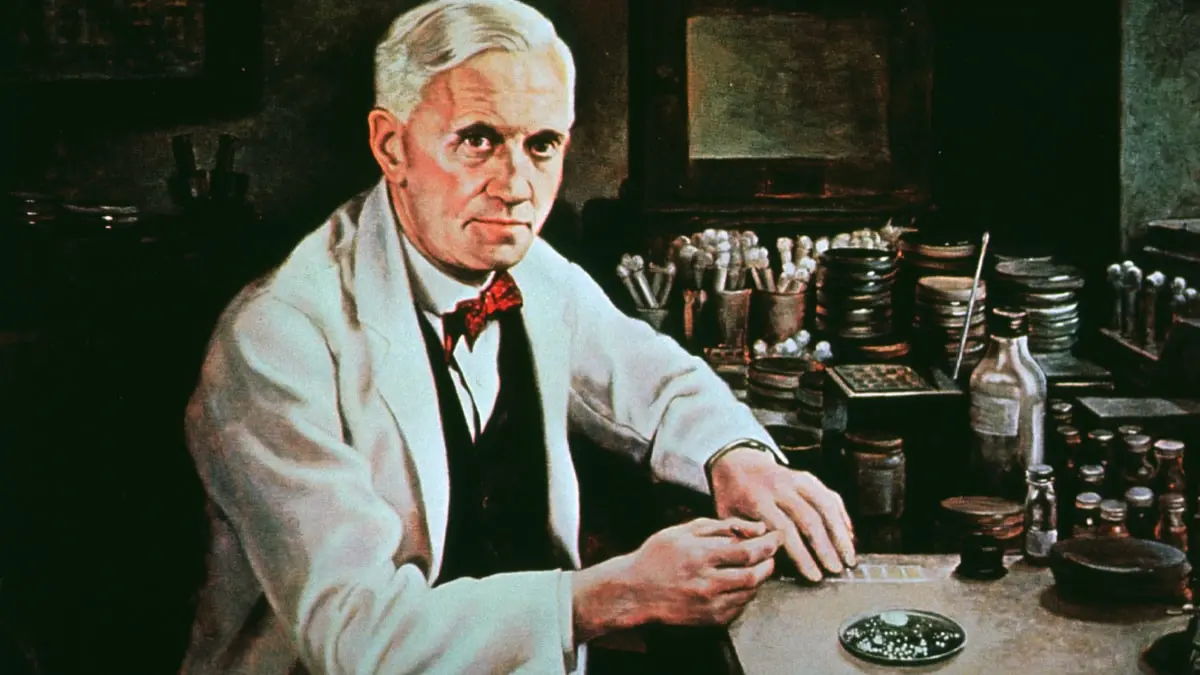 Chistyakov devoted his last years to unraveling what role the nucleus plays in the process of mitosis., one of the first to observe and describe cell division in plants in 1874.
Chistyakov devoted his last years to unraveling what role the nucleus plays in the process of mitosis., one of the first to observe and describe cell division in plants in 1874.
Flemming was one of the first cytologists and the first to describe in detail the movement of chromosomes during mitosis, or cell division.. Ultimately, Flemming described the entire process of mitosis, from the duplication of chromosomes to their even division into two resulting cells, in a book published in 1882.
4. Microscopy is one of the most important methods for studying cells.
 Because most cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye, the study of cells was heavily dependent on the use of microscopes. Really, the very discovery of cells arose from the development of the microscope.
Because most cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye, the study of cells was heavily dependent on the use of microscopes. Really, the very discovery of cells arose from the development of the microscope.
Modern, detailed understanding of cellular architecture is based on several types of microscopy. Because there is no single “correct” representation of a cell, it is important to understand the characteristics of the key cell view methods, the types of images they produce, and their limitations.
Schleiden and Schwann, using a primitive light microscope, first described individual cells as the basic unit of life, and light microscopy has continued to play an important role in biological research.
The development of electron microscopes has significantly expanded the possibilities for resolving subcellular particles and has provided a lot of new information about the organization of plant and animal tissues.
3. The division of life forms into two kingdoms
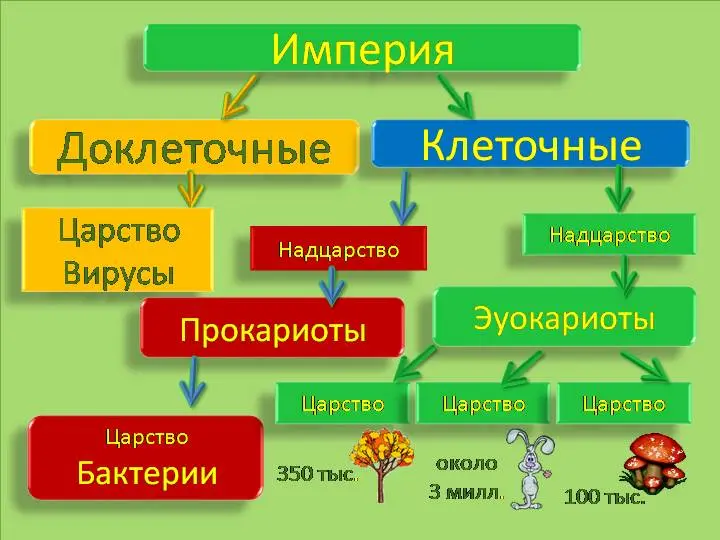 Scientists have announced that a five-year effort to restore evolutionary relationships among all of Earth’s green plants has resulted in the most complete “tree of life” of any group of living beings on the planet. The team of scientists showed that the group traditionally thought of as “plants” are actually four separate lines or “kingdoms” with one group, fungi, being more associated with animals than with plants.
Scientists have announced that a five-year effort to restore evolutionary relationships among all of Earth’s green plants has resulted in the most complete “tree of life” of any group of living beings on the planet. The team of scientists showed that the group traditionally thought of as “plants” are actually four separate lines or “kingdoms” with one group, fungi, being more associated with animals than with plants.
The team disproved the traditional belief that the so-called “land invasion” was caused by seawater plants. Instead, the research team found that primitive freshwater plants provided the ancestral stock from which all green plants now on Earth originated, and that this ancestor gave rise to every green plant now living on Earth.
2. Groups of similar cells form tissues
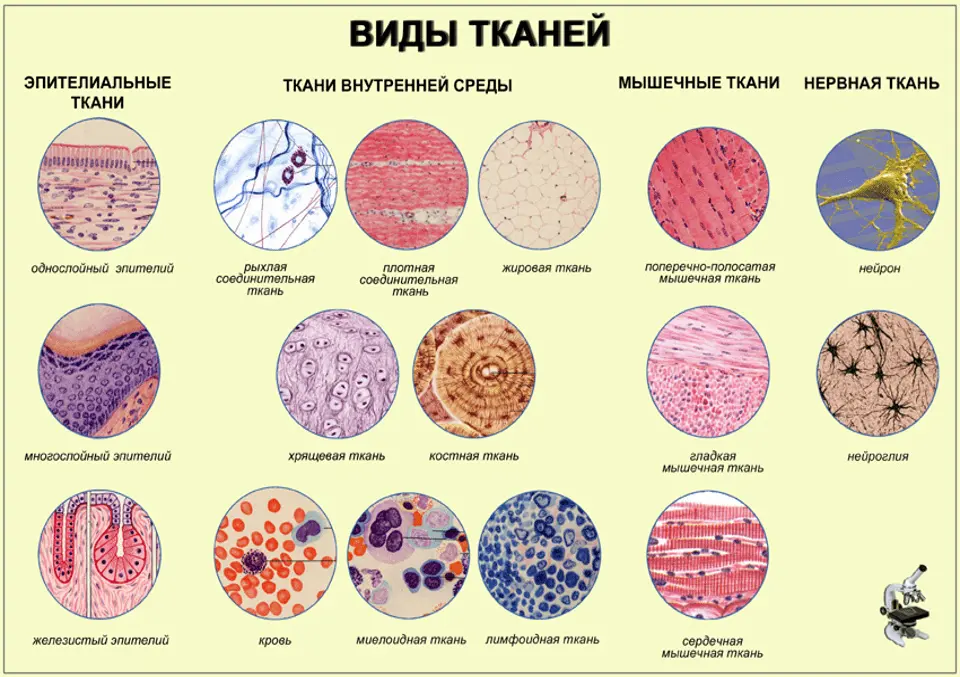 The human body has many levels of structural organization. The easiest level is the chemistry level, which includes tiny building blocks like atoms. Cells are the smallest functional units of life. In the simplest living beings – single-celled, but in complex life forms – cells also exist at the level of tissues.
The human body has many levels of structural organization. The easiest level is the chemistry level, which includes tiny building blocks like atoms. Cells are the smallest functional units of life. In the simplest living beings – single-celled, but in complex life forms – cells also exist at the level of tissues.
Tissues are groups of similar cells that share a common function.. The four main tissue types are epithelial, muscle, connective and nervous tissue.
1. The cell nucleus contains DNA molecules
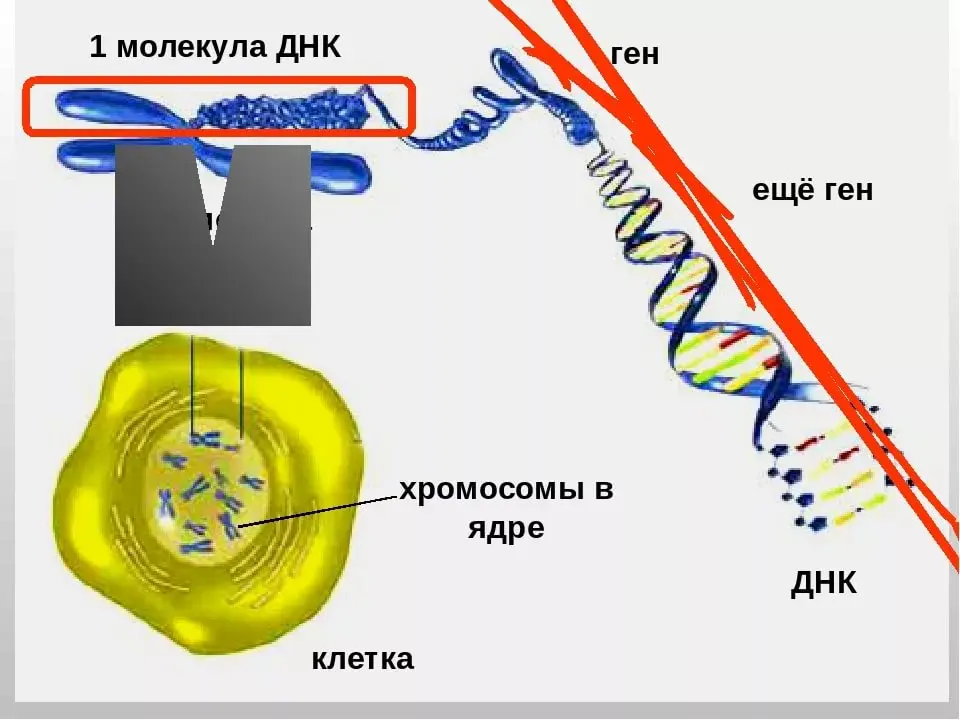 The nucleus is a highly specialized organelle that serves as the information and administrative center of the cell.. This organelle has two main functions: it stores the cell’s genetic material, or DNA, and coordinates the activities of the cell, which include growth, intermediate metabolism, protein synthesis, and reproduction (cell division).
The nucleus is a highly specialized organelle that serves as the information and administrative center of the cell.. This organelle has two main functions: it stores the cell’s genetic material, or DNA, and coordinates the activities of the cell, which include growth, intermediate metabolism, protein synthesis, and reproduction (cell division).
Only the cells of advanced organisms known as eukaryotes have a nucleus. Usually there is only one nucleus per cell, but there are exceptions such as slime mold cells and the Siphonales group of algae.
Simpler single-celled organisms (prokaryotes), such as bacteria and cyanobacteria, do not have a nucleus. In these organisms, all informational and administrative functions of the cell are distributed throughout the cytoplasm.