Contents
The formation of a blood clot in the arterial or venous system of the brain, in the sinuses of its hard shell is diagnosed as vascular thrombosis. This condition poses a great danger not only to health, but also to the very life of the patient, provokes a stroke. Thrombosis occurs more frequently in the elderly, although cases occur in every age population.
Classification of pathology
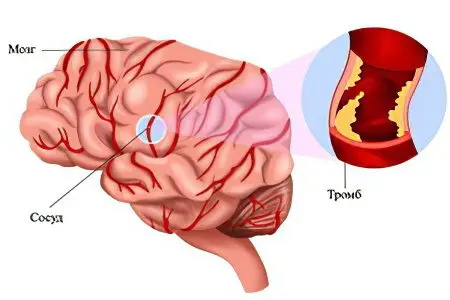
Depending on the location of the pathological process, there are types of thrombosis:
Extracranial (extracranial);
Itcranial (intracranial).
Extracranial thrombosis is not as dangerous as the intracranial form of pathology. It may be asymptomatic or present with minimal neurological signs of circulatory disturbance. Compensation for the functions of vessels temporarily dropped out of the blood circulation occurs due to collateral blood flow. In this scenario of extracranial thrombosis, ischemia of brain structures will be minimal.
The most common location of thrombosis is the venous sinuses, which are reservoirs for moving blood into the jugular veins. Thrombosis of the venous sinuses is manifested by significant complications.
With the development of thrombosis in the intracranial arteries, the clinical picture of the disease is similar to the clinical picture of a stroke.
Before a stroke, harbingers appear, indicating a beginning cerebrovascular accident:
Drowsiness,
Dizziness,
Headache,
Visual impairment
Violation of sensitivity and motor functions.
Causes of cerebral thrombosis
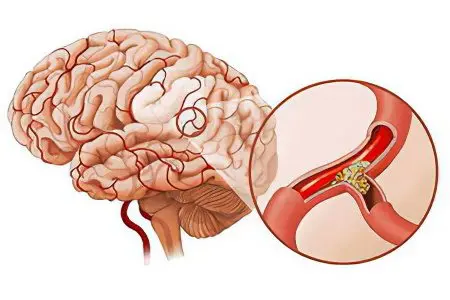
At risk are the elderly, patients with hypertension and diabetes. Improper nutrition, alcohol abuse, smoking, frequent psycho-emotional overload are factors that provoke thrombosis.
Reasons for the formation of a predisposition to the formation of blood clots:
Hypodynamia,
Increased platelet count;
Heart disease, anemia, meningitis in history;
Decreased immunity;
Excess weight;
Postoperative complications;
Childbirth, complications of pregnancy;
Head injuries, mechanical damage to blood vessels;
Sinusitis, otitis.
Thrombosis of the arteries of the brain occurs due to blockage of the arteries by cholesterol plaques, due to thromboembolism of the heart vessels, complications of inflammatory processes.
Thrombosis of the venous sinuses occurs due to thrombophlebitis (inflammation of the venous walls). Diseases that increase the likelihood of developing thrombosis of the venous sinuses:
Purulent wounds of the skull, soft tissues of the head;
Stomatitis;
Tuberculosis;
Viral and fungal infections;
Complications after craniotomy, after anesthesia, surgery;
Head trauma;
Neoplasms of the brain of any etiology;
Late toxicosis of pregnancy;
Hypertension of pregnant women;
Caesarean section, postpartum complications;
Pathology of blood and hematopoietic organs;
Side effects of hormone therapy, taking oral contraceptives;
Dehydration of the body.
Symptoms and manifestations of cerebral thrombosis

Cerebral group of symptoms:
Headache of high intensity;
Nausea and vomiting;
Impaired sensitivity of the limbs, facial skin;
Asymmetry of facial muscles;
Reduced hell;
Weak filling of the pulse;
Convulsions;
Increased intracranial pressure;
Paralysis and paresis;
Photophobia.
Focal symptoms that manifest differently in certain areas:
double vision;
Narrowing of the field of view, a decrease in its sharpness;
skin cyanosis;
Difficulty moving the eyeballs, their protrusion.
Symptoms caused by intoxication of the body:
Hyperthermia;
Chills, aching joints;
Weakness, lethargy;
Drowsiness.
With thrombosis of the venous sinuses caused by an infected thrombus, the patient is diagnosed with confusion, fever, excessive sweating, earthy skin color.
Diagnostics
Blockage of cerebral vessels by a thrombus is an emergency condition that requires urgent diagnosis. There is a rapid test that allows us to assume the presence of pathology before instrumental examination.
What is offered to the patient:
Show language. Due to a violation of the blood circulation of the brain, the patient’s tongue will bend, will sink in one direction.
smile. A symmetrical smile during ischemia will not be possible, it will turn out to be one-sided.
Raise your hands up. A patient with thrombosis will not be able to do this.
Say a short sentence of a few words like “we’re going to the store for bread.” Violation of the blood supply to the brain will make speech slow and slurred.
Diagnostic methods:
Doppler ultrasound;
Angiography;
Rheoencephalography;
MRI.
Treatment of cerebral thrombosis
After the diagnosis is made, it is urgent to start a course of therapy for the pathological process.
Methods of treatment:
The use of drugs to dissolve a blood clot and restore blood circulation.
Intra-arterial thrombolysis is the introduction of a catheter into a large vessel to deliver a drug that absorbs a blood clot to a blood clot.
In dangerous cases, surgery to remove the clot.
When choosing methods of treatment, the doctor takes into account the localization of the pathology, the age of the patient, history and other factors. To restore the amplitude of movements, therapeutic massage is provided, physical education is practiced.
In the treatment of thrombosis of the venous sinuses, antibiotic treatment is mandatory to eliminate the source of infection.
Delayed treatment can cause serious complications and even death.
Complications
The result of oxygen starvation of the brain are serious complications:
Paralysis;
Heart attack, stroke;
Disorder of speech and cognitive functions (memory, ability to read and write);
Visual impairment.
Severe forms of cerebral thrombosis end in the death of the patient. It occurs as a result of an embolism, when a blood clot detached from the vessel wall moves through the circulatory system until it cuts off the blood supply to a vital organ.
Prevention measures

To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to analyze the causes that cause it.
Preventive measures that reduce the likelihood of thrombosis:
A varied menu that excludes fatty foods, smoked meats, extractives;
Quit smoking and alcohol;
Weight control;
Timely treatment of inflammatory diseases, infections;
Monitoring blood sugar levels in diabetic patients;
Physical activity for at least 30 minutes a day.
The earlier the diagnosis of thrombosis, the higher the likelihood of a favorable outcome of the disease.









