Contents
Thyroid adenoma – what is it?
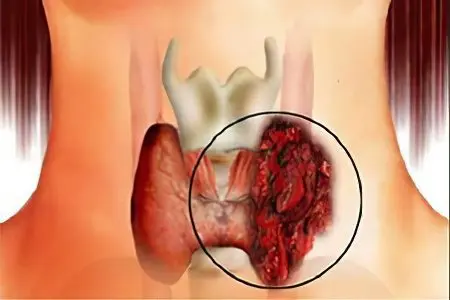
Thyroid adenoma It is a benign tumor that occurs mainly in older patients. It can be of various sizes and shapes. There is a high risk that over time the tumor will become malignant. For this reason, timely diagnosis is important for successful treatment.
An adenoma is often mistakenly considered any nodular formation. However, this concept implies that the tumor consists of cells of a special type. Another feature of the adenoma is that it enhances the work of the thyroid gland. As a result, the production of thyroid hormones increases, which are released into the blood in a larger volume. Only a biopsy can reliably determine the type of tumor cells. On its basis, diagnosis is carried out and a decision is made on the method of treatment.
Reasons for the development of thyroid adenoma
The development of the disease is facilitated by adverse environmental conditions, problems in the functioning of the nervous system and hormonal disorders. The action of toxic substances also has a negative effect on the body and can lead to adenoma.
Patients who have relatives with adenoma should be more careful: it is believed that there is a genetic predisposition to the formation of this tumor.
Symptoms of thyroid adenoma
As the first symptoms of the disease, weight loss, excessive sweating, increased heart rate, the appearance of anxiety and irritability are noted. When the adenoma greatly increases in size, external changes on the neck are noticeable. In addition, the patient experiences pain, and breathing and swallowing are difficult.
Among all types of benign neoplasms to which the thyroid gland is susceptible, toxic adenoma has the most pronounced symptoms. This type of tumor is accompanied by the production of the greatest amount of thyroid hormones, so the patient undergoes drug treatment before the operation. However, taking drugs often does not give the full effect. Removal of thyroid adenoma is the only effective approach.
Types of operations for thyroid adenoma
If the tumor has not become malignant, they resort to enucleation of the node. During this procedure, both the capsule and the neoplasm itself are removed. Thyroid tissue is preserved as much as possible. It is important that they have an unchanged shape, size and structure, like a healthy organ. During the operation, an incision is made on the thyroid gland, through which the cyst and capsule are carefully removed, which are then biopsied. After removal of the tumor, a revision and suturing of the wound is performed.
If the neoplasm has become malignant, or the thyroid gland is damaged to a significant extent, the following types of interventions are carried out:
Hemithyroidectomy. In this case, half of the organ is removed. At the beginning of the operation, an incision is made to gain access to the operated area. After that, the vessels that supply the blood to the thyroid gland are tied up, and the main part of the procedure begins. The organ is separated from the tissues surrounding it, the diseased half is removed, the healthy half is placed in place, the blood supply is restored, the wound is sutured;
Subtotal resection. Unlike hemithyroidectomy, most of the organ is eliminated here, but the left and right lobes are partially preserved. After such an operation, the thyroid gland is no longer able to independently cope with the production of hormones. To maintain its functions, a constant intake of synthetic hormonal drugs is necessary;
Thyroidectomy. This is the most radical surgical option required if the tumor is malignant. In a thyroidectomy, the thyroid gland is completely removed. The body will need help after the operation, as thyroid hormones are no longer produced. You should be prepared for the fact that taking hormonal drugs will need to be carefully maintained for the rest of your life.
The possibility of complications cannot be ruled out. Patients after thyroidectomy often suffer from impaired calcium metabolism in the body, problems with the larynx and voice. In addition, the intervention may result in bleeding and damage to the nerve cells around the thyroid gland. Deprived of some parts, the body ceases to produce hormones in the required volumes.
Features of the operation for thyroid adenoma
If the doctor insists on surgical intervention, you should immediately set a date for it. Delay can lead to various complications: an increase in the size of the tumor or its malignancy (malignancy).
Preliminary, all necessary analyzes and studies are carried out that are required by the anesthetist and surgeon to select the optimal anesthesia option and determine the tactics of intervention. These specialists should be asked all your questions about thyroid surgery in order to get rid of unnecessary fears and worries. Usually, the surgeon immediately warns of possible complications, which are of two types: non-specific, for example, suppuration in the wound area, bleeding, which do not pose a big problem and are well treated. Damage to the larynx, nerves and nearby tissues are considered specific.
Surgical intervention is performed under general anesthesia. With the competent work of the anesthesiologist, anesthesia does not give side effects. The duration of the operation is several hours. In some cases, after its completion, drainage is installed. It will be removed a day after surgery. Over the next day, the patient needs to stay in bed in a regular ward, where he gets immediately after removal of the thyroid adenoma. After a few more days, you can go home, having previously discussed the treatment in the postoperative period with your doctor.
Usually, postoperative therapy involves taking hormonal drugs, which is carried out for a long time or for life. Regular visits to the endocrinologist prevent recurrence of thyroid adenoma. Monitoring should be based on analyses. Their results allow you to adjust drug treatment and monitor hormone levels. Simple observation by the patient of his condition and careful administration of drugs will help to avoid complications.









