Contents
- 10 Perfluorotrimethylamine (N(CF3)3)
- 9. Radon (Rn)
- 8. Perfluorobutane (C4F10)
- 7. Tellurium hexafluoride (TeF6)
- 6. Perfluoroethyl iodide (CF3CF2I)
- 5. Decafluorodiethyl ether (C4F10O)
- 4. Tellurium hypofluorite (F5TeOF)
- 3. Iodine heptafluoride (IF7)
- 2. Hexamethyltungsten (W(CH3)6)
- 1. Tungsten hexafluoride (WF6)
Three aggregate states of matter are known, and one of them is gaseous. There are many gases. New ones are opening all the time. In this article, you will learn about the heaviest gases.
But what does heavy mean? No one collected gas into the flask and weighed it on the scales. Moreover, there are not even half a liter of some volatile substances on the entire planet.
The “gravity” of a substance is determined by its molecular weight – the approximate mass of all its molecules. However, the number itself does not tell much about the substance. It is better to compare with air. If we divide the relative molecular weight by 29, we find out how much a given gas is heavier than air.
It is worth mentioning. This list is not the most reliable, because many gases are synthesized daily. It is impossible to compare everything that man has created. Known substances are described here, but there are certainly inert gases heavier than those presented.
10 Perfluorotrimethylamine (N(CF3)3)
If we take ammonia NH4 and replace hydrogens with methyl radicals –CH3, also replacing hydrogen with fluorine, we get perfluorotrimethylamine.
N(CF3)3 boils at -6C. That is, if you take the flask with liquid outside, then already at -6 degrees it will begin to boil and evaporate. The relative molecular weight of the gas is 221. Divide by 29 and find out that perfluorotrimethylamine is 7,6 times heavier than air.
9. Radon (Rn)

Radon, unlike the others on the list, is not synthesized by man. This is a chemical element that occupies position 86 in the periodic table. Radon is an almost non-reactive radioactive gas.
The half-life is 4 days. That is, if you take a container with radon and put it in a room, after four days half of the taken gas will remain in the flask. The rest will break down into lighter elements. And radon itself is a decay product of the radioactive element radium. So do not do this experience, let it remain mental.
Radioactive radon is present everywhere: in schools, on the streets, in the air, soil and even in water. Practical work is carried out at physics lessons. Students go down to the basement and measure the level of radiation. But why in the basement?
This is because radon is a heavy gas. Relative molecular weight – 222. Dividing by 29, we find out that it is about 7-8 times heavier than air. As the heavier matter sinks down, most of the radon is downstairs, in basements and mines. However, the average level of radiation in the air is small, so do not be afraid to go down into the basements now.
8. Perfluorobutane (C4F10)

Perfluorobutane – this is ordinary C4H10 butane, in which hydrogen atoms have been replaced by fluorine. C4F10 – an inactive substance. It is reluctant to react, and therefore does not pose a threat to the body. Even the best oxidizing agents, nitric and sulfuric acids, do not act on it.
Perfluorobutane has found a variety of uses. Firefighters use gas as a filler for fire extinguishers, doctors use it as a contrast agent for ultrasound, for engineers it is a refrigerant. The molecular weight of the gas is 238 amu. Thus, the substance is 8,2 times heavier than air.
7. Tellurium hexafluoride (TeF6)
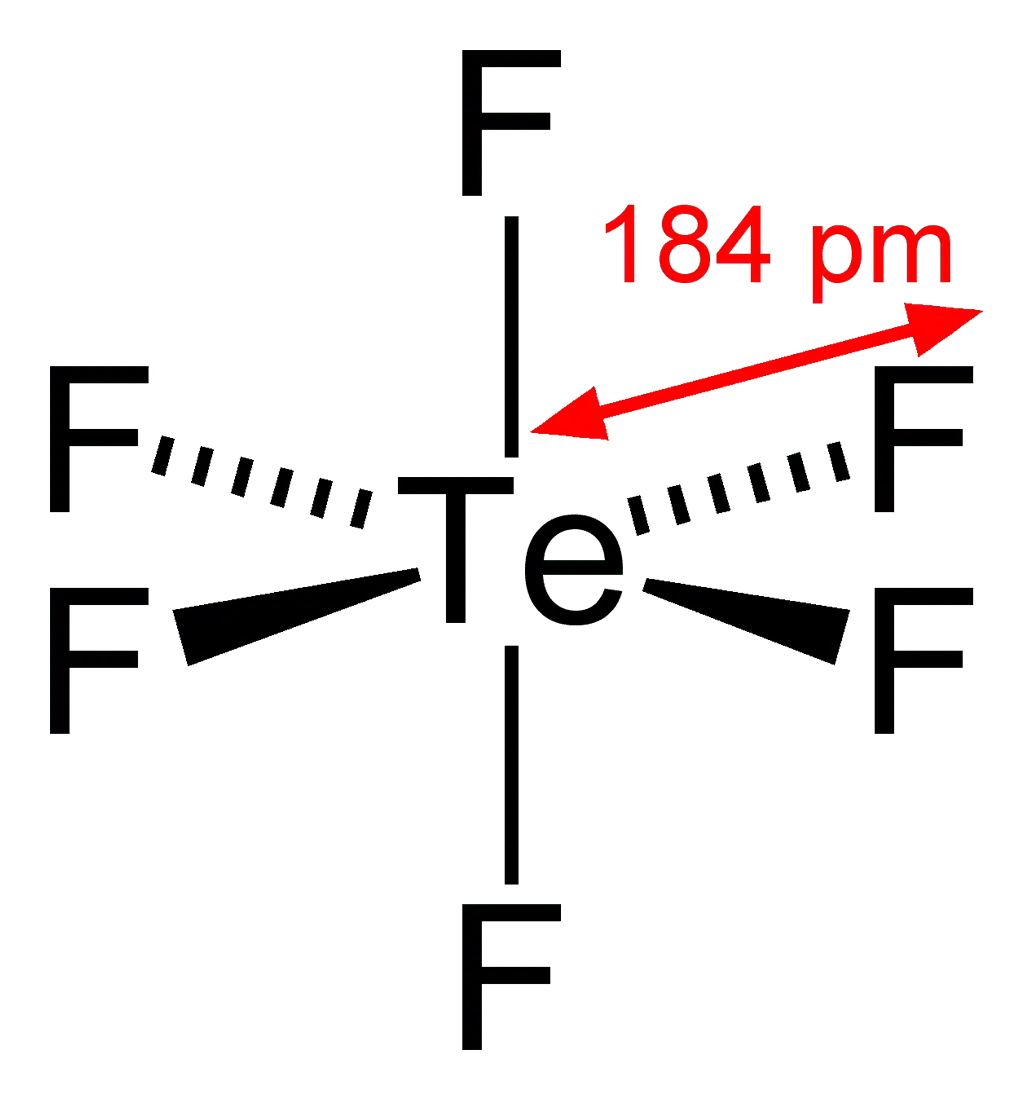
Telluriumhung with fluorine like a Christmas tree is TeF6. Like most gaseous tellurium compounds, hexafluoride has an extremely unpleasant odor. But it’s still half the trouble. The colorless gas is highly toxic and hazardous to health. It also reacts with water, decomposing in it and forming new compounds. The molecule weighs approximately 241,6 amu, and therefore is 8,33 times heavier than air.
You may have already noticed that fluorine constantly appears in the composition of heavy gases. But there are elements heavier than fluorine, why not replace hydrogens with them? The fact is that fluorine is the most “aggressive” element. The atom lacks only one electron to achieve balance. So he gladly takes electrons from other elements. In a molecule, it is easier to replace light hydrogen with heavier fluorine – it actively reacts and makes the molecule heavier.
6. Perfluoroethyl iodide (CF3CF2I)
The substance comes from iodetana – a colorless liquid that turns yellow in air due to the presence of iodine. Iodetan may be a carcinogen, i.e. cause malignant tumors. Also, the compound has a weak narcotic effect.
CF3CF2I – this is iodoethane, in which hydrogen was again replaced by fluorine. As the composition changes, so do the properties of the substance. So, it is reported that the gas is used for anesthesia. This means that it is no longer as harmful as iodetan. The mass of perfluorethide iodide is 245,9, the substance is 8,5 times heavier than air.
5. Decafluorodiethyl ether (C4F10O)
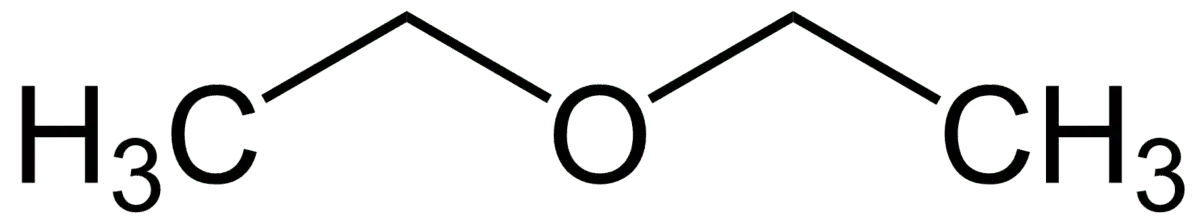
Diethyl ether C4H10 was obtained back in the XNUMXth century, after which it was discovered three more times. The great surgeon N.I. Pirogov was the first to use diethyl ether for anesthesia during operations. Since then, the substance has been adopted as an anesthetic.
By replacing hydrogens with fluorine, people got C4F10O . Most likely, this ether is also suitable for anesthesia. But no one has verified this. The relative molecular weight is 254, the gas is 8,8 times heavier than air.
4. Tellurium hypofluorite (F5TeOF)

Weight F5TeOF – 259,6 amu, 9 times heavier than air. It boils at a temperature of +0,6 C. Accordingly, at a lower temperature it is a liquid. Judging by the fact that hypofluorite is a tellurium compound, this gas is also toxic and smells unpleasant.
3. Iodine heptafluoride (IF7)
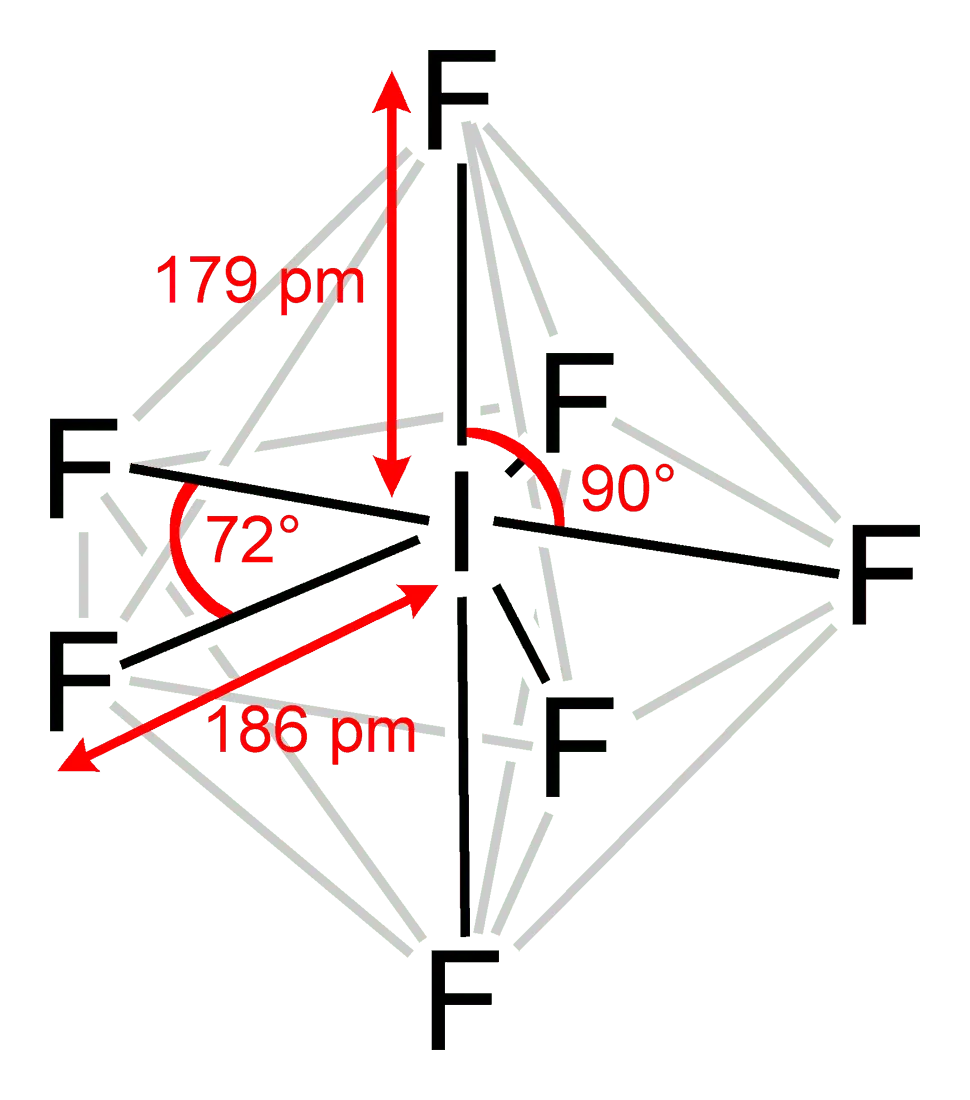
IF7 – a colorless gas with a pungent odor, the highest iodine fluoride. Both elements I and F completely filled the electron shells. Reached “perfect balance, to which all chemical elements aspire.
Looking at the formula, I want to add chlorine to the compound and get an even heavier IClF6 molecule. However, this does not work out in practice. It just so happens that there are no compounds in which more than two types of halogens are present.
Iodine heptafluoride is an extremely active substance. This is a strong oxidizing agent, it gladly “attacks” metals, and in contact with organic matter causes a fire. Because of this activity, IF7 is dangerous for the human body. The compound is highly irritating to mucous membranes.
The gas is almost 9 times heavier than air, the molecular weight is 259,6 (like the previous substance from the list).
2. Hexamethyltungsten (W(CH3)6)
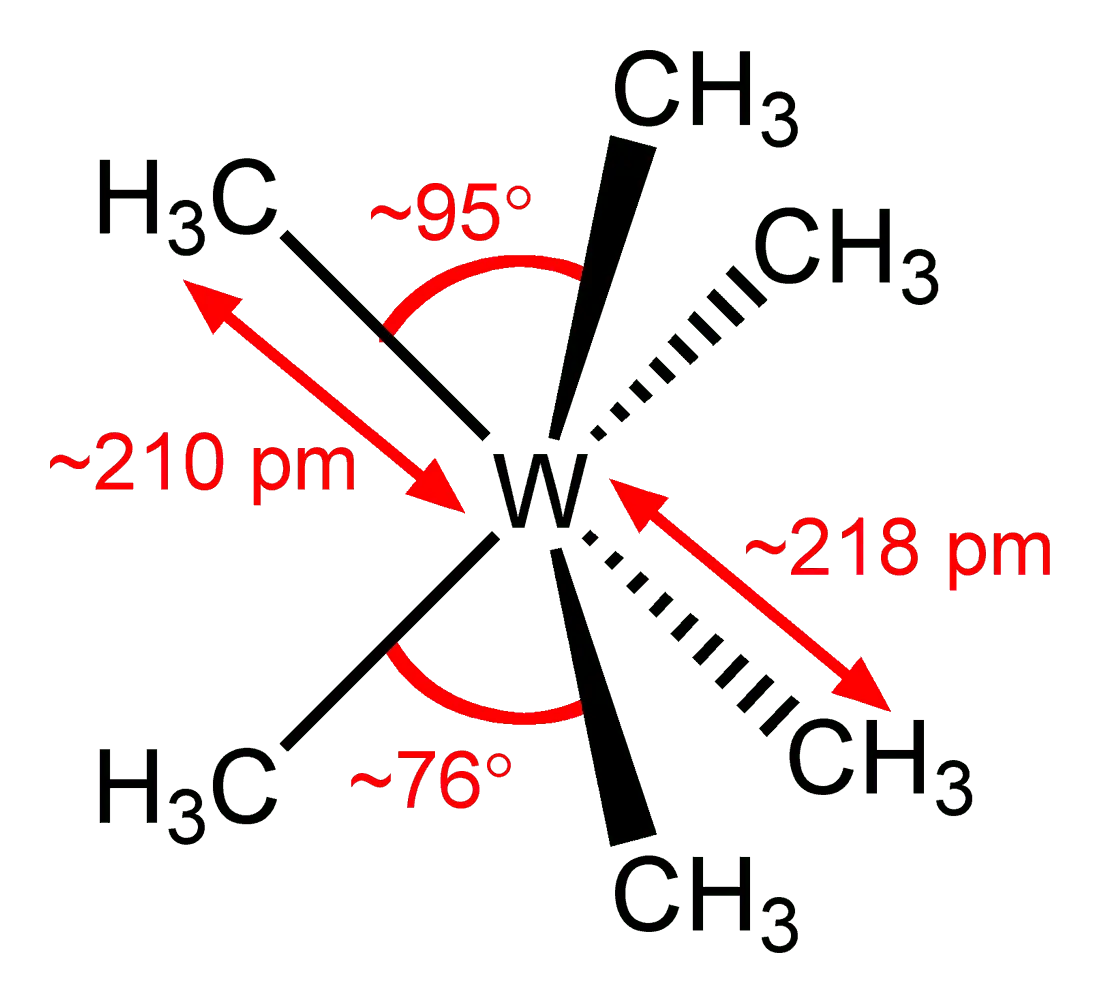
If the atom of tungsten, from which incandescent lamps are made, from all sides “stick around” methyl radicals –CH3, you get hexamethyltungsten.
The compound is explosive in air and in a vacuum. And generally very unstable. W(CH3)6 It turned out to be a stretch on this list, because the substance breaks up almost immediately after formation. The molecule weighs 274,05 amu, and therefore is 9,45 times heavier than air.
1. Tungsten hexafluoride (WF6)
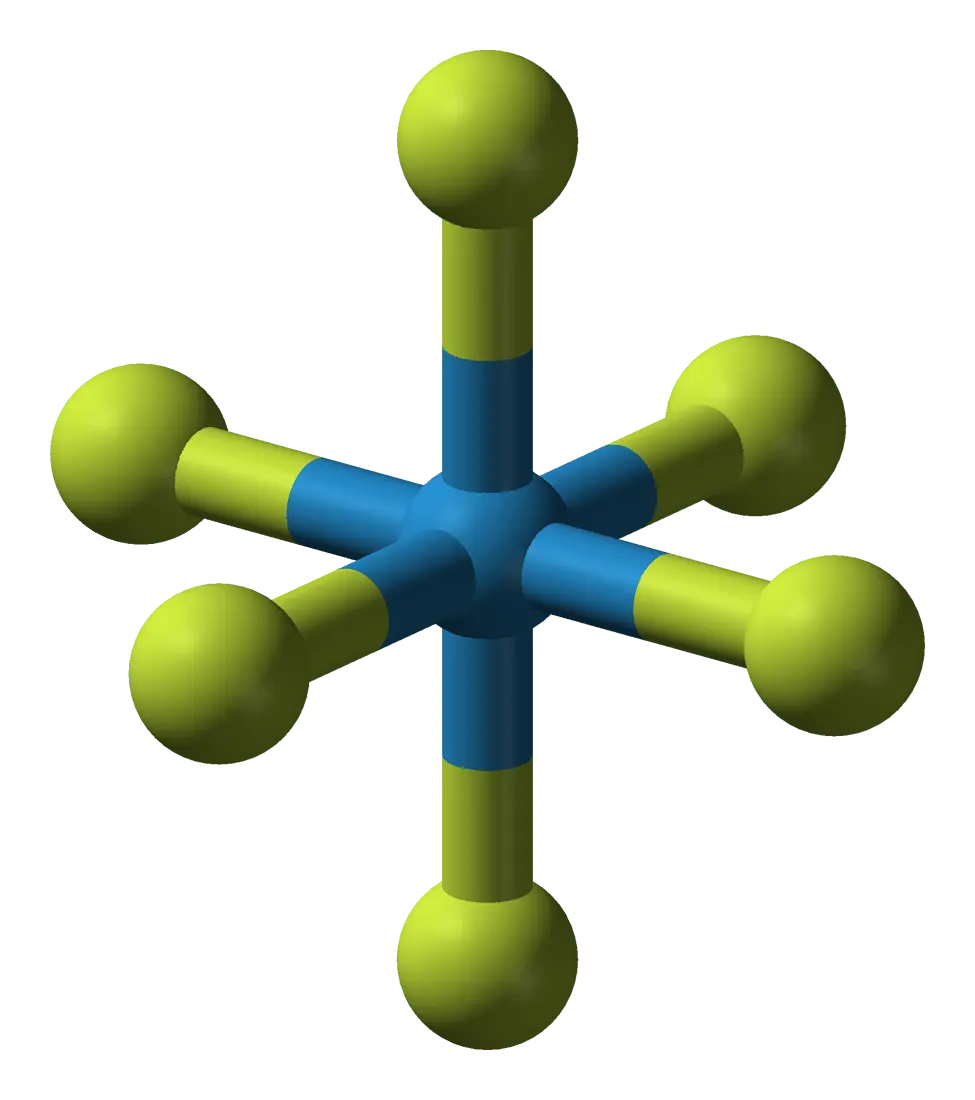
The heaviest gas in the top – WF6, tungsten hexafluoride. It is a salt of hydrofluoric acid HF and tungsten W. The substance is gaseous at temperatures above +17 C, so it is on the verge of a liquid. In humid air, it begins to smoke and turn blue.
WF6 is a corrosive compound, as well as the most dangerous inorganic poison. However, the gas is used in the production of semiconductors and tungsten coatings.
Relative molecular weight tungsten hexafluoride – 297.3. The gas is more than 10 times heavier than air. WF6 becomes the champion among the heaviest gases.