What do you remember when you hear the word typhoid? War… famine… dirt… lice… typhus. And it seems that it is far in the past. But even today you can get sick with typhus, which is carried by ticks. Tick-borne relapsing fever has been noted on almost all continents; in Our Country, natural foci are found in the North Caucasus.
The cause of the disease is bacteria of the genus Borrelia (one of 30 species of Borrelia), which enter the wound at the site of tick suction, and from there they are carried throughout the body with the bloodstream. There they multiply, some of them die from antibodies, which causes an increase in temperature to 38-40 ° C, which lasts 1-3 days. Then the temperature returns to normal for 1 day, after which that part of the Borrelia that did not die from antibodies multiplies again, dies and causes a new attack of fever, for 5-7 days. Again 2-3 days without fever. And just such attacks can be 10-20! (If it is not treated).
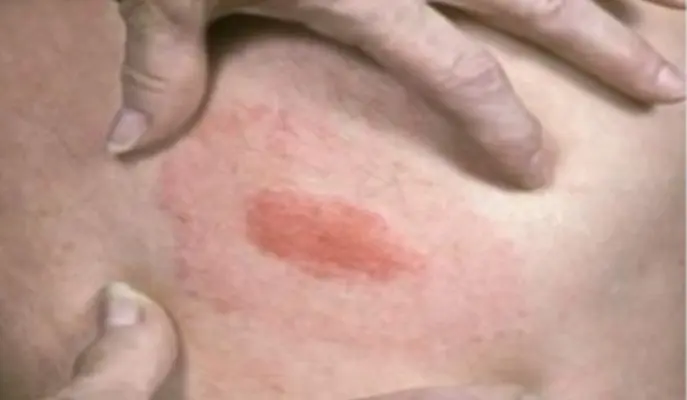
An interesting phenomenon is observed at the site of a tick bite: a rash up to 1 cm in size is formed there, protruding above the surface of the skin. A red ring appears around it, disappearing after a few days. And the rash itself lasts 2-4 weeks. In addition, itching appears, which bothers the patient for 10-20 days.
If this disease is not treated, the person gradually recovers, deaths occur only as an exception. But why suffer if borrelia are sensitive to antibiotics: penicillin, tetracyclines, cephalosporins. They are prescribed for 5 days, and the temperature usually returns to normal on the first day of treatment.









